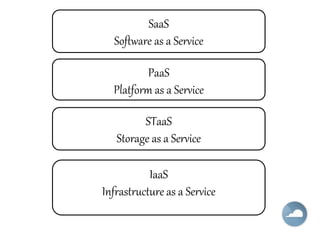
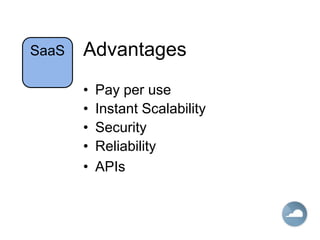
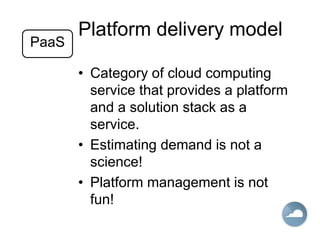
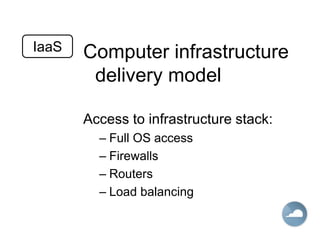
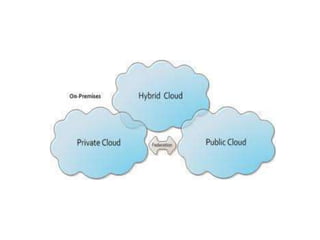
Cloud computing allows users to access computing resources like data storage, servers, databases, networking, software, analytics and more without direct interaction with the underlying infrastructure. It provides services through three main models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). IaaS provides on-demand access to virtualized computing resources. PaaS provides a platform and solutions stack. And SaaS provides software applications delivered through a browser. Common advantages of cloud computing include pay per use, instant scalability, security, reliability and APIs.