This document provides an overview of cloud computing, including what it is, the cloud service models of SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS, cloud storage types, and advantages and disadvantages. Cloud computing relies on sharing computing resources over the internet rather than local servers. It allows users to access applications and store/edit files online, providing benefits such as flexibility, scalability, and reduced costs compared to traditional computing. However, cloud computing also presents security and reliability risks due to its reliance on internet connections and remote servers.







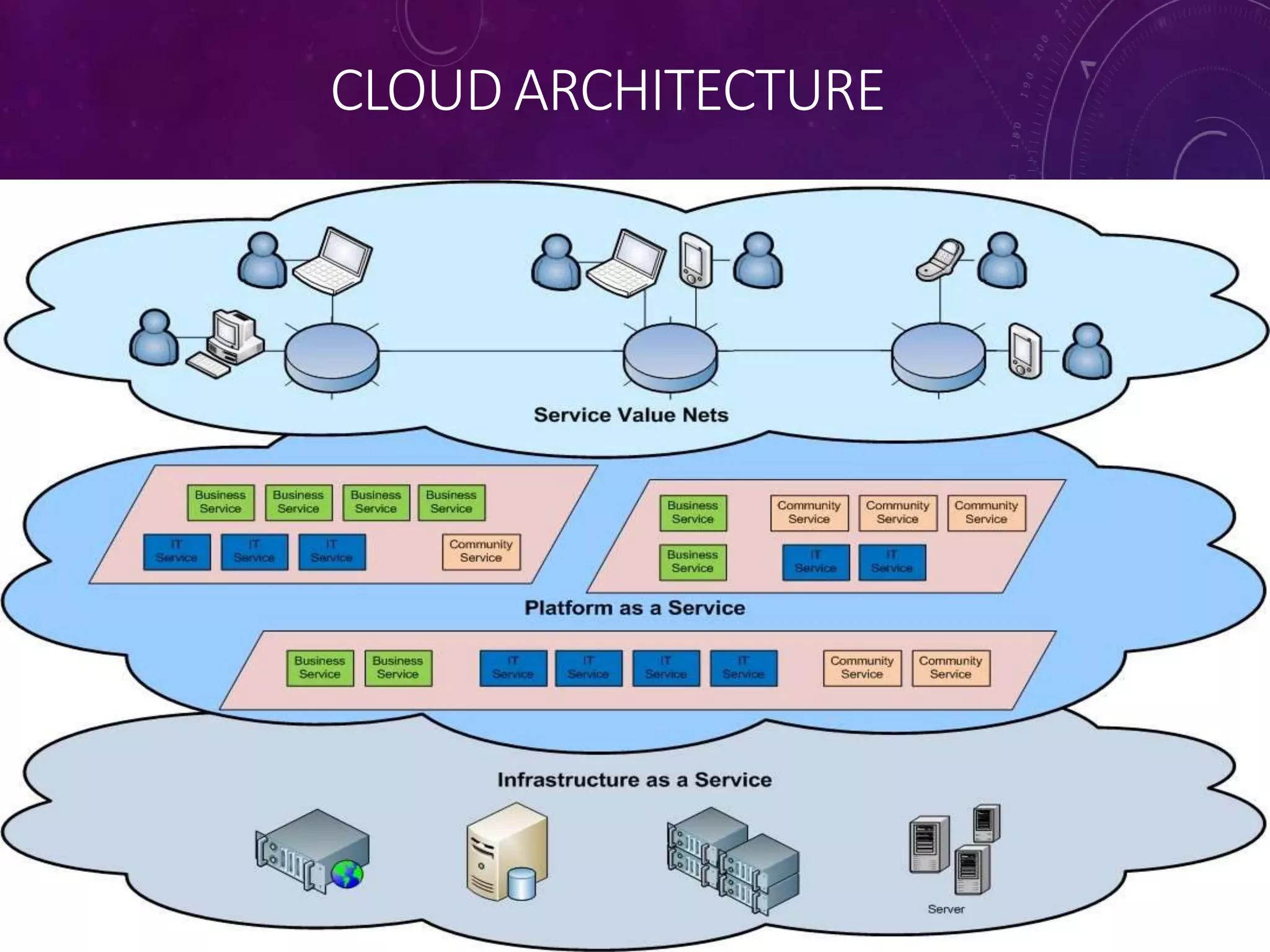






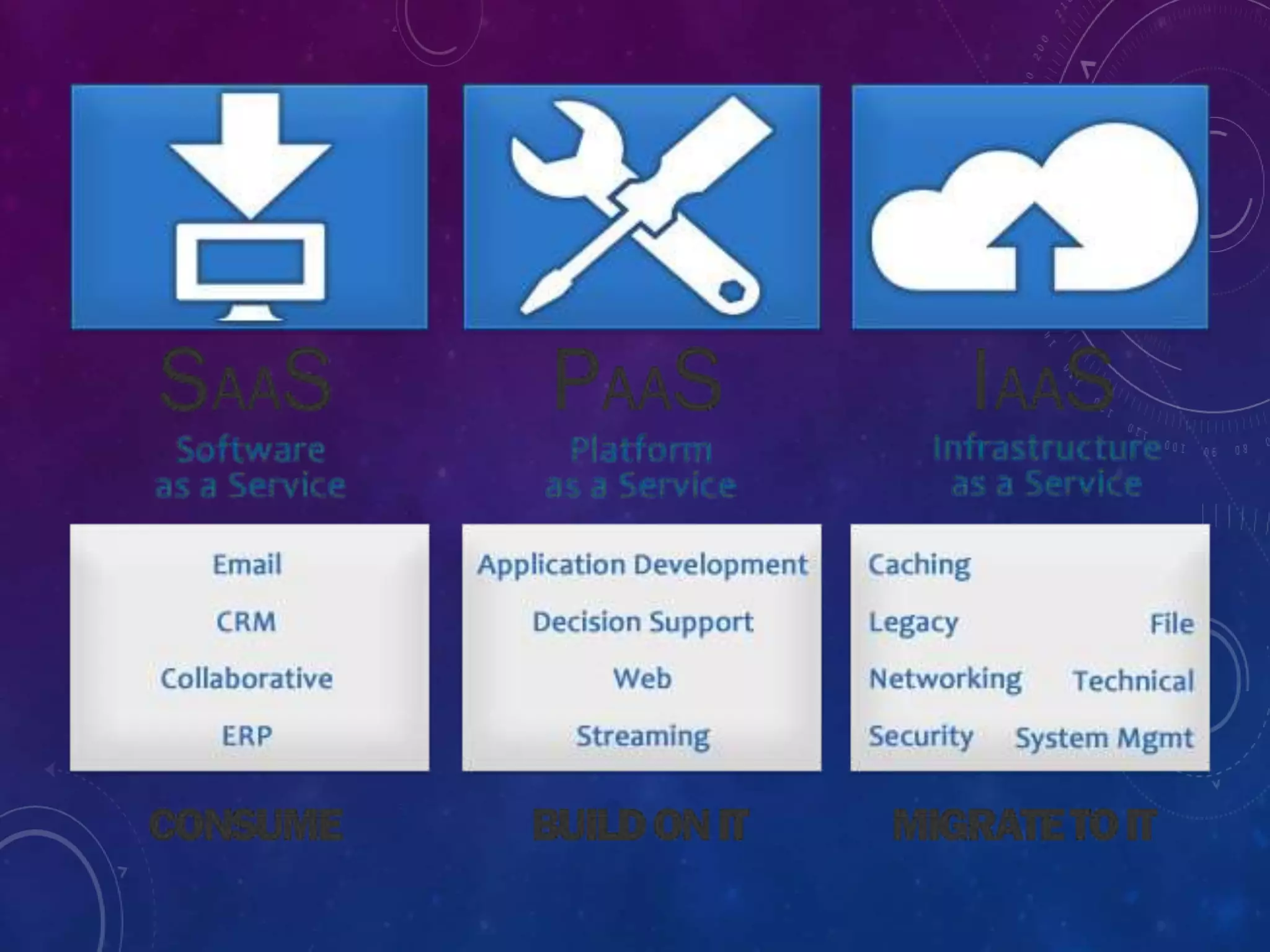
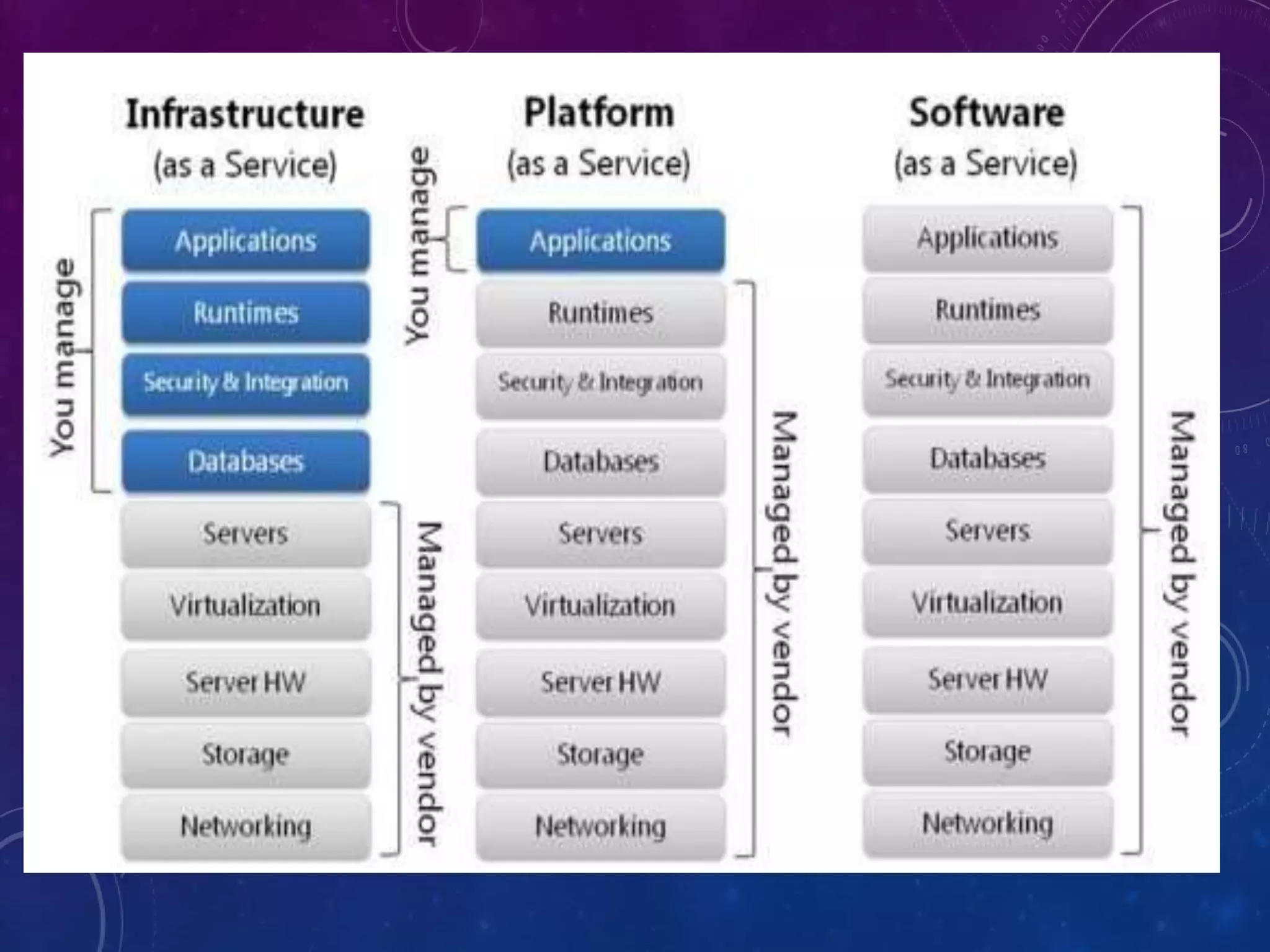
![IAAS
• In the most basic cloud-service model, providers of
IaaS offer computers physical or (more often) virtual
machines and other resources. IaaS clouds often offer
additional resources such as a virtual-machine disk
image library
• virtual local area networks (VLANs), and software
bundles.[49]
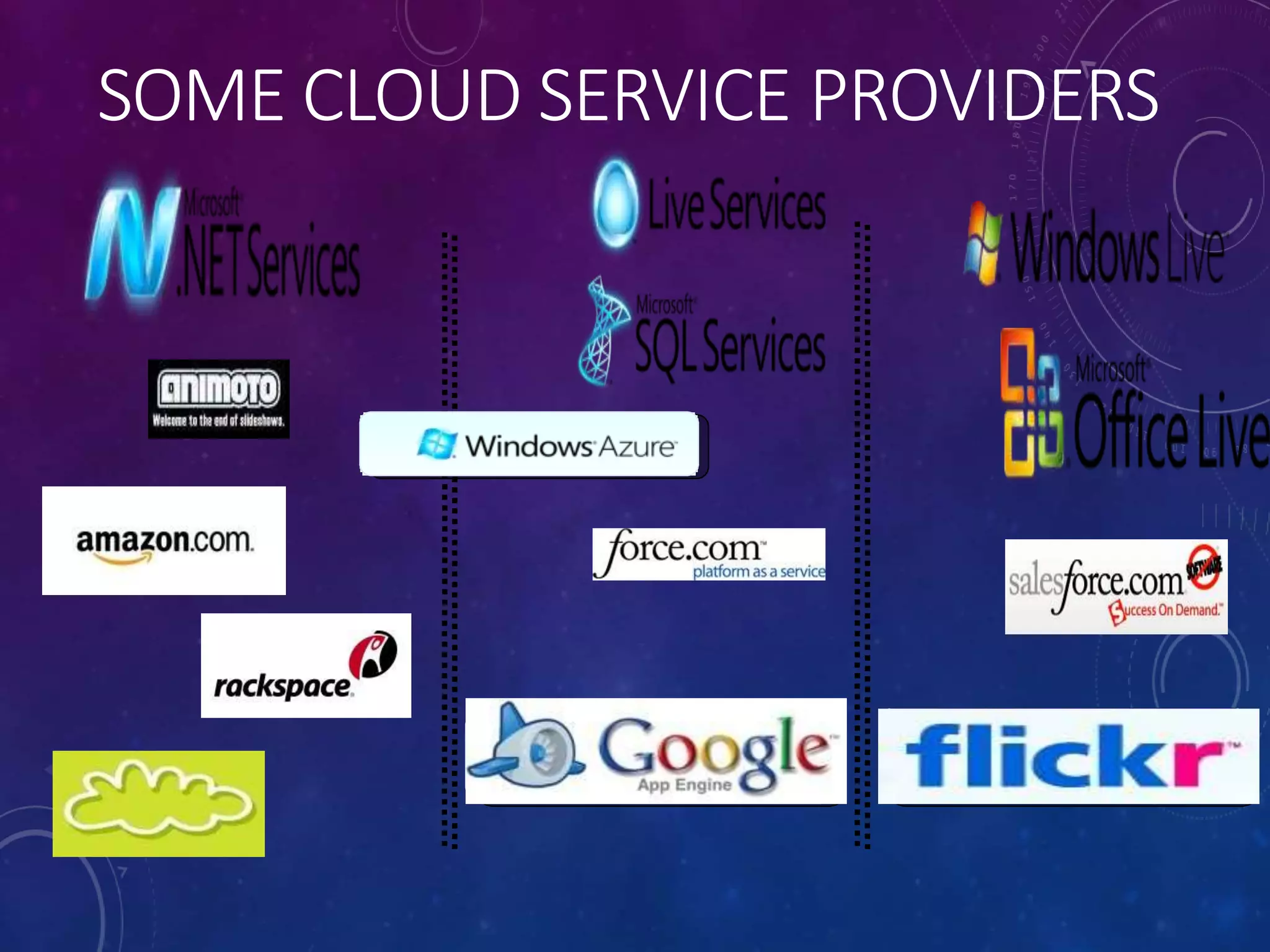
• Examples of IaaS providers include: Amazon EC2,
Azure Services Platform, DynDNS, Google Compute
Engine, HP Cloud, iland, Joyent](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminaroncloudcomputing-180517113015/75/Seminar-on-cloudcomputing-15-2048.jpg)