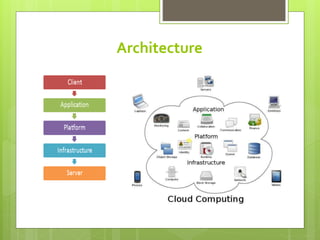
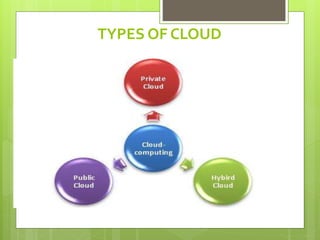
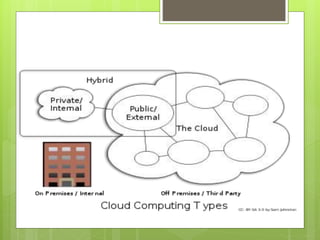
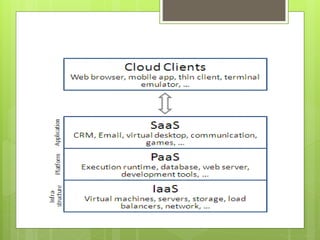
Cloud computing involves delivering computing services over the internet instead of on local hard drives. It has its origins in the 1950s with mainframe computing and evolved with virtual machines in the 1970s and VPN services in the 1990s. There are different types of cloud including public, private, and hybrid clouds. Cloud services provide software, platforms, and infrastructure as a service and offer benefits like scalability, reliability, and reduced costs but also have disadvantages like potential bandwidth issues and performance impacts.