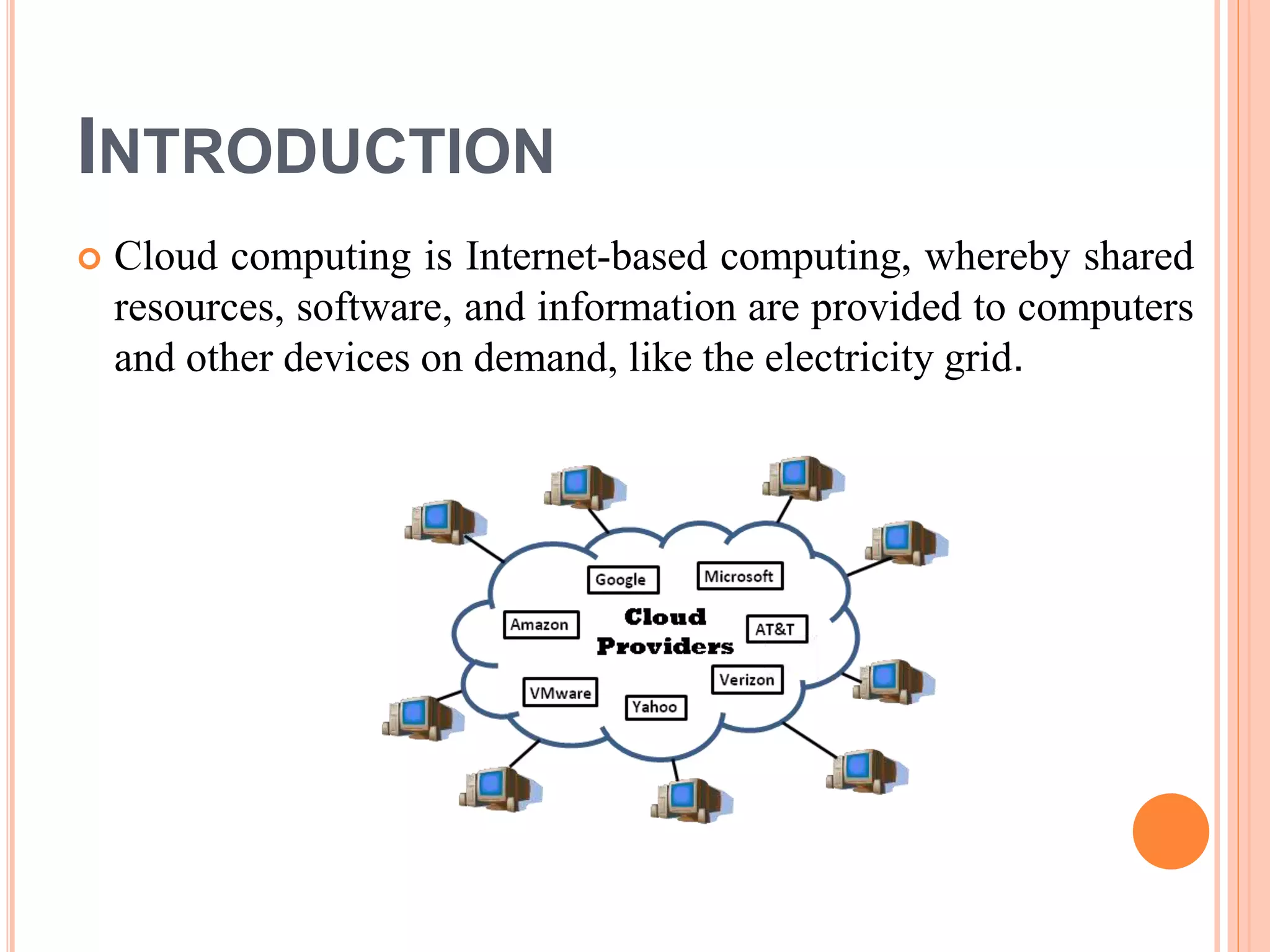
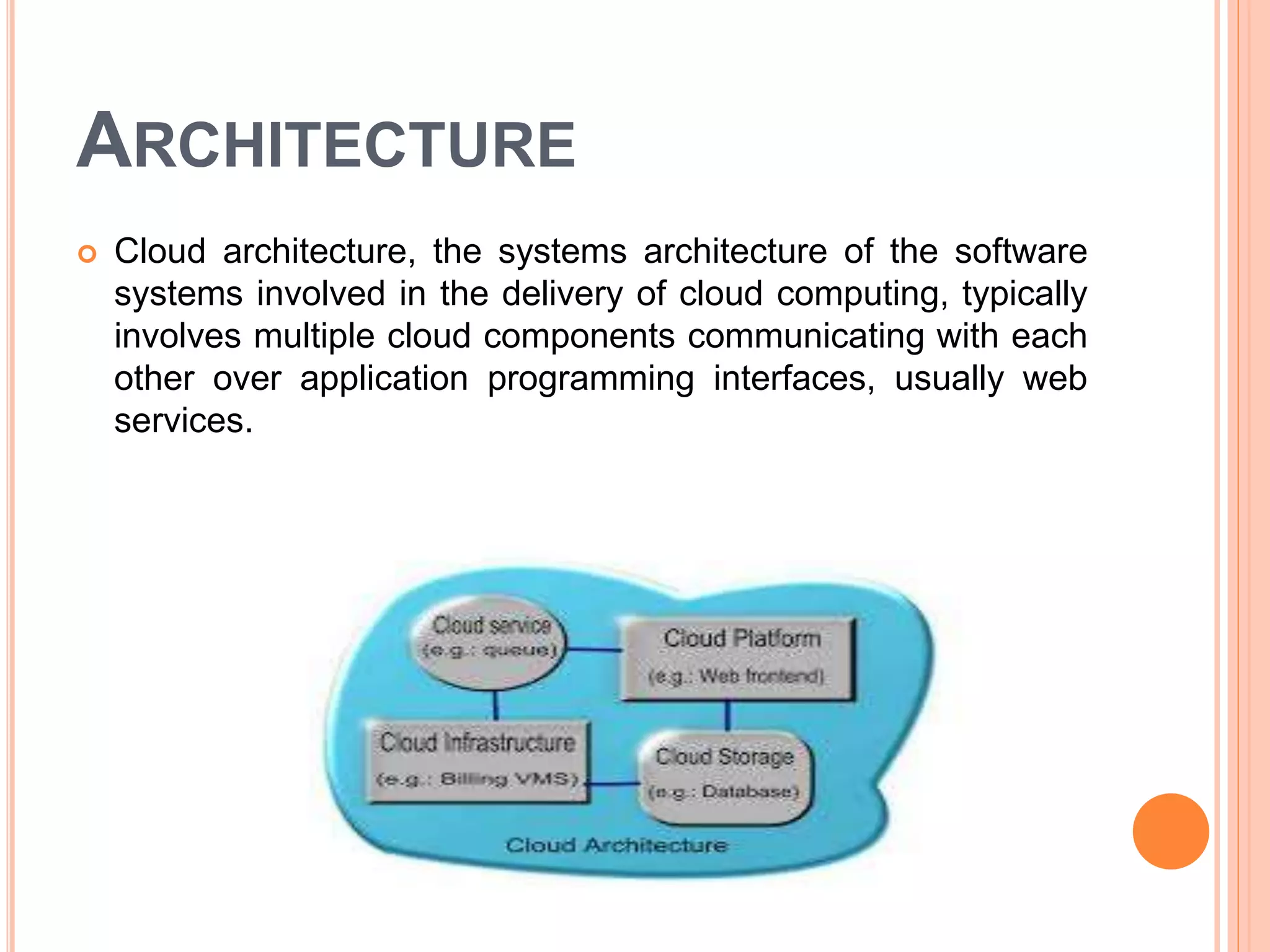
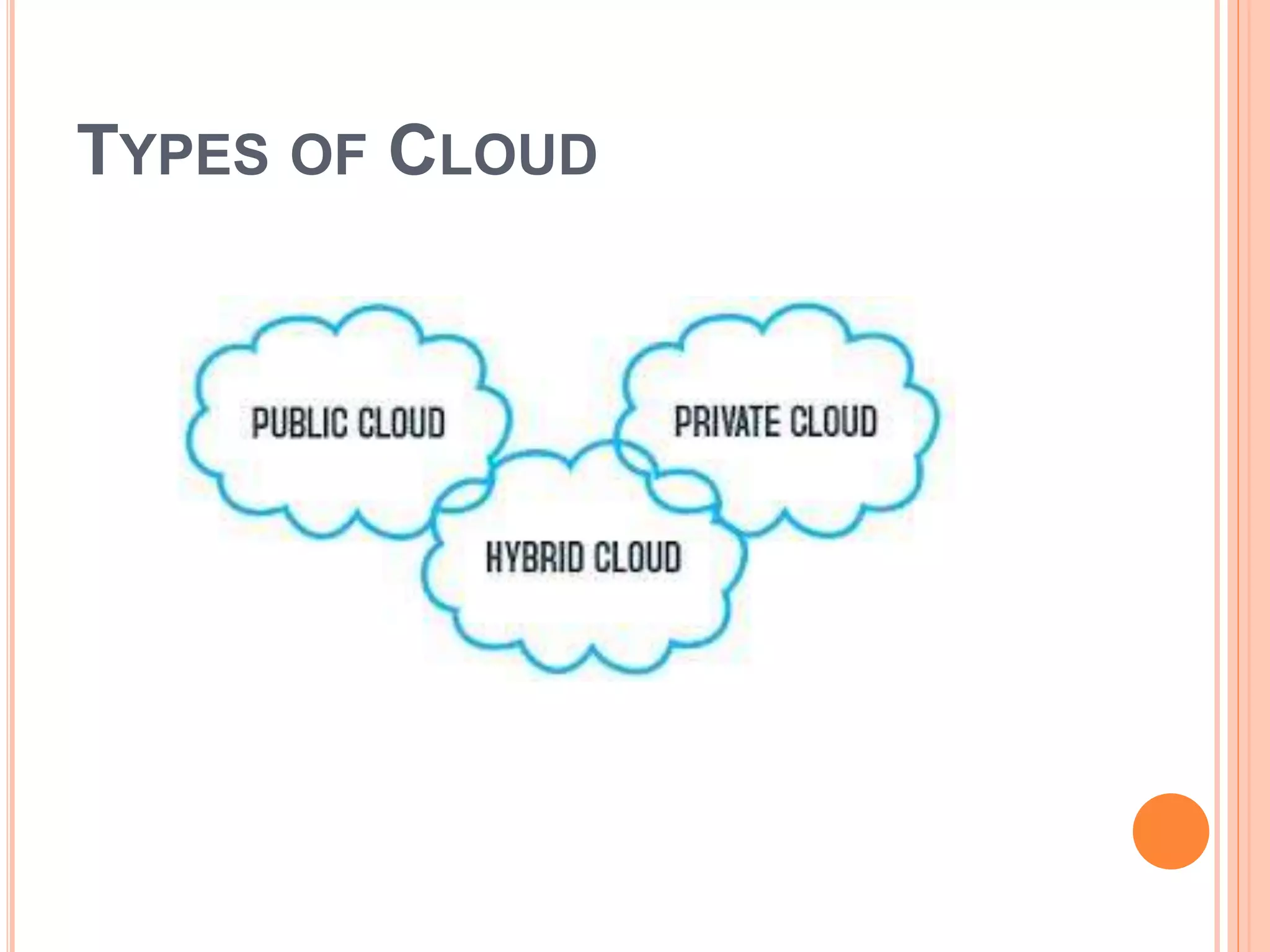
This presentation provides an overview of cloud computing, including its definition, history, components, architecture, types, advantages and disadvantages. Cloud computing allows users to access shared computing resources like software, storage and servers over the internet. It has grown popular since the 2000s with companies like Amazon, Google and Microsoft offering cloud services. The main types of cloud include public, private and hybrid clouds that vary in their access and management.