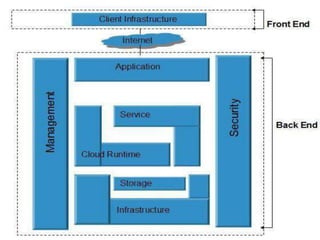
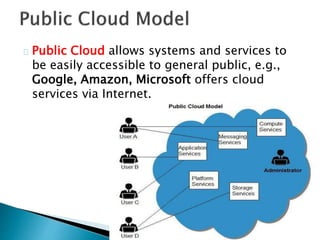
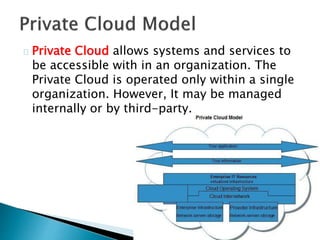
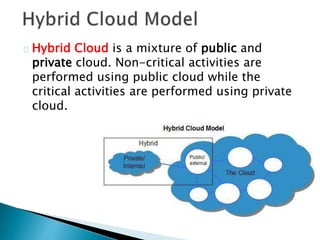
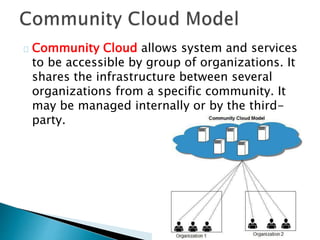
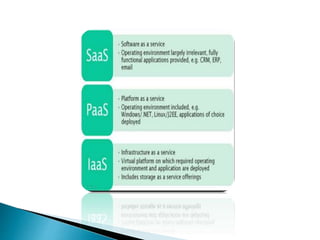
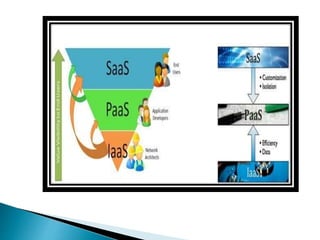
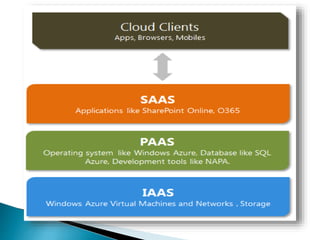
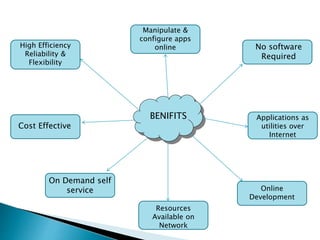
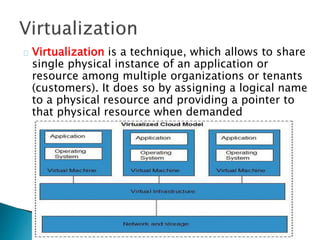
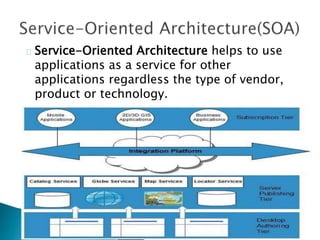
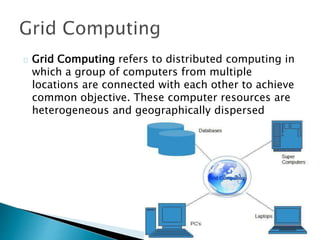
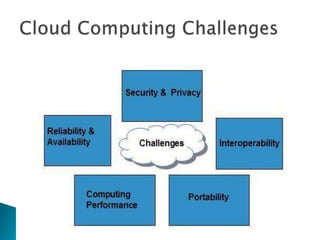
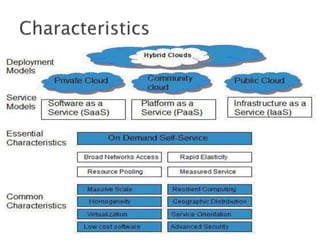
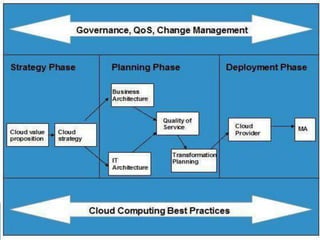
The document provides an overview of cloud computing, explaining its architecture, models, and services, including public, private, hybrid, and community clouds. It discusses the importance of security and privacy in cloud services, outlining potential risks and the need for measures like encryption. Additionally, it highlights the benefits of cloud computing, such as efficiency and flexibility, while also acknowledging challenges like data management and provider dependency.