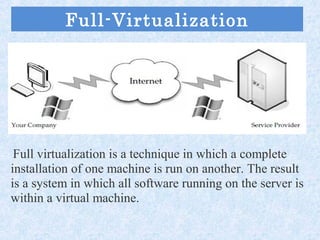
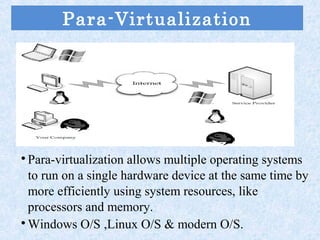
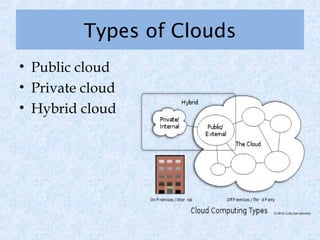
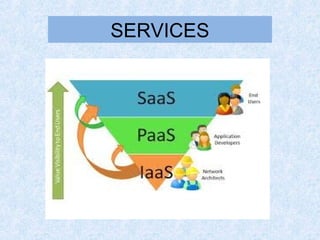
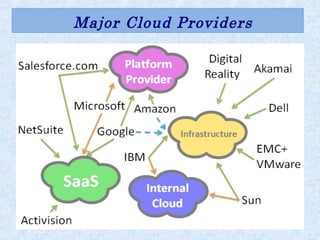
Cloud computing is a revolution in IT that provides great job opportunities. It uses shared computing resources over the Internet instead of local servers or personal devices. There are different types of cloud including public, private, and hybrid. Cloud services include SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS. Cloud provides advantages like scalability, availability, and pay-per-use which reduces costs. Major cloud providers are expanding offerings and making acquisitions. Cloud jobs are expected to grow significantly in coming years.














![REFERENCES
[1] Cloud Computing:A Practical Approach by Anthony T. Velte Toby
Velte, Ph.D.Robert Elsenpeter-McGraw-Hill
[2] Cloud Computing Implementation,Management,
and Security John W. Rittinghouse James F. Ransome-CRC
Press.
[3] Executive’s Guide to Cloud Computing by Eric A. Marks Bob
Lozano-John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
[4] Cloud Computing for Dummies by Judith Hurwitz, Robin Bloor,
Marcia Kaufman, and Dr. Fern Halper.
[5] http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/cloud/default.aspx#tab2-small](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudcomputing-120818042351-phpapp01/85/Cloud-computing-20-320.jpg)
