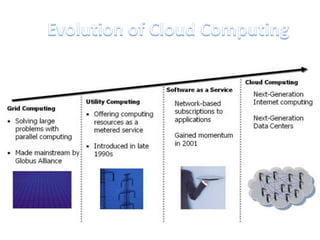
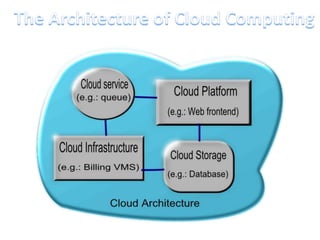
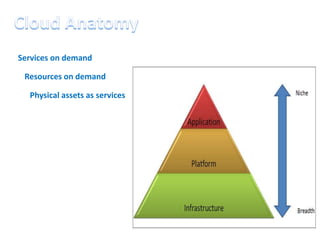
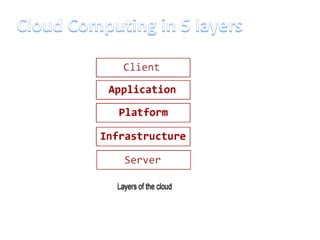
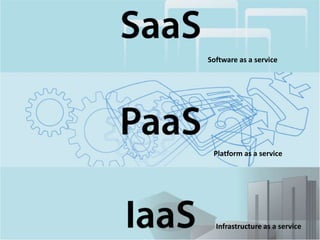
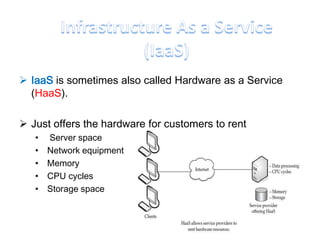
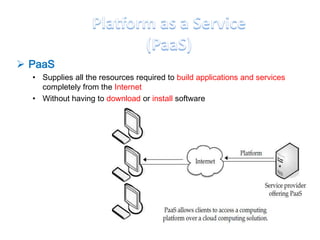
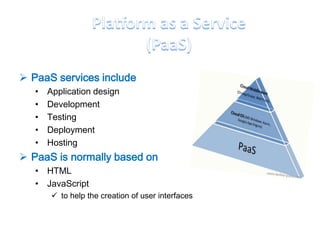
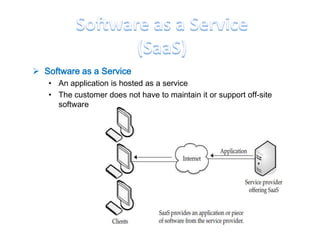
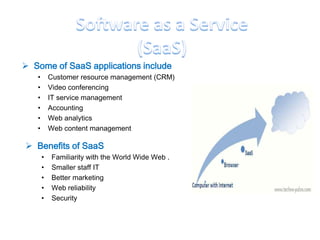
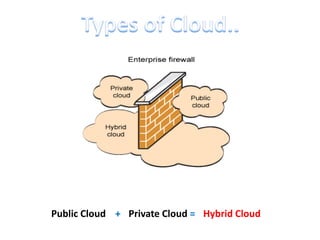
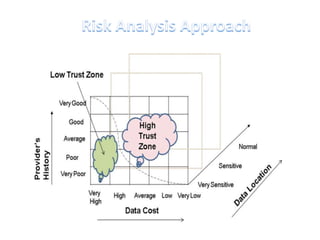
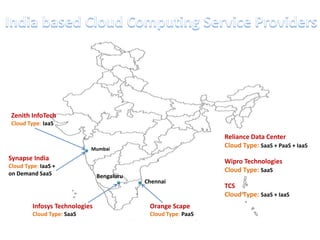
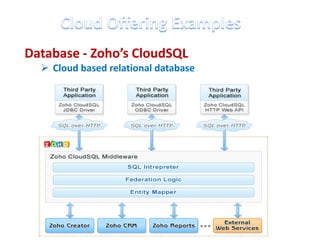
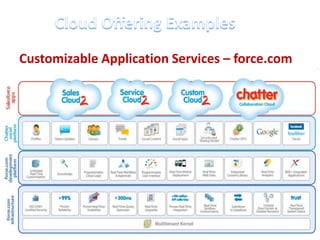
This document discusses cloud computing including its architecture, key facts, risks, applications and future. It defines cloud computing as dynamically scalable and virtualized resources provided over the Internet. The document outlines the layers of cloud computing including software as a service (SaaS), platform as a service (PaaS) and infrastructure as a service (IaaS). It also discusses the benefits of cloud computing like flexibility, scalability and cost savings but notes security risks remain a challenge. The future of cloud computing is predicted to include more hybrid public-private models and growth in developing regions.