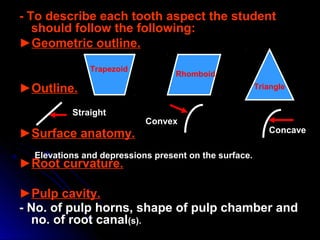
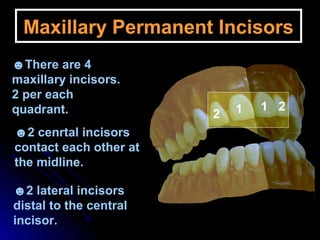
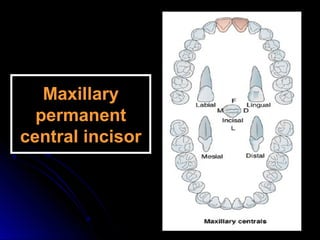
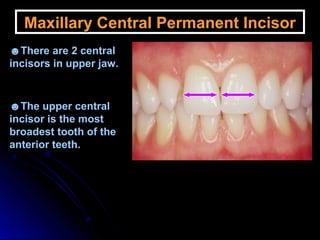
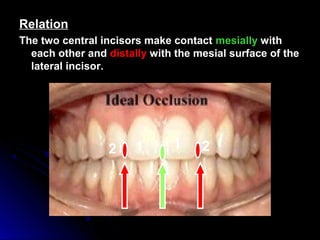
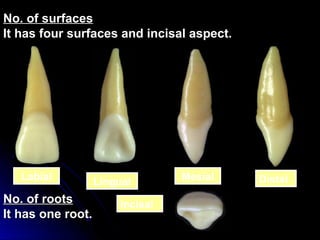
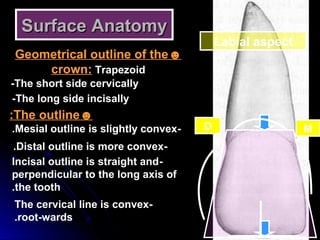
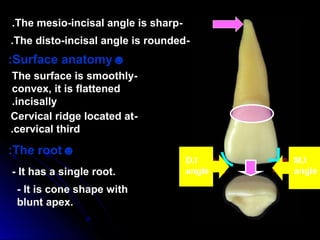
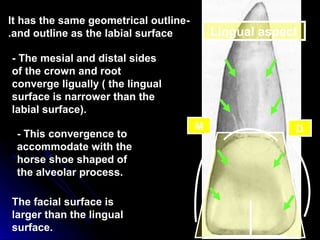
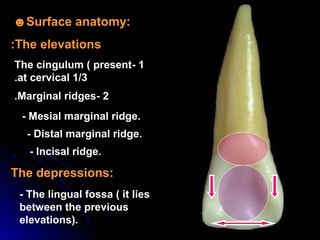
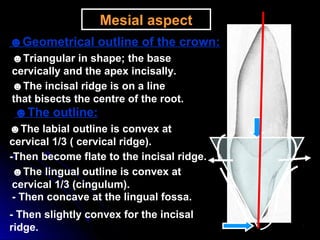
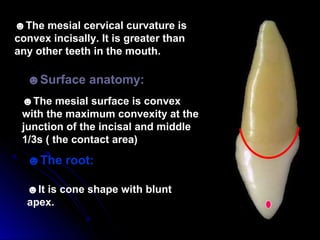
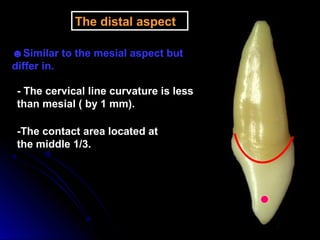
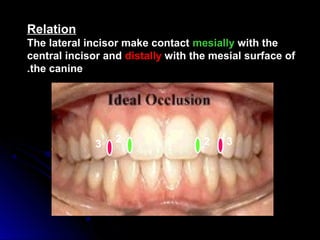
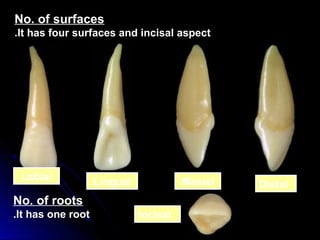
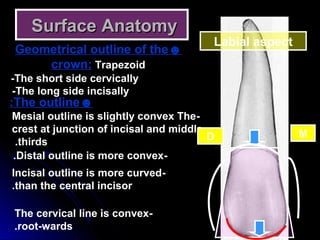
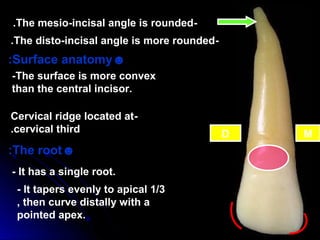
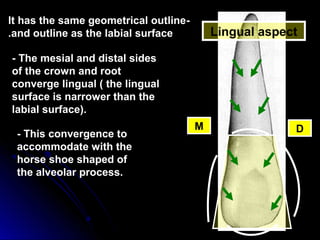
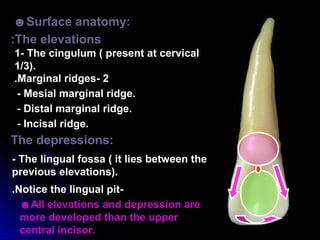
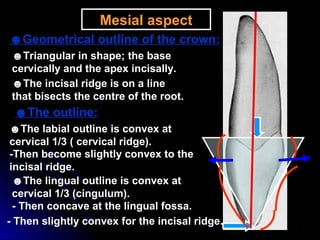
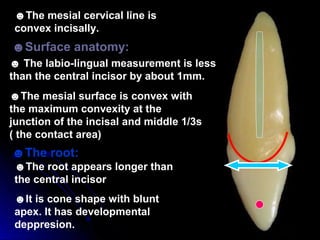
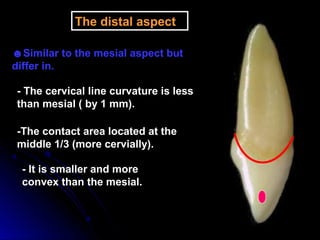
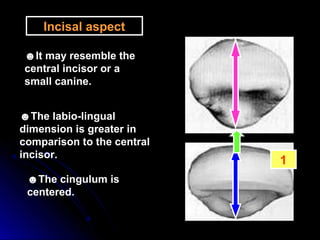
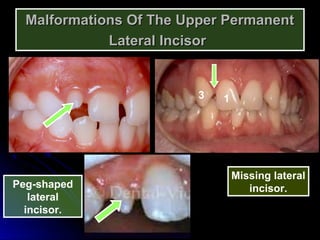
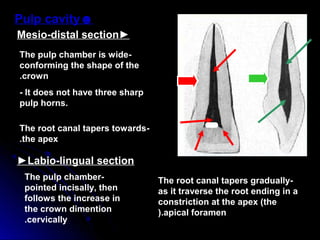
The document describes the anatomy of permanent teeth, focusing on the maxillary central and lateral incisors. It discusses the chronology of development, number of surfaces, relations to other teeth, and detailed surface anatomy of each tooth. For the central incisor, it notes it has four lobes, one root, and makes contact mesially with the other central incisor and distally with the lateral incisor. For the lateral incisor, it is similar but has a more curved incisal edge, more developed ridges and depressions, and contacts the central incisor mesially and canine distally. Both teeth have trapezoid crowns tapering to the root with characteristic elevations, depressions and