Embed presentation
Downloaded 21 times



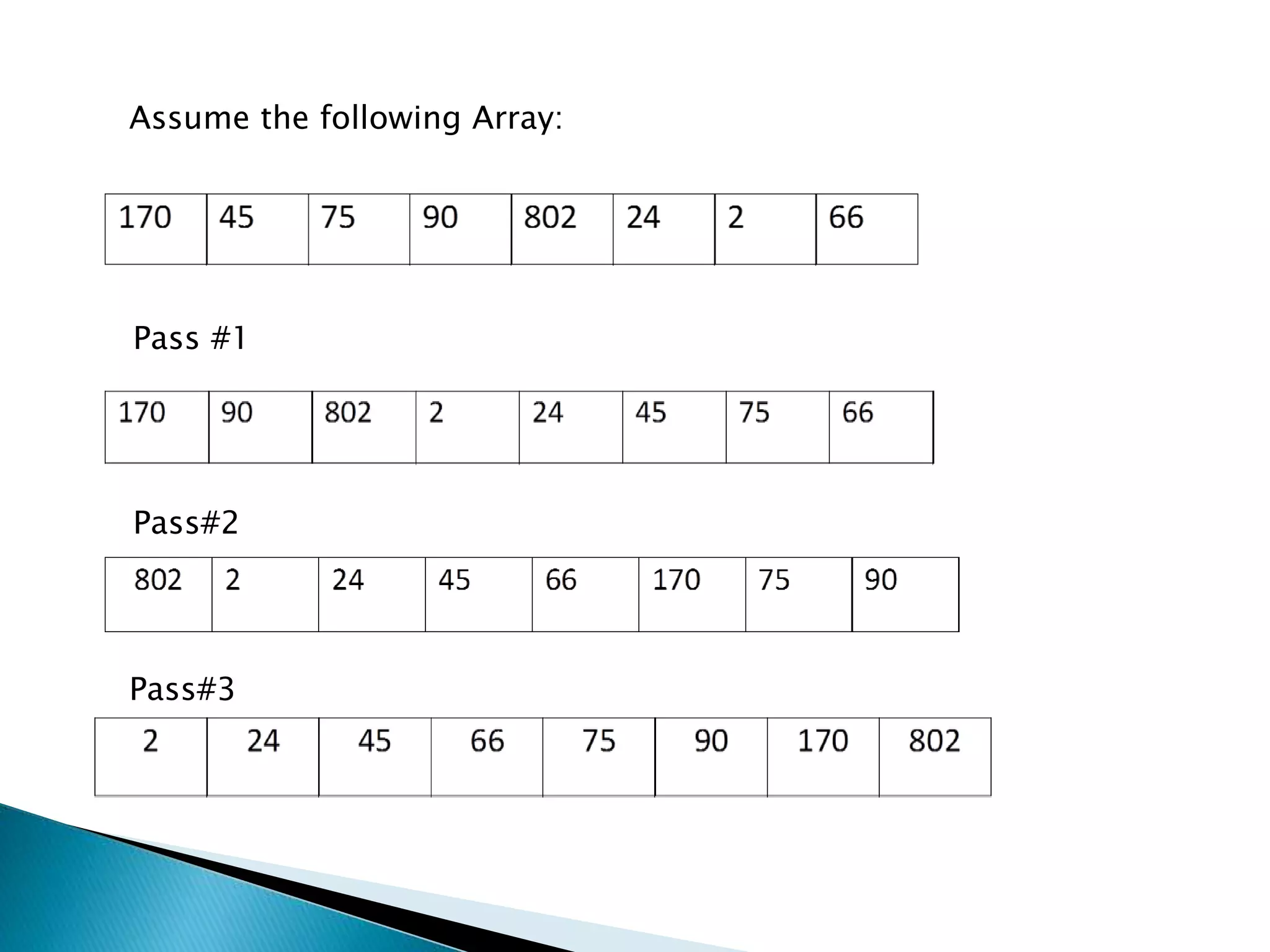
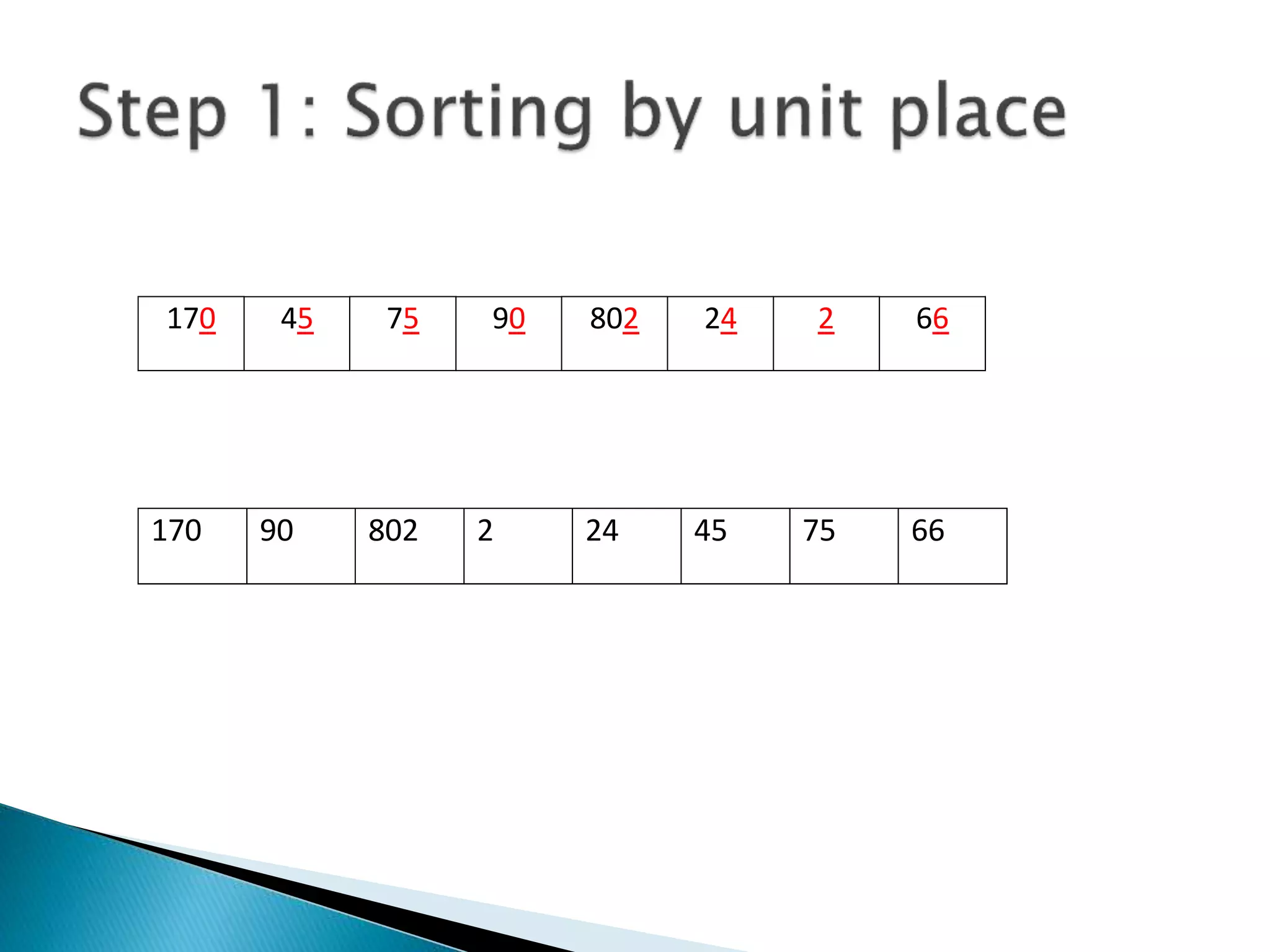



The document describes Radix sort, a sorting algorithm that sorts numbers by their individual digits by making multiple passes through the data. It works by first sorting the numbers based on the units place value, then the tens place, and so on. This is more efficient than other general-purpose sorting algorithms for large data sets with uniformly distributed values. Radix sort runs in O(d(n+k)) time, where d is the number of digits, n is the number of elements, and k is the maximum value of a digit.







