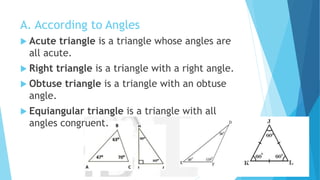
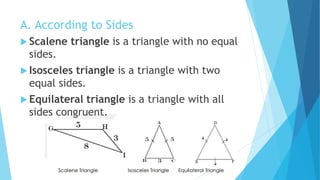
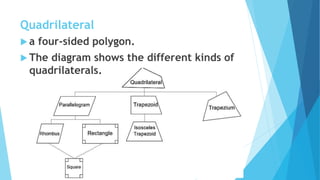
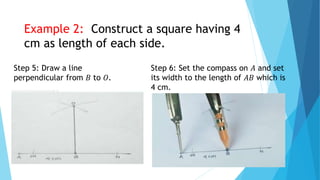
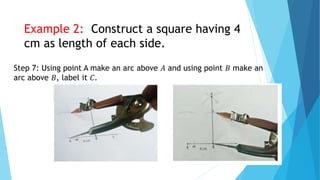
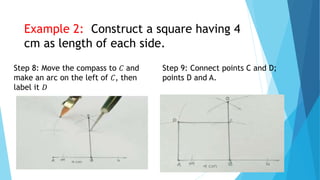
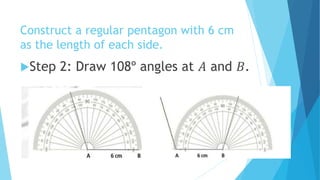
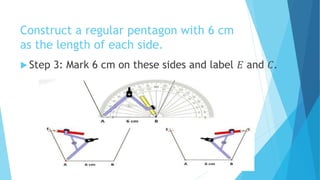
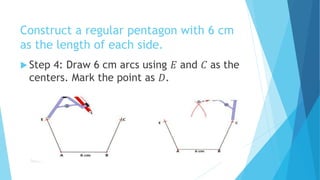
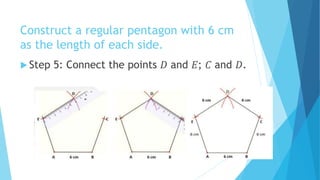
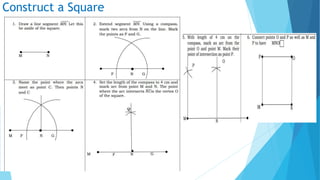
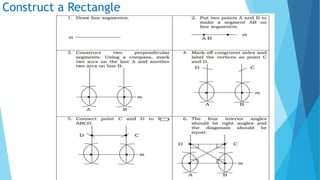
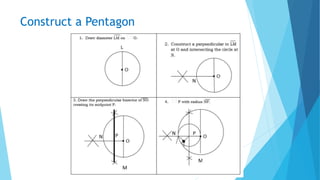
This document provides information about constructing different types of polygons and solving problems involving polygons. It defines triangles, quadrilaterals, and regular polygons. It discusses classifying triangles by angles and sides. It describes different types of quadrilaterals including parallelograms, rectangles, squares, trapezoids, isosceles trapezoids, and trapeziums. The document provides step-by-step examples for constructing triangles, squares, rectangles, pentagons, and hexagons. It includes examples of constructing polygons given specific side lengths or included angles. Finally, it provides practice problems for constructing various polygons.