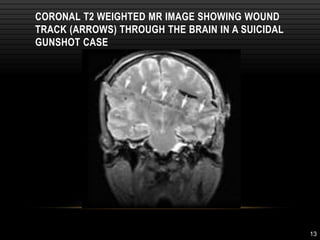
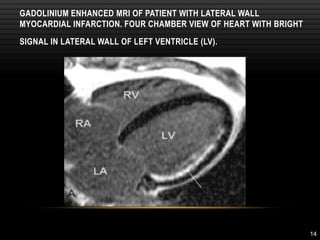
The document discusses minimally invasive autopsy techniques, including both external and internal examinations, as well as advanced imaging technologies like CT and MRI for post-mortem analysis. It outlines the benefits and drawbacks of virtual autopsies, highlighting their non-invasive nature and the challenges such as costs and data manipulation. The virtual autopsy is presented as an evolving forensic tool that may complement or replace traditional autopsy methods while adhering to ethical considerations.