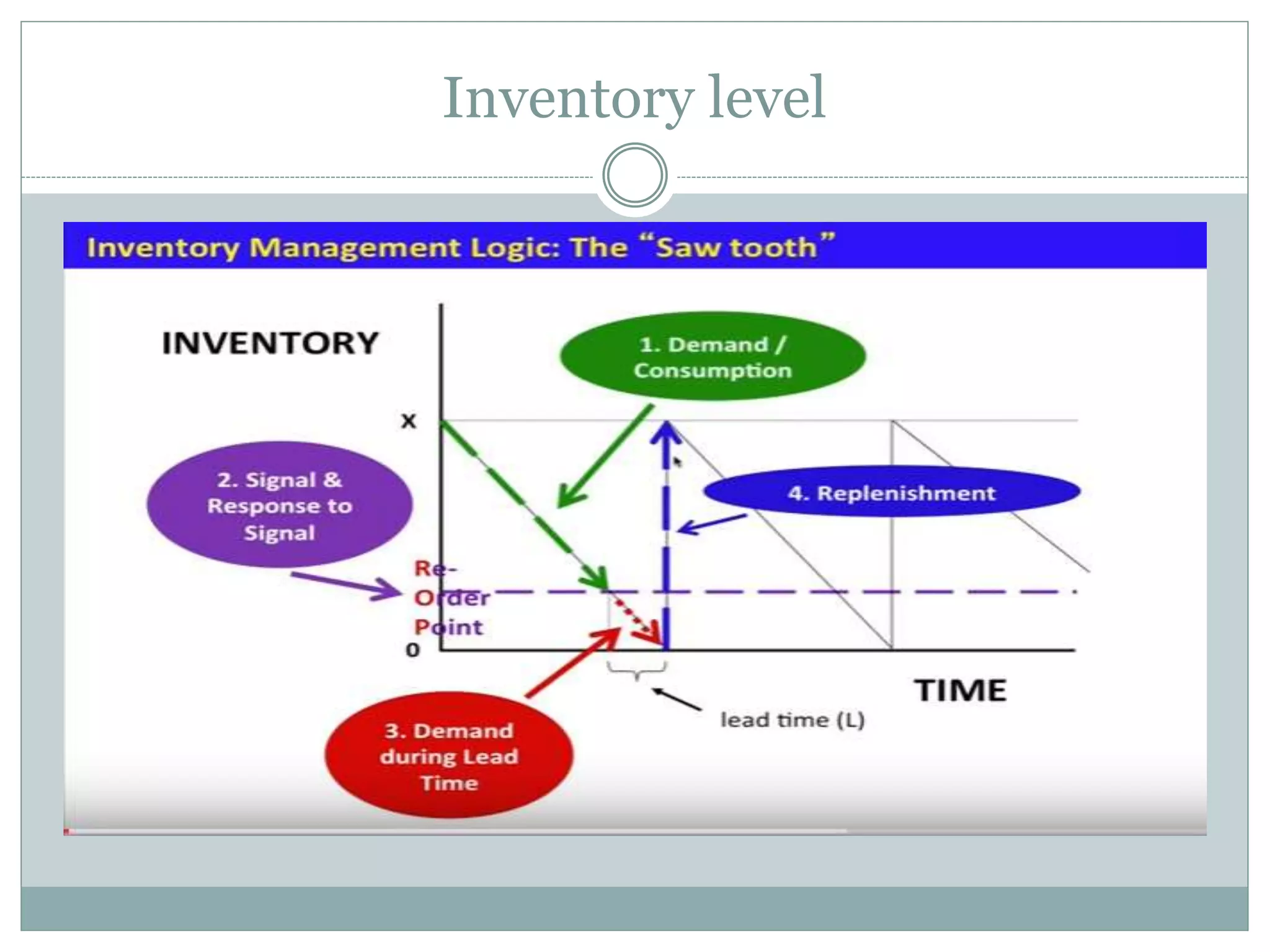
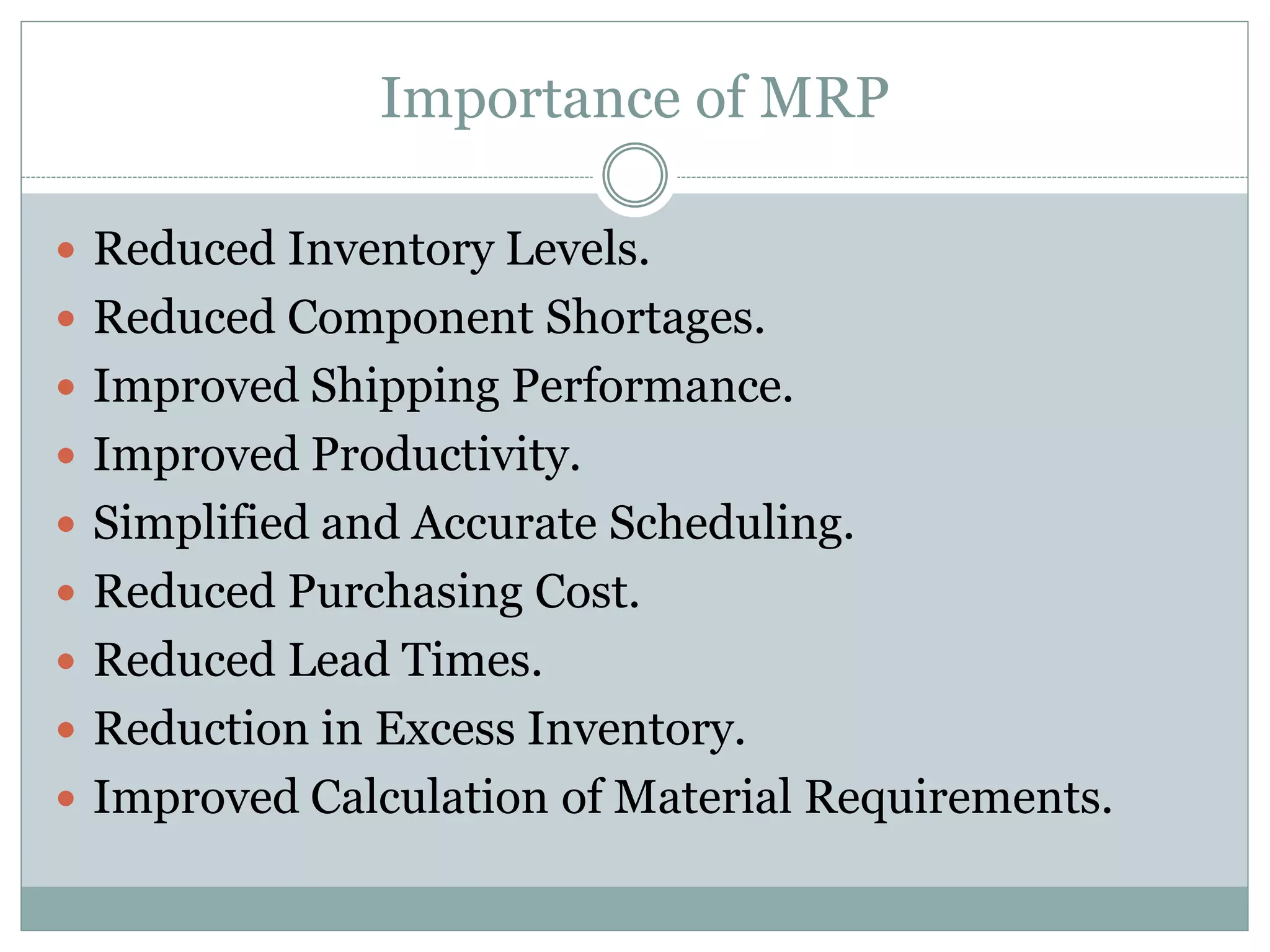
This document discusses Material Requirements Planning (MRP) and its importance. MRP is a computer-based production planning and inventory control system that aims to ensure the right materials are available when needed. MRP uses inputs like the master production schedule, bill of materials, inventory levels, lot sizes, and safety stocks to calculate material requirements and output recommendations for production amounts, staffing levels, and projected inventory balances. Implementing MRP can reduce inventory levels and costs, improve scheduling accuracy, and increase productivity by preventing component shortages.