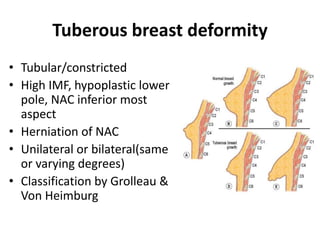
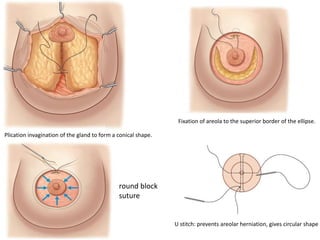
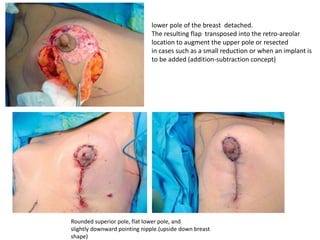
Mastopexy, or breast lift surgery, addresses breast ptosis or sagging through surgical techniques to reshape and lift the breasts. The document discusses various mastopexy techniques including periareolar, vertical scar, and Benelli mastopexy. It also covers patient evaluation and classifications of breast ptosis. The goals of mastopexy are to restore a youthful breast shape while minimizing scarring and recurrence of ptosis over time.