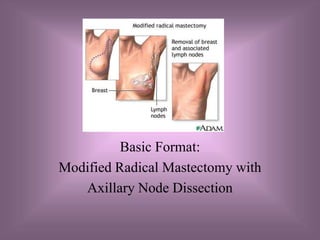
The document outlines the procedures for a modified radical mastectomy with axillary node dissection, including the objectives, relevant anatomy and pathophysiology, diagnostic evaluations, surgical steps from incision to closure, specimen handling, and postoperative considerations.