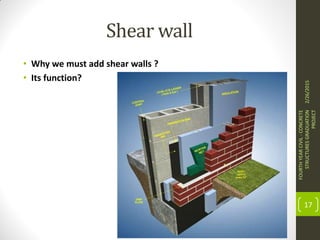
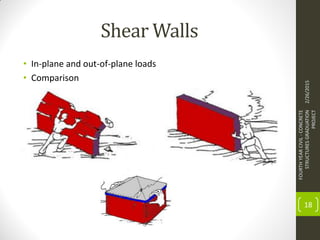
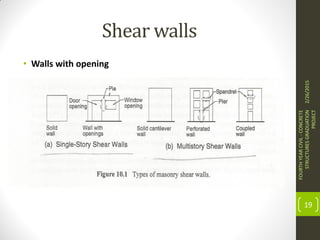
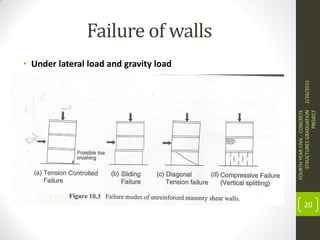
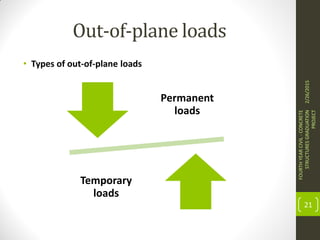
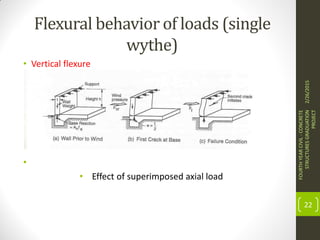
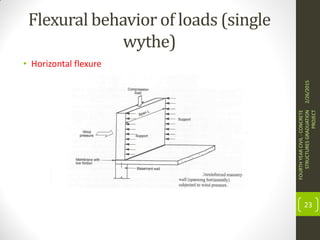
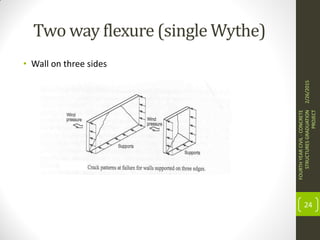
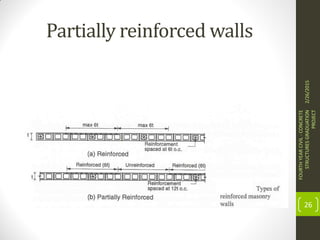
This document outlines the topics covered in a graduation project on the behavior and design of masonry structures. It discusses the historical background of masonry construction, properties of masonry materials, common building units used, reinforcement, and loads. Design considerations are presented for masonry beams, shear walls, flexural behavior under various loads, and partially reinforced walls. The project provides information needed to research and design reinforced masonry structures.