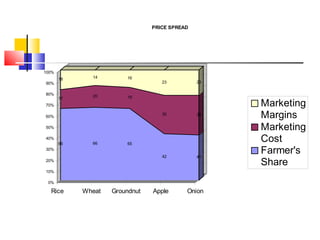
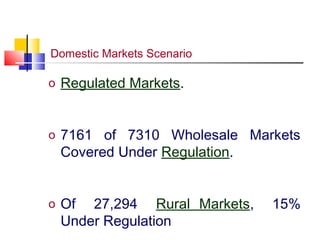
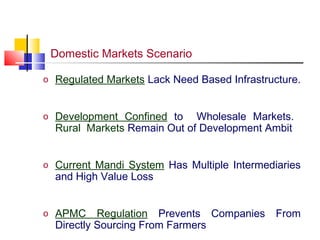
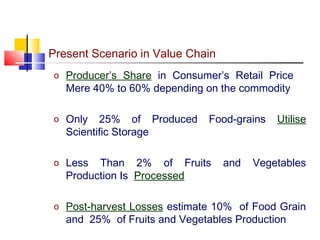
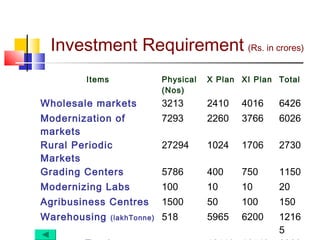
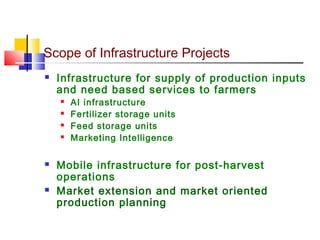
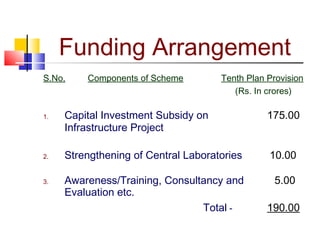
The document discusses agricultural marketing reforms and infrastructure in India. It notes that while production efforts receive 90% of attention, only 10% goes to marketing and post-harvest phases. This results in farmers receiving a small share of the consumer price for crops. The document calls for a paradigm shift towards a more market-driven agricultural system. It outlines various problems with the current system and proposes a roadmap for reforms that includes enabling private investment, strengthening markets, and improving grading, standardization and quality certification. The scheme for developing agricultural marketing infrastructure and grading is also summarized.