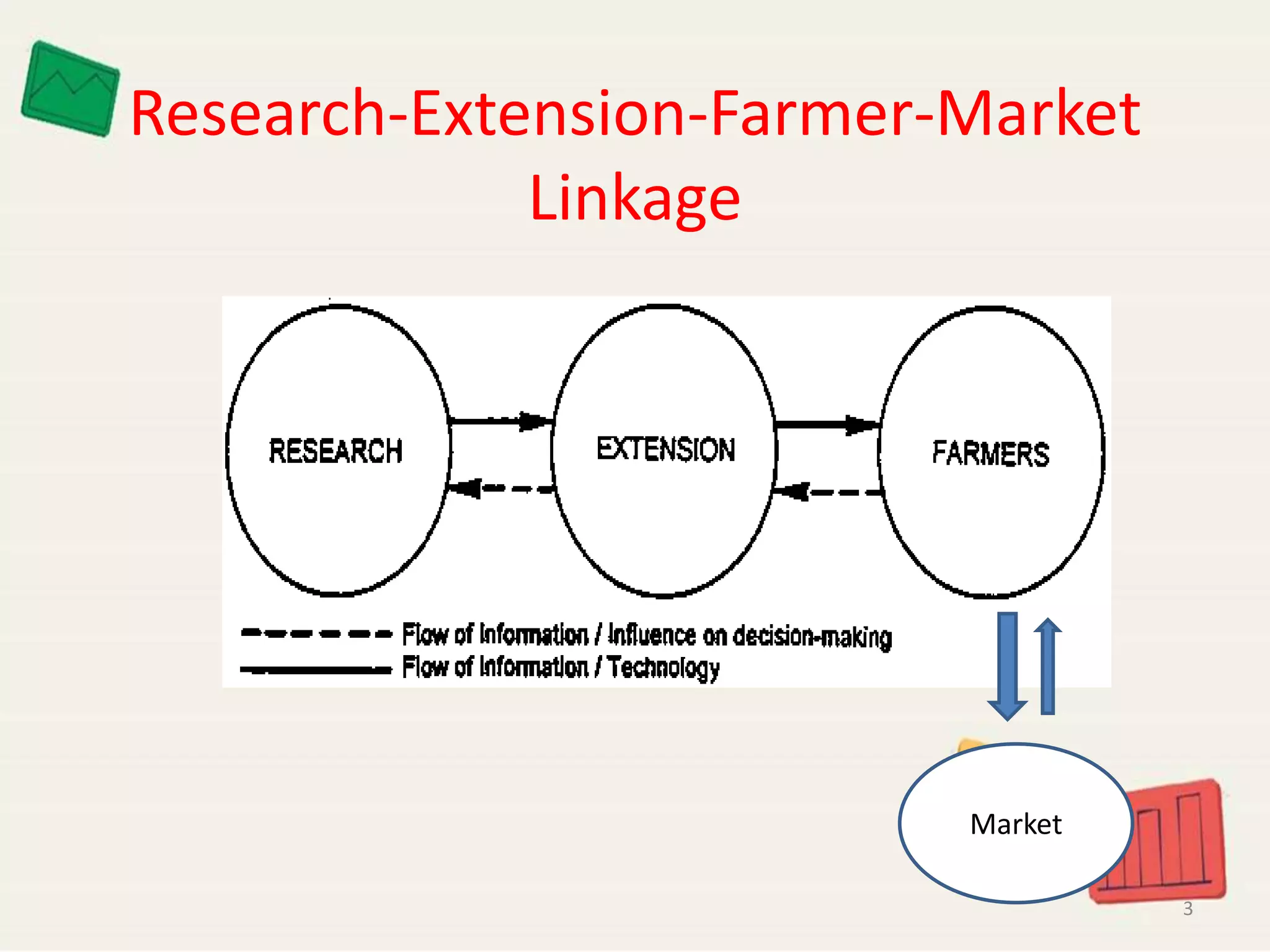
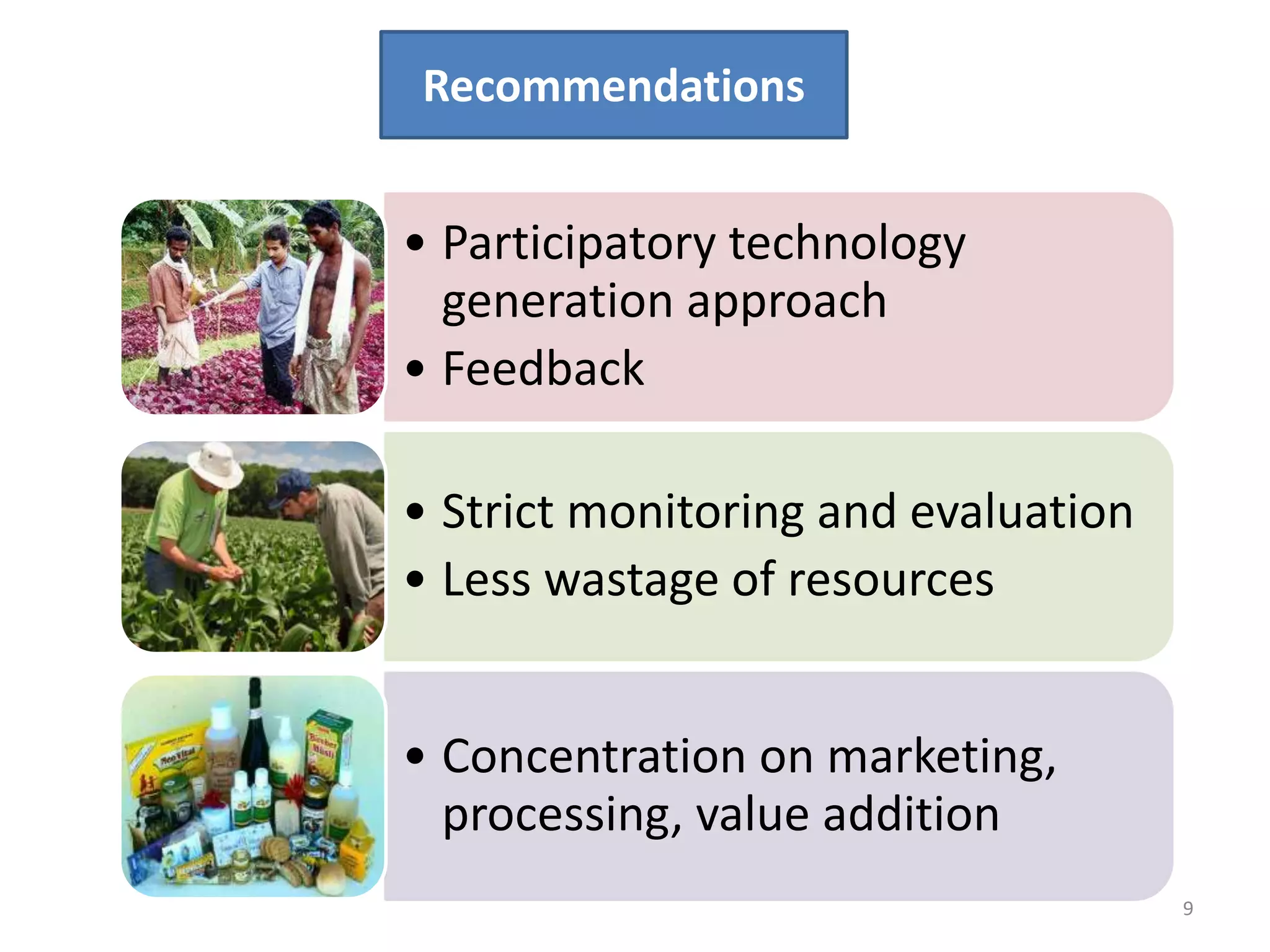
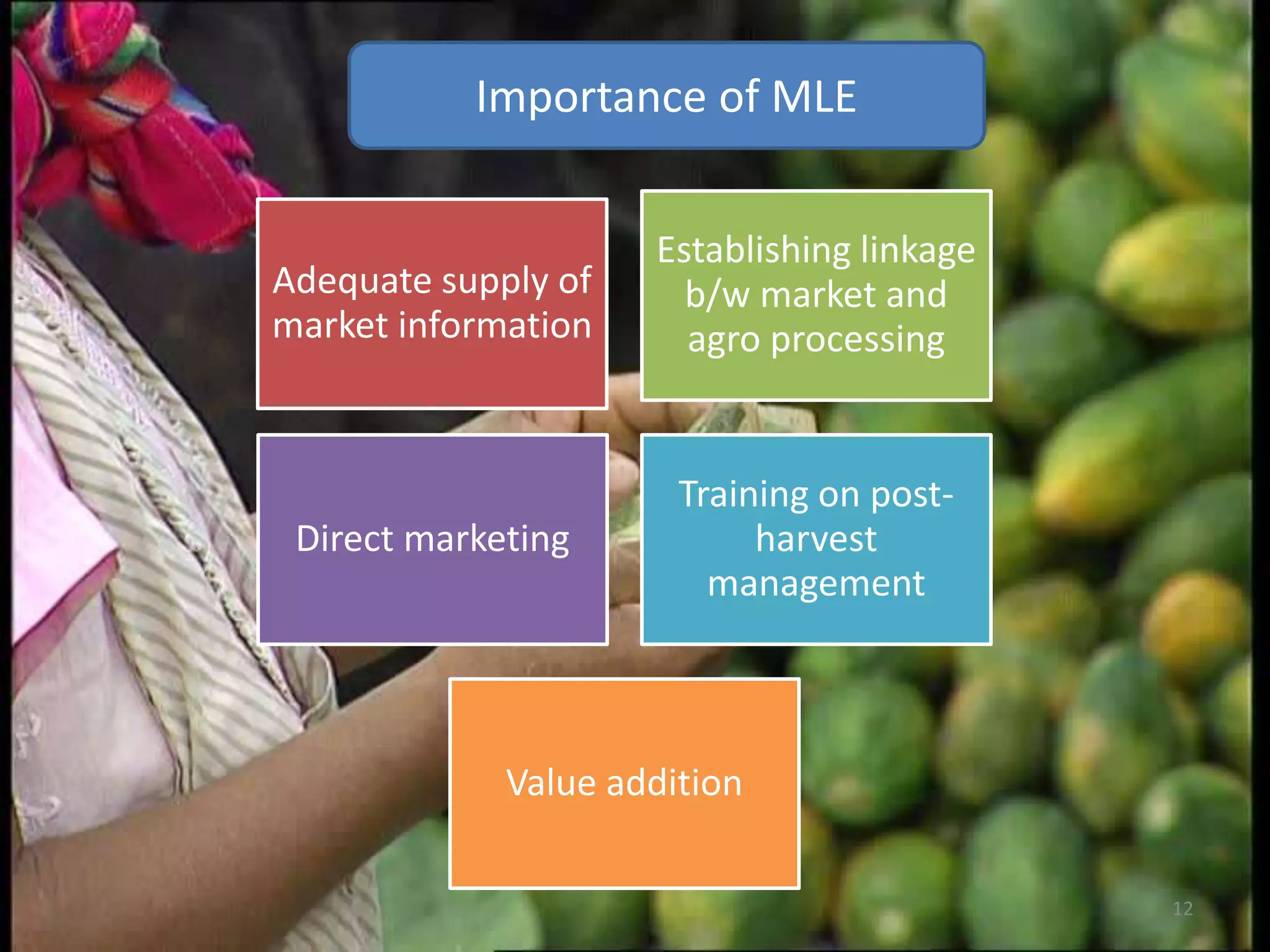
The document discusses the importance of research-extension-farmer-market linkages in agriculture, particularly for small and marginal farmers in Punjab. It highlights the issues of low adoption of technology and ineffective knowledge transfer, and recommends participatory approaches to enhance market-led extension. Innovations in direct marketing initiatives are presented as solutions to improve profitability and address production challenges.