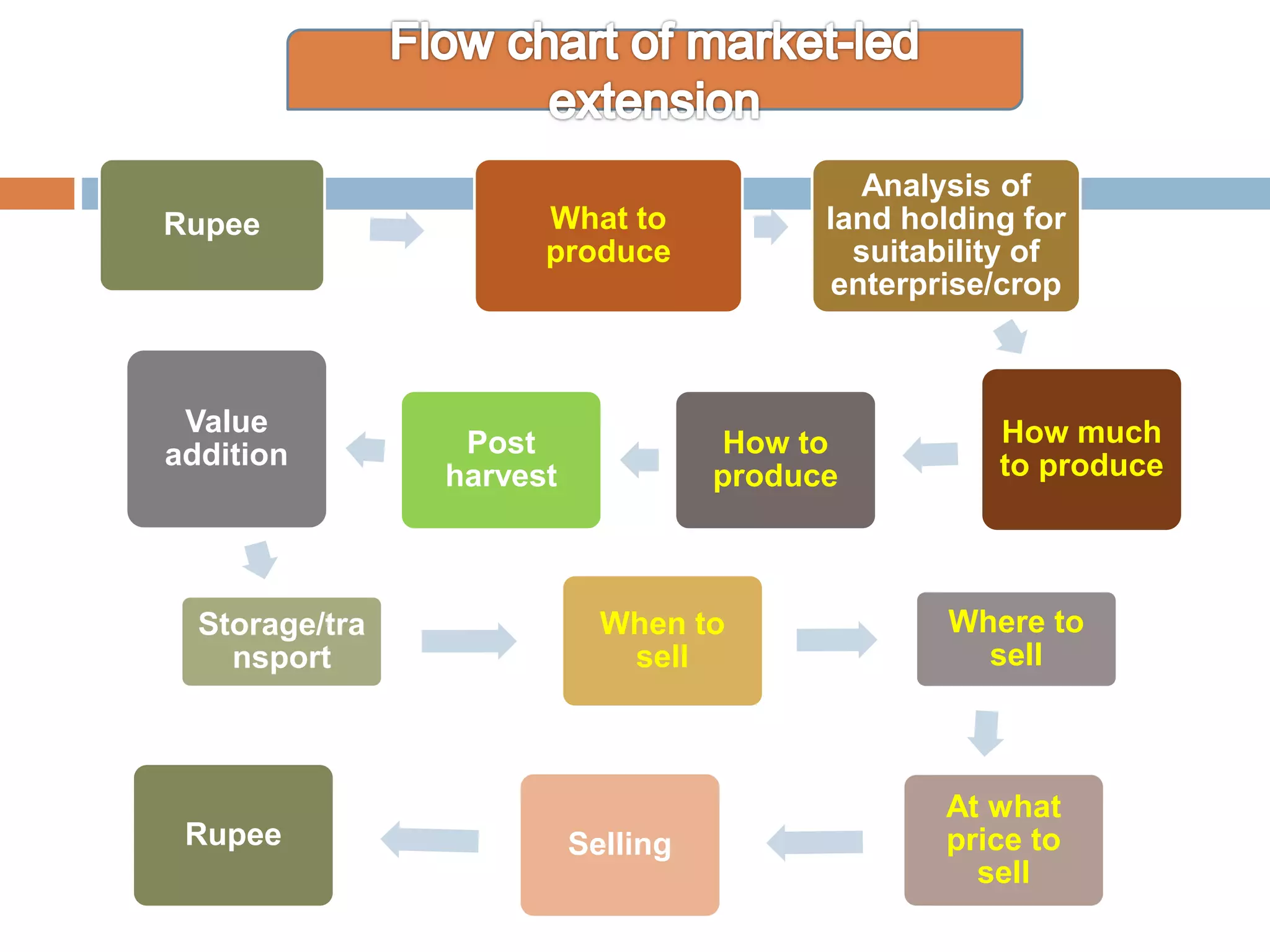
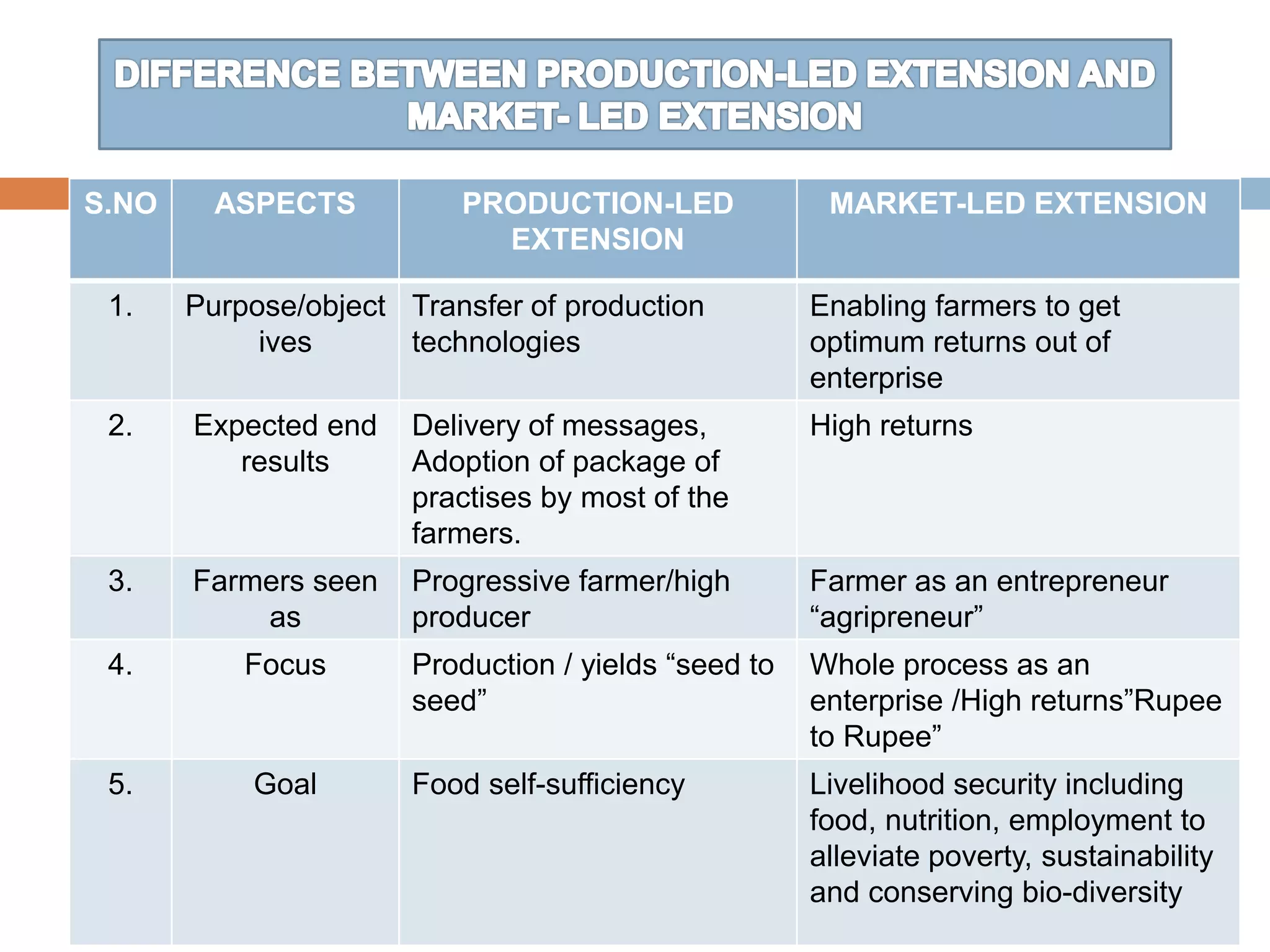
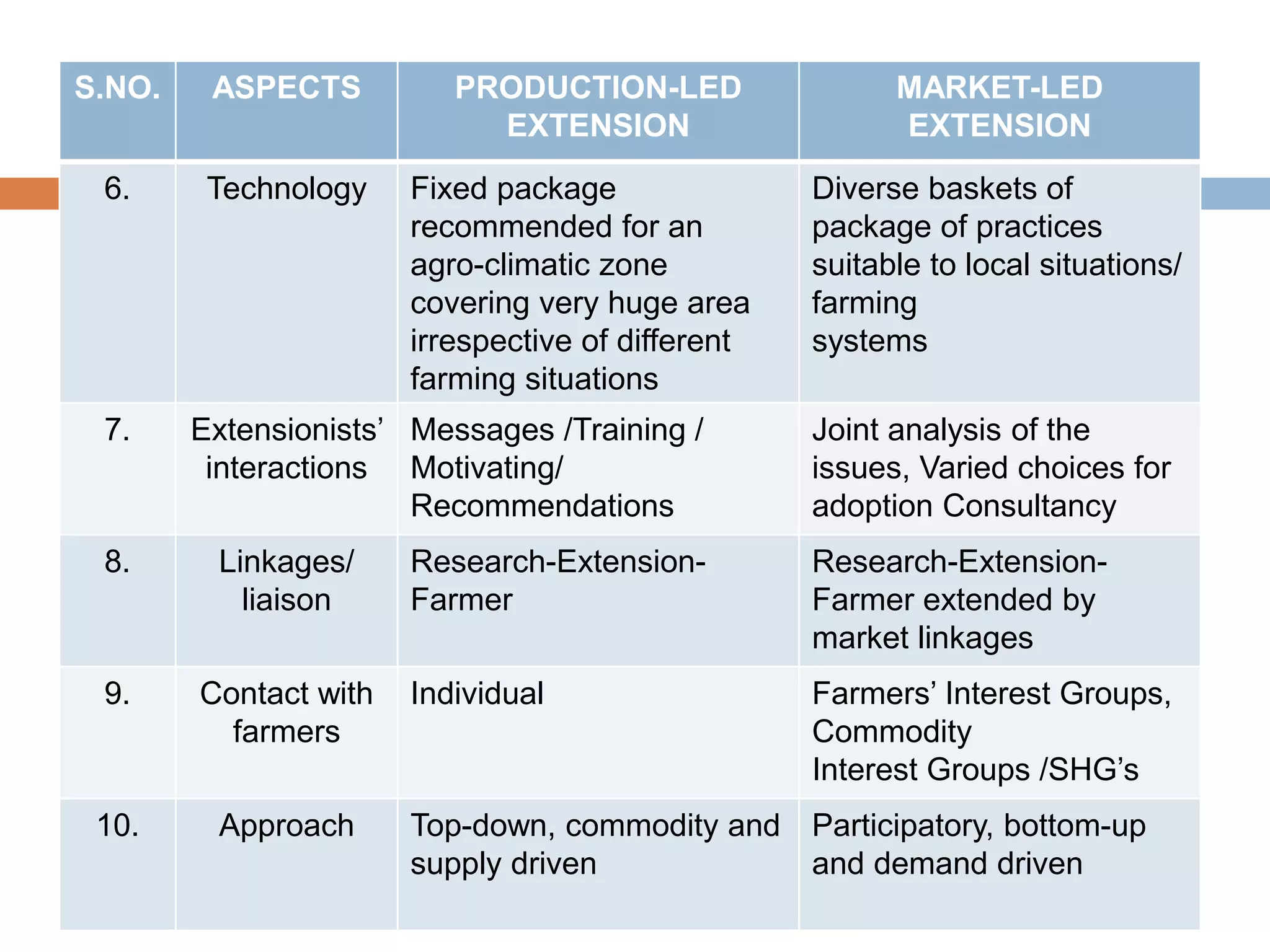
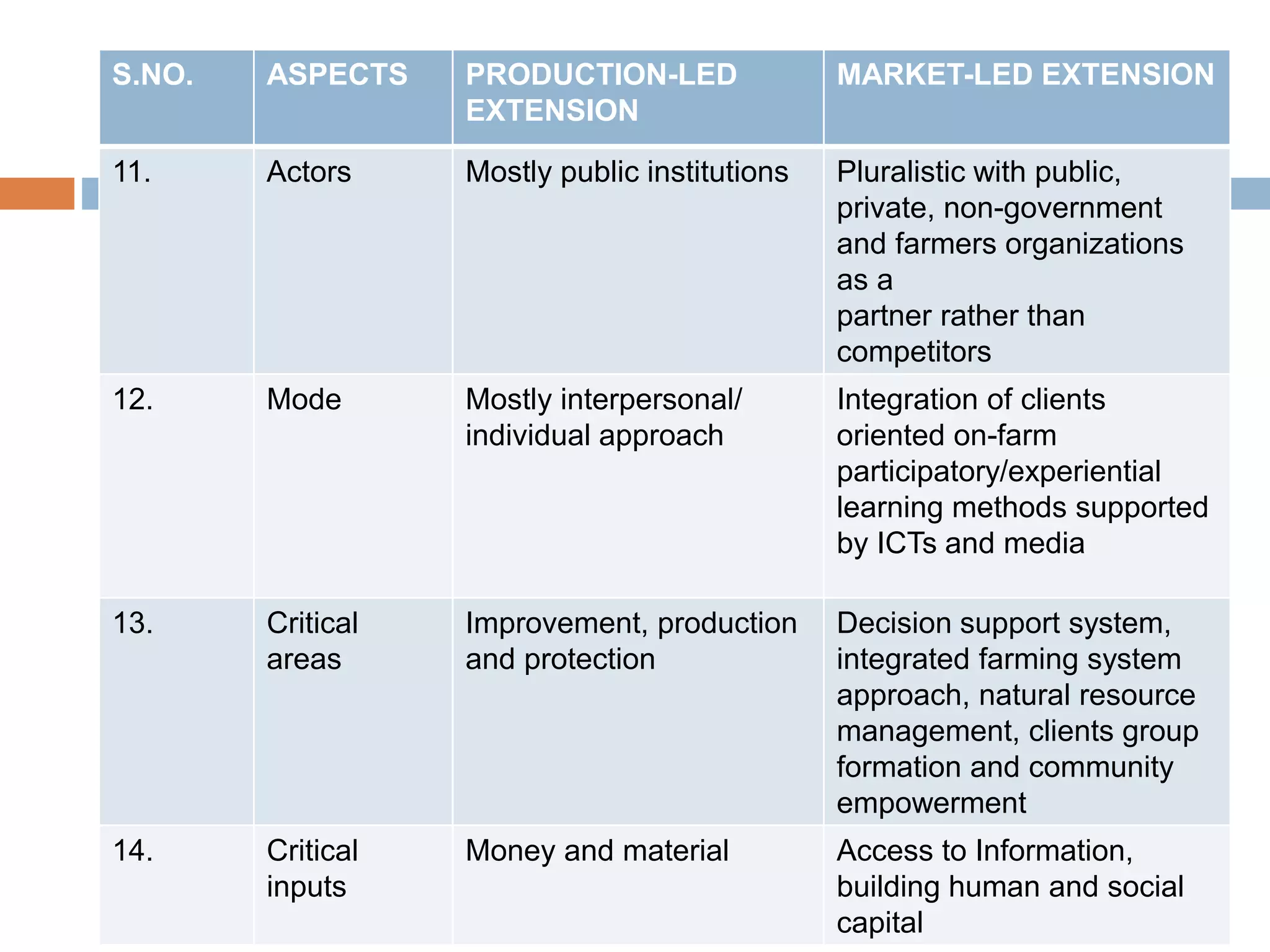
The document discusses the evolution of agricultural extension in India, emphasizing a shift from production-led to market-led extension to help farmers realize better economic returns. It highlights the need for farmers to adapt to market demands, improve knowledge and skills in marketing, and utilize technology for market intelligence. Additionally, it addresses challenges such as inadequate market information, the influence of middlemen, and the necessity of forming farmer interest groups to enhance their market capabilities.