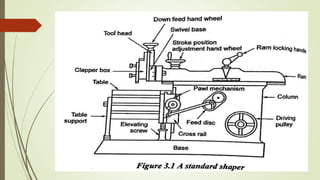
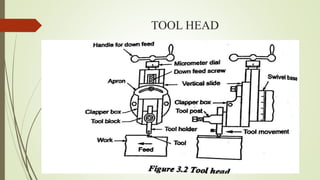
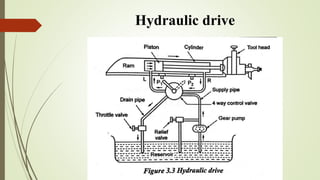
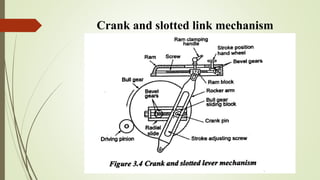
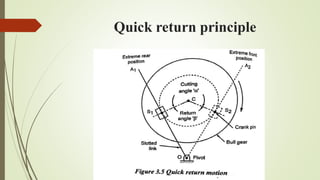
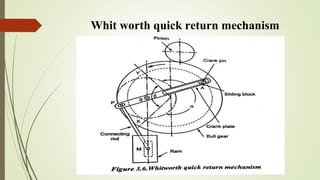
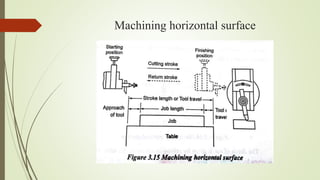
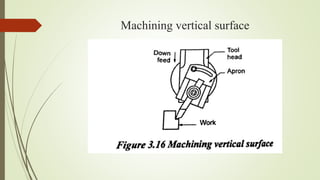
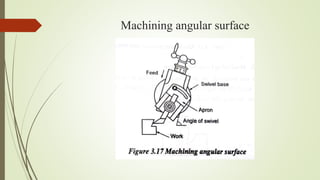
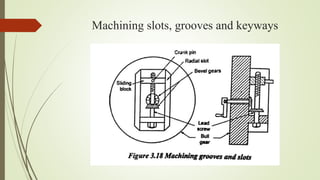
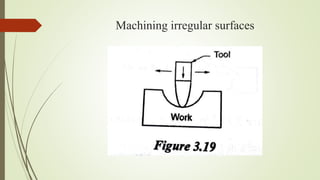
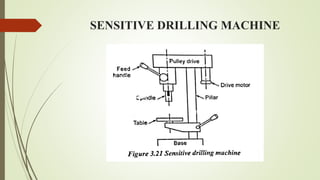
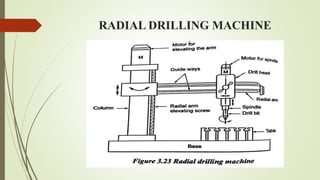
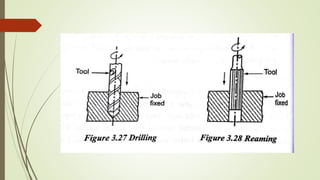
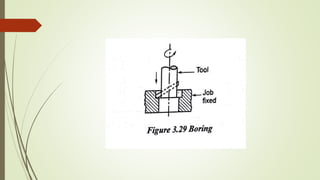
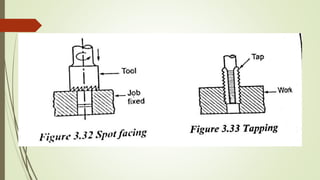
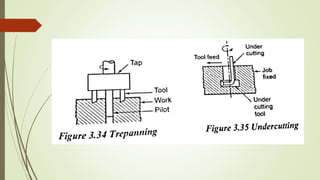
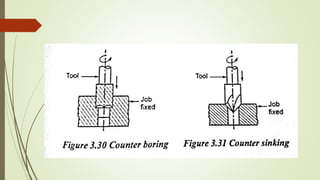
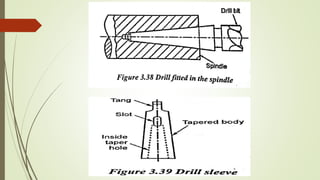
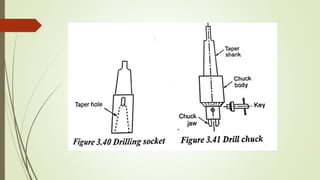
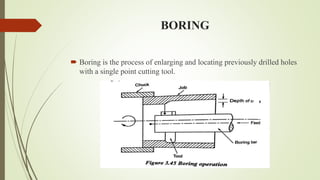
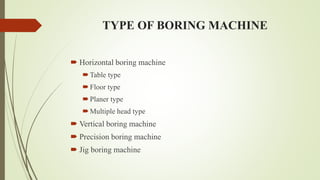
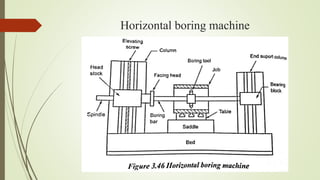
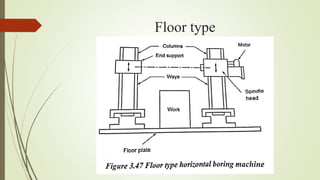
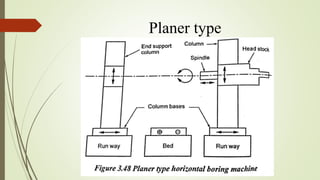
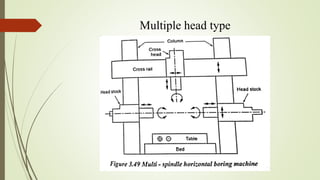
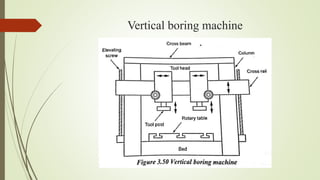
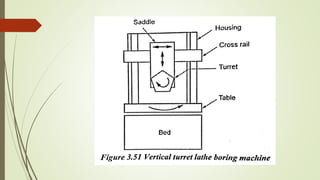
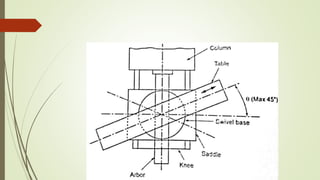
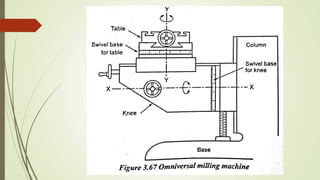
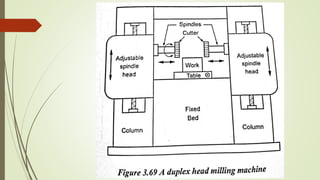
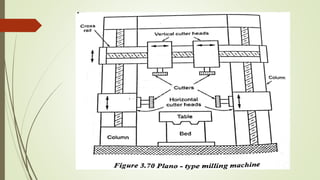
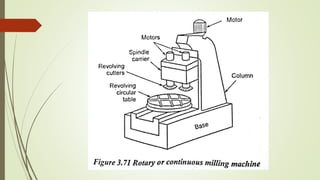
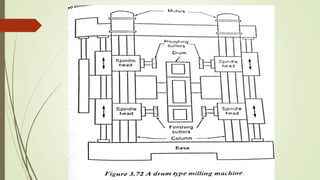
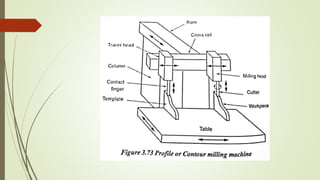
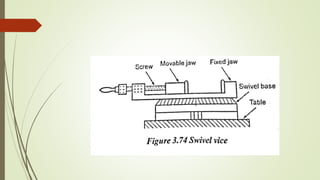
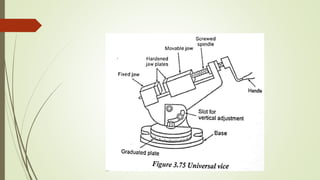
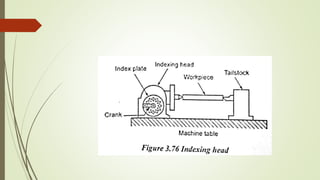
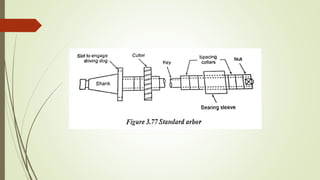
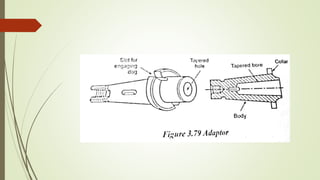
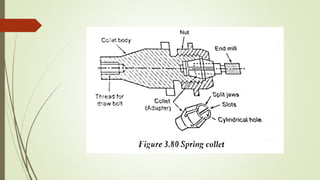
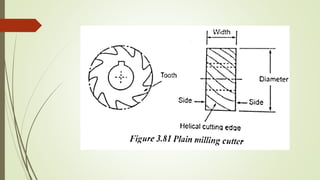
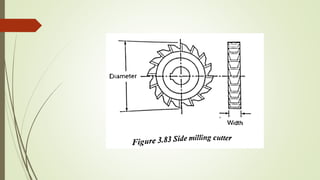
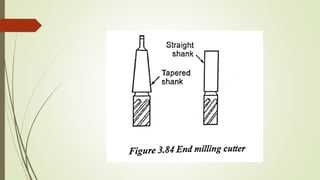
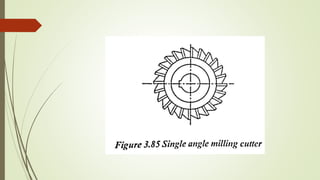
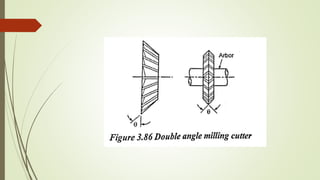
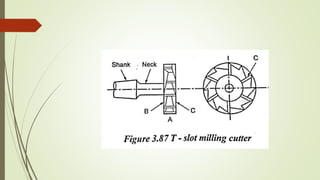
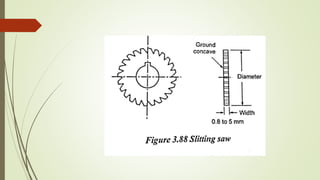
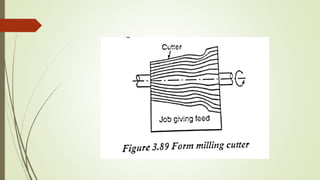
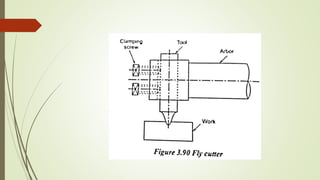
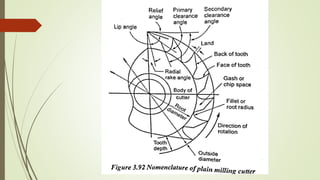
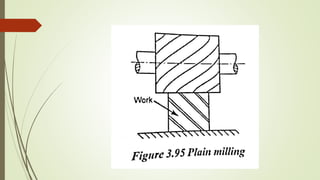
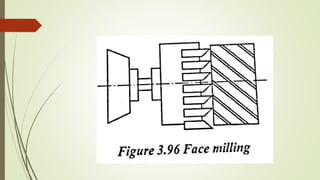
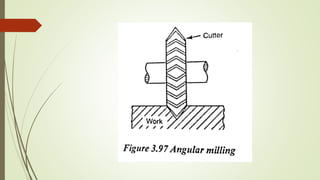
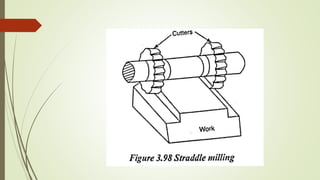
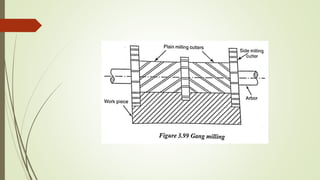
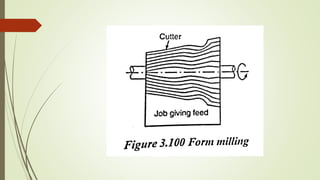
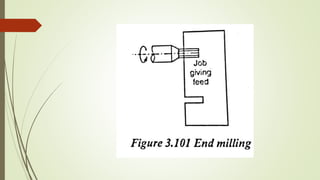
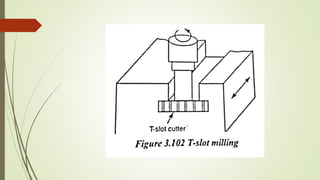
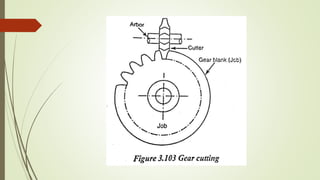
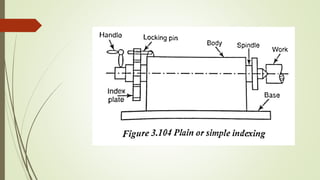
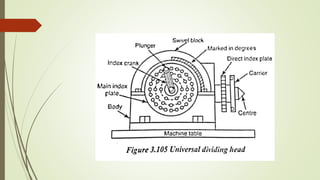
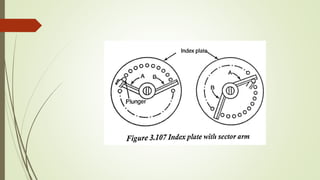
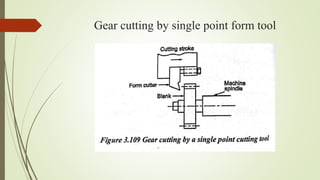
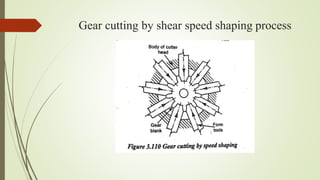
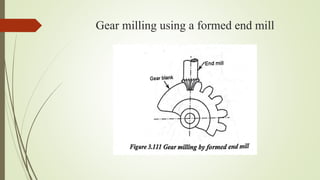
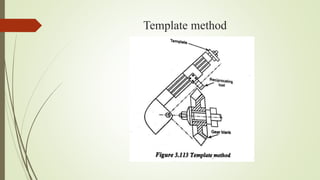
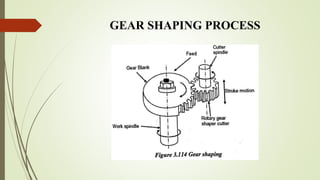
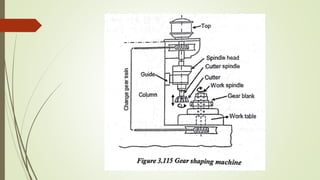
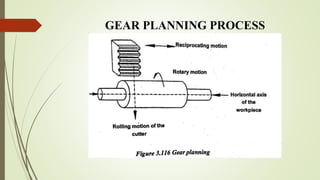
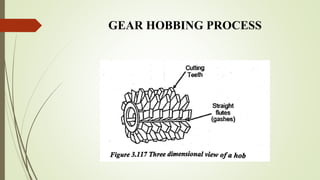
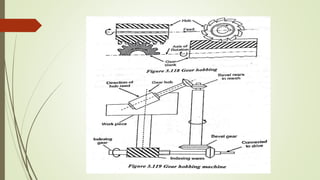
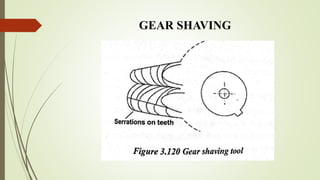
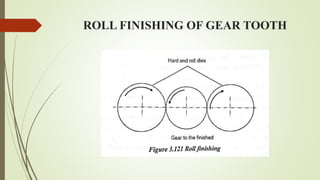
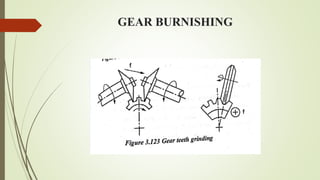
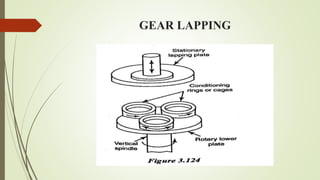
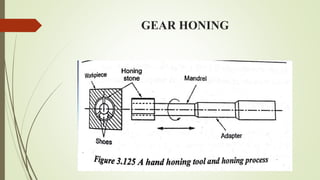
The document provides an overview of various machining operations including drilling, milling, boring, tapping, and gear cutting, detailing the machines and processes used for each. It covers classifications of machines, types of cutting tools, and specific operations such as shaper, drilling machine types, and gear milling techniques. Additionally, it explains components and specifications of these machines, emphasizing their functionalities in producing flat and other surface machinations.