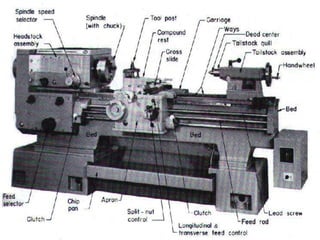
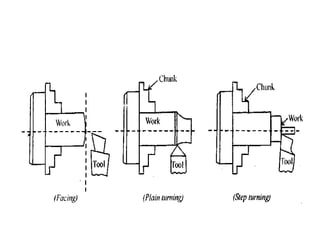
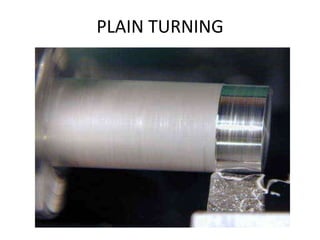
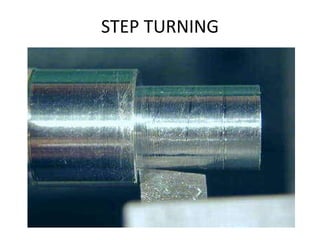
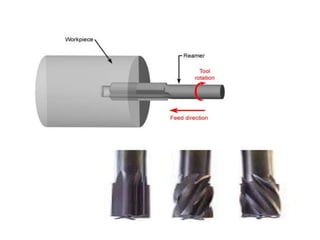
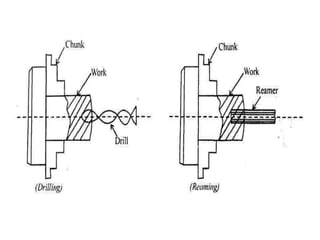
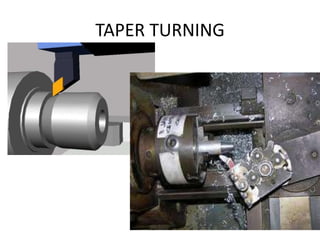
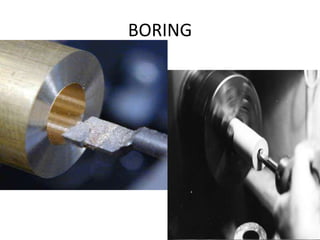
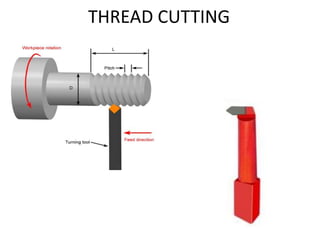
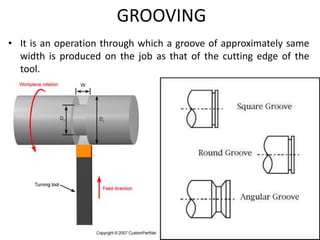
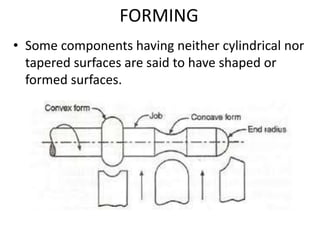
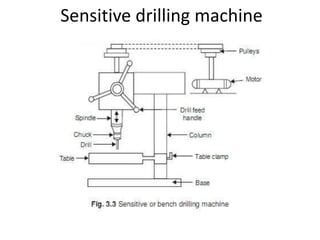
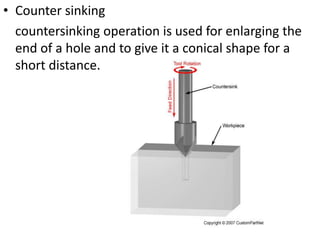
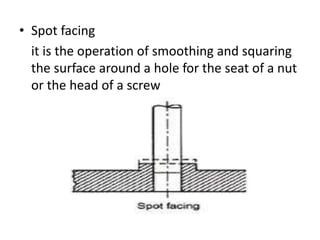
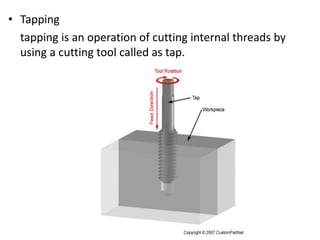
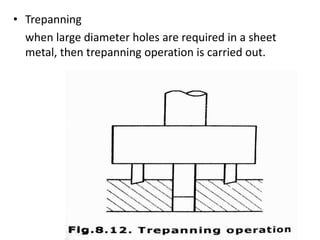
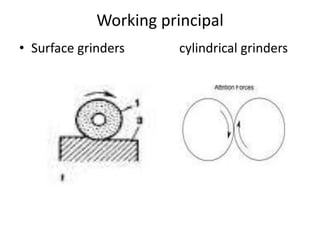
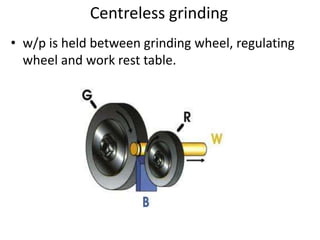
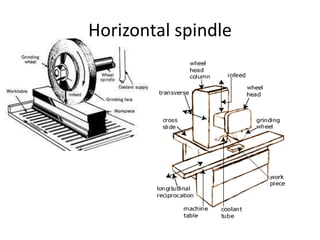
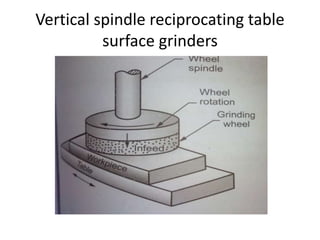
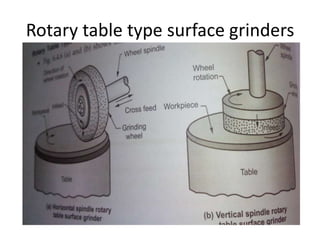
The document is a comprehensive study of machine tools, particularly focusing on lathe machines, drilling machines, and grinding machines used in metal cutting and surface finishing. It classifies machine tools based on purpose and size of chip removed, detailing operations and components of each type, including their functionalities and manufacturing processes. The document outlines specific operations such as turning, drilling, and grinding, along with their variations and applications in mechanical engineering.