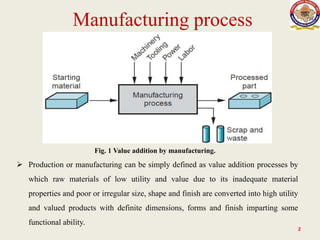
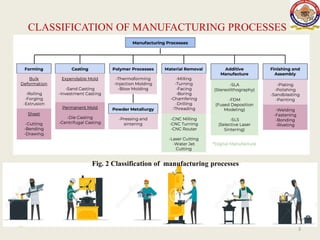
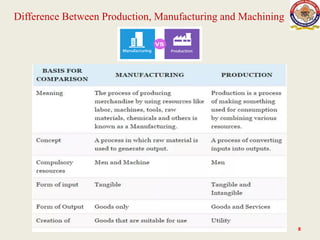
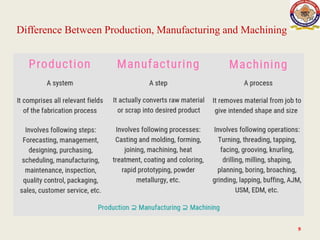
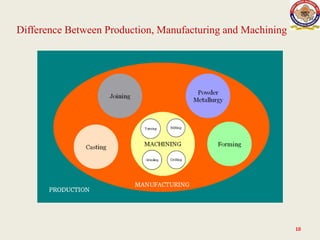
The lecture on manufacturing processes, presented by Raj Kumar Bairwa, outlines the value-added transformation of raw materials into high-utility products. Manufacturing processes are classified into four main categories: shaping or forming, joining, removal, and regenerative manufacturing. The lecture also distinguishes between production as a comprehensive system that includes various steps leading to product fabrication and manufacturing as the specific conversion of raw materials into final products.