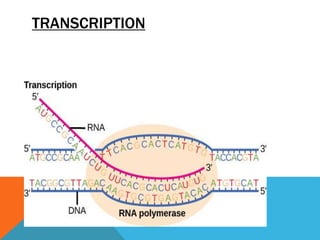
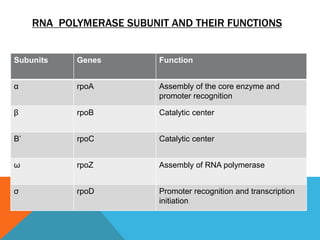
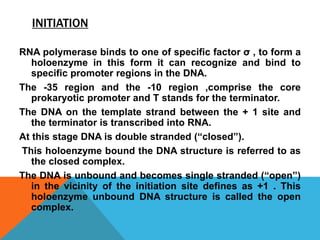
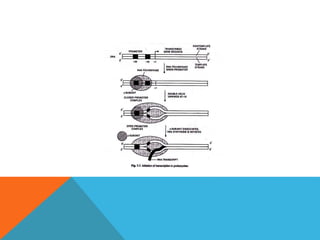
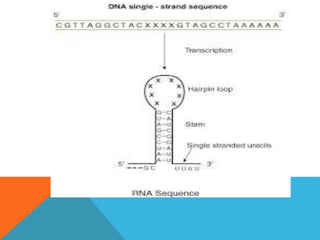
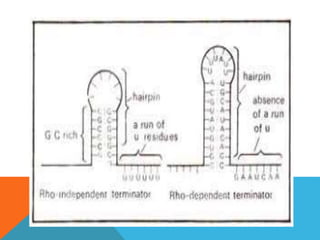
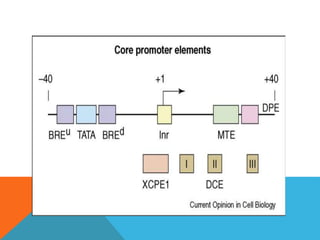
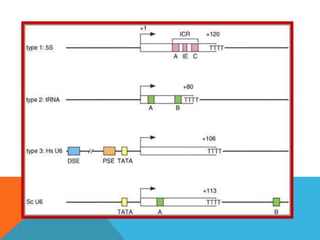
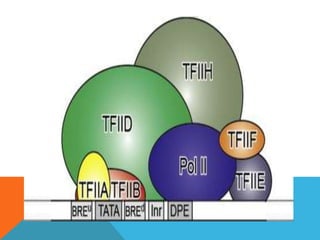
Transcription is the process of synthesizing RNA using DNA as a template. It involves three main stages - initiation, elongation, and termination. In initiation, RNA polymerase binds to the promoter region of DNA and unwinds it to form an open complex. In elongation, RNA polymerase moves along the DNA template adding complementary RNA nucleotides. Termination occurs when the polymerase encounters a terminator sequence and dissociates from the DNA. Prokaryotes and eukaryotes use different RNA polymerases and have variations in their transcription mechanisms.