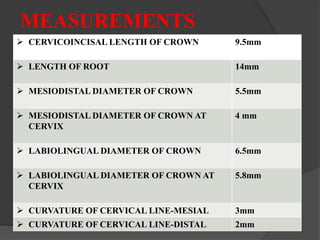
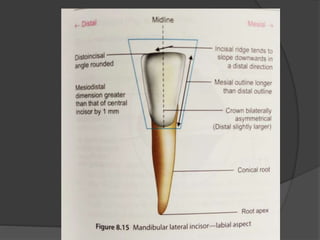
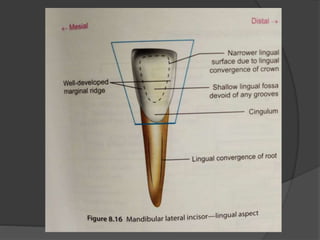
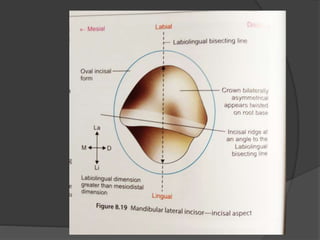
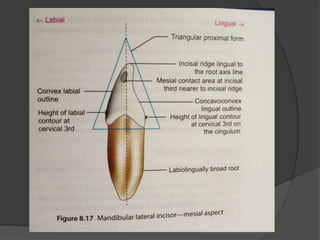
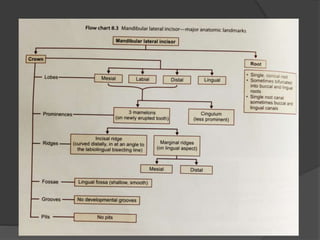
The document provides detailed information on the morphology, chronology, and anatomy of mandibular lateral incisors, including eruption times and measurements. It describes specific traits such as crown shape, root structure, and contact areas, highlighting the differences between various dental numbering systems. Additionally, it notes anatomical features like the pulp chamber size and root canal variations.