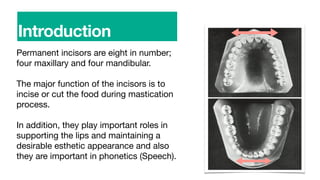
Permanent incisors are the eight front teeth, with four in the maxilla and four in the mandible. Their primary functions are to incise food during chewing and to support the lips. They also play roles in speech and aesthetics.
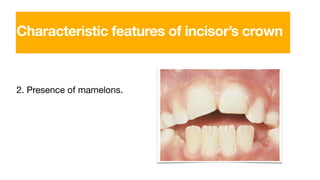
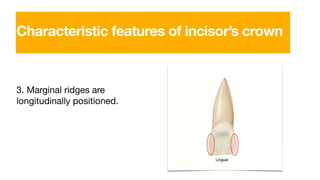
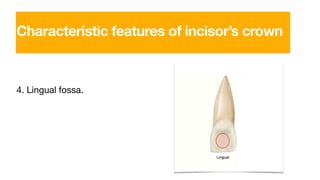
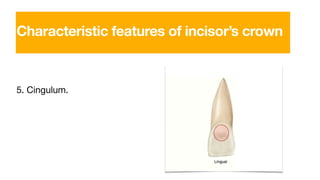
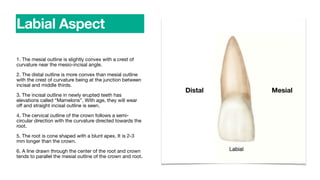
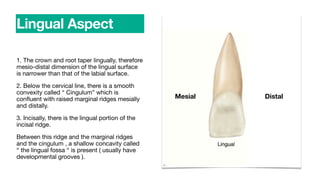
The permanent maxillary central incisor has a square or rectangular shape with a straight mesial outline and rounded distal outline. It is the widest anterior tooth and has identifying features like mamelons on the incisal ridge in newly erupted teeth, and a well-developed cingulum, marginal ridges, and lingual fossa. It has a single tapered root.
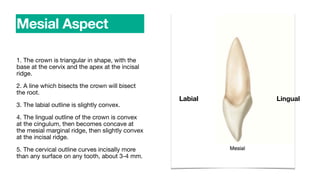
The permanent mandibular central incisor has a triangular crown shape with the