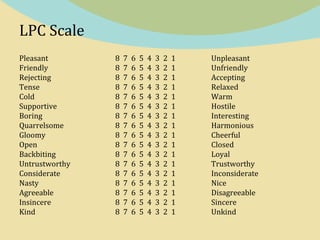
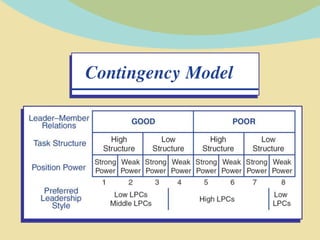
This document provides an overview of Fiedler's Contingency Theory of Leadership. It introduces Fred Fiedler, the originator of the theory, and provides biographical details about him. The core concepts of the theory are explained, including situational favorableness, leadership styles (measured by the LPC scale), and how the theory assesses whether a leader will be effective based on the interaction between their style and the situation. Advantages like its prescriptive nature and ability to identify leaders are outlined. Disadvantages around applying it in changing environments and accurately choosing contingency approaches are also noted.