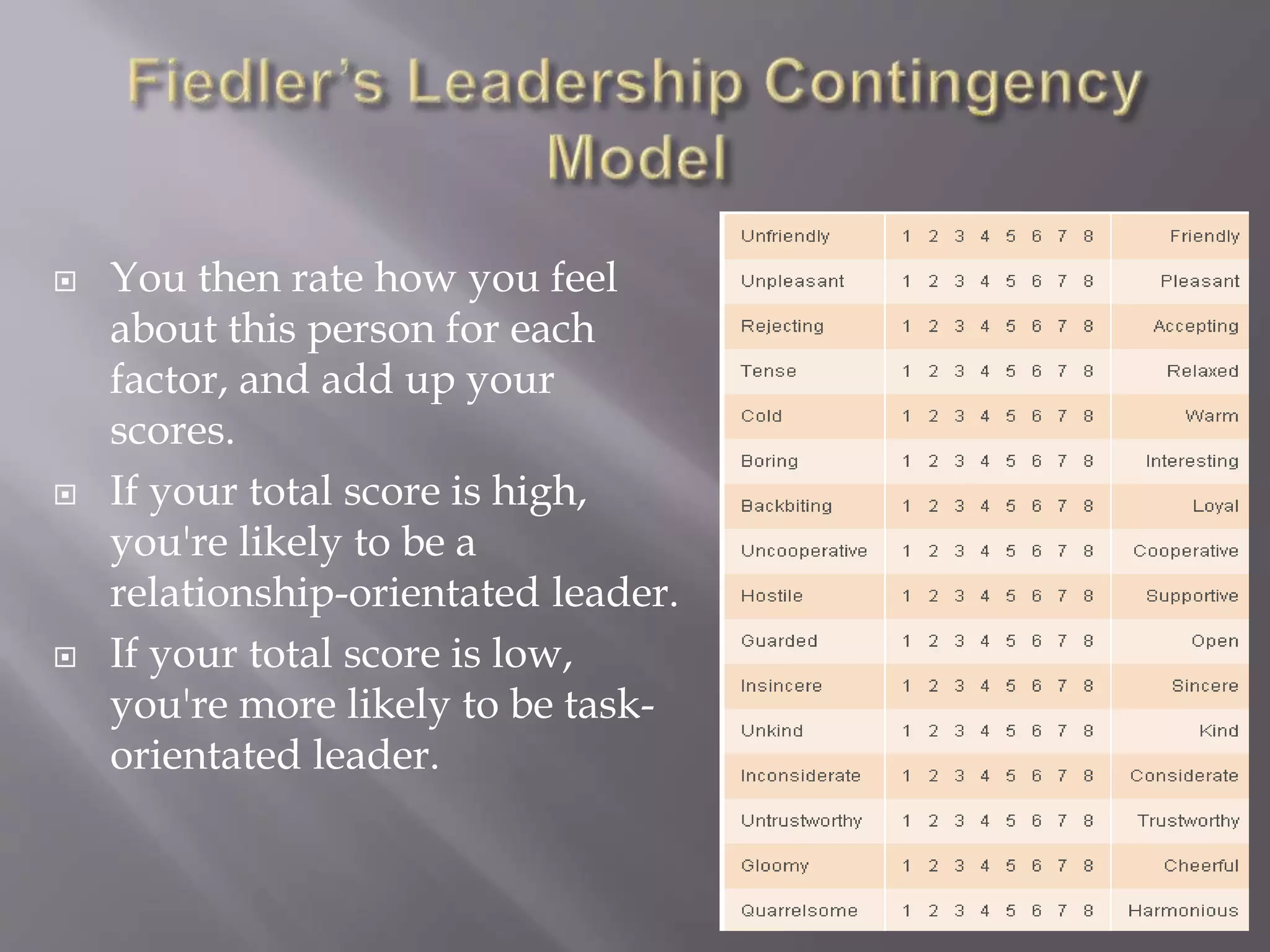
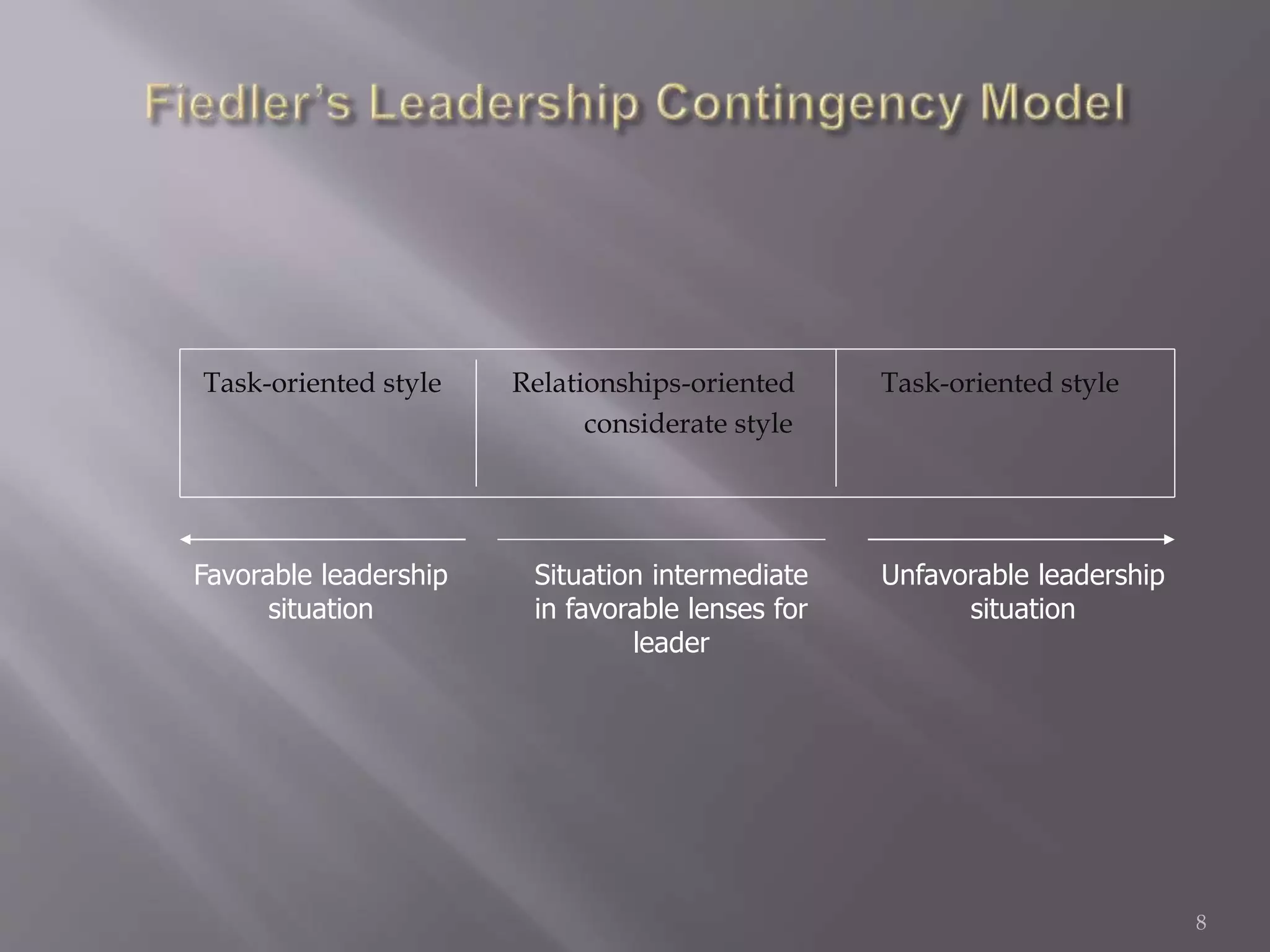
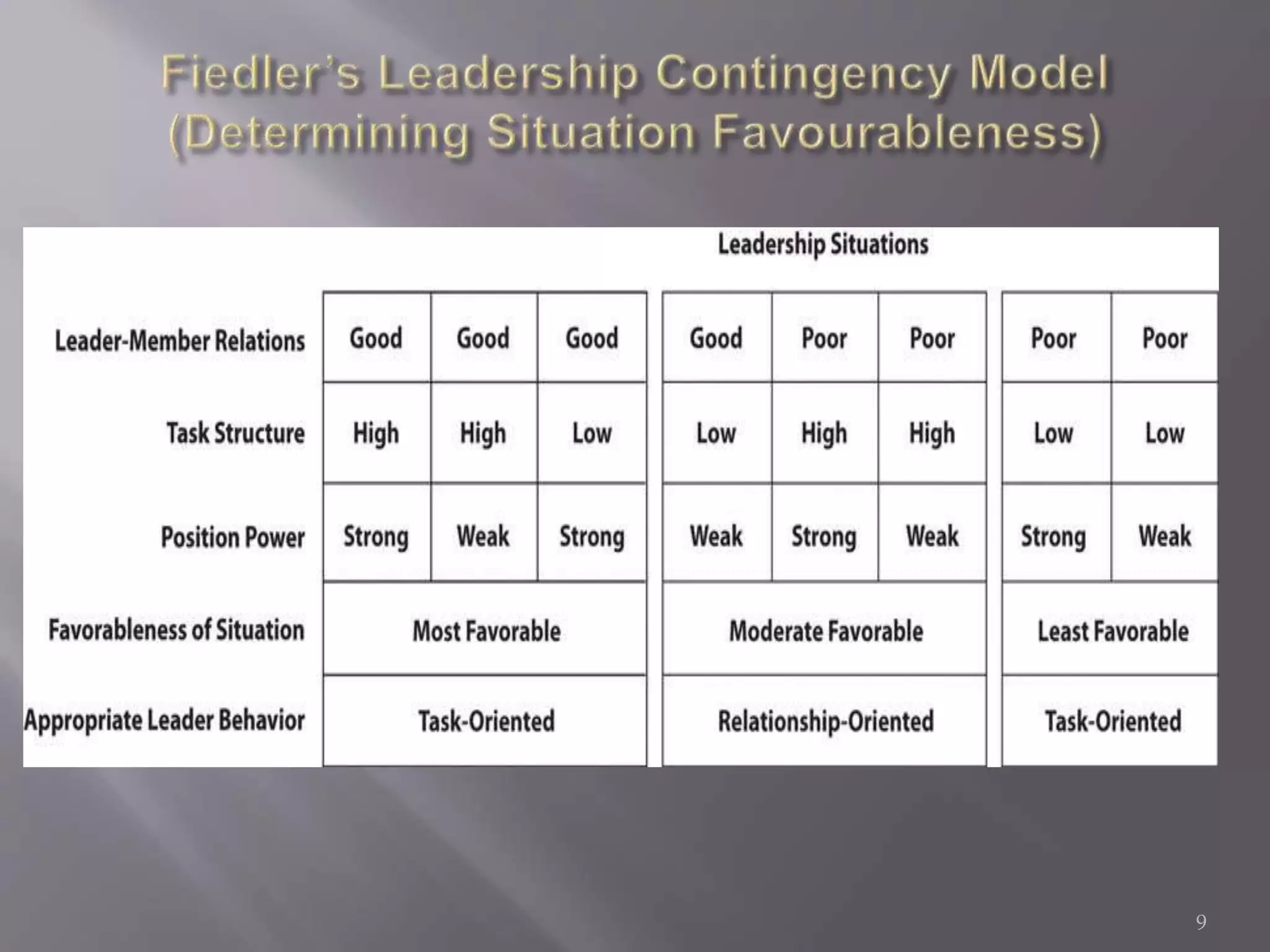
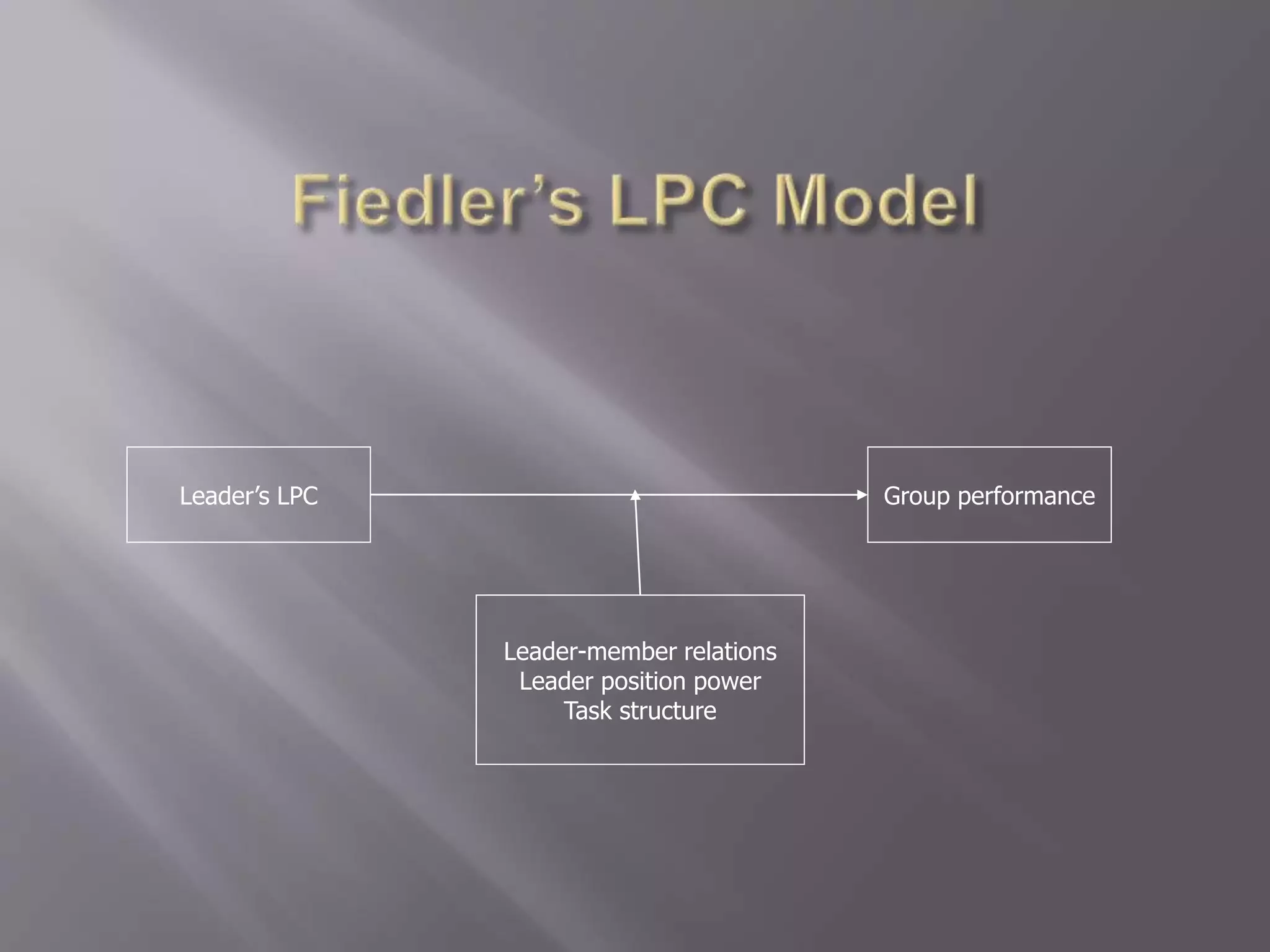
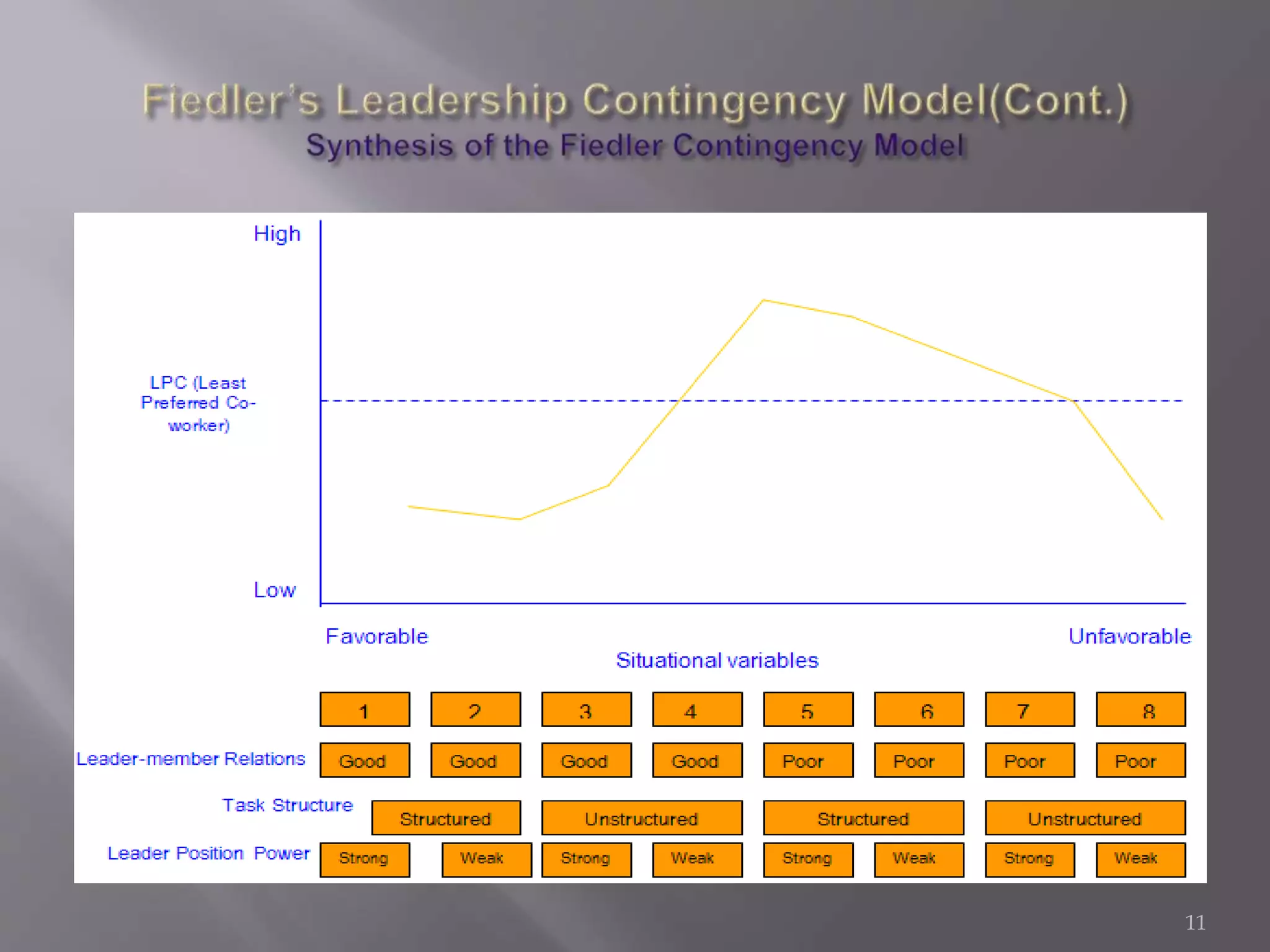
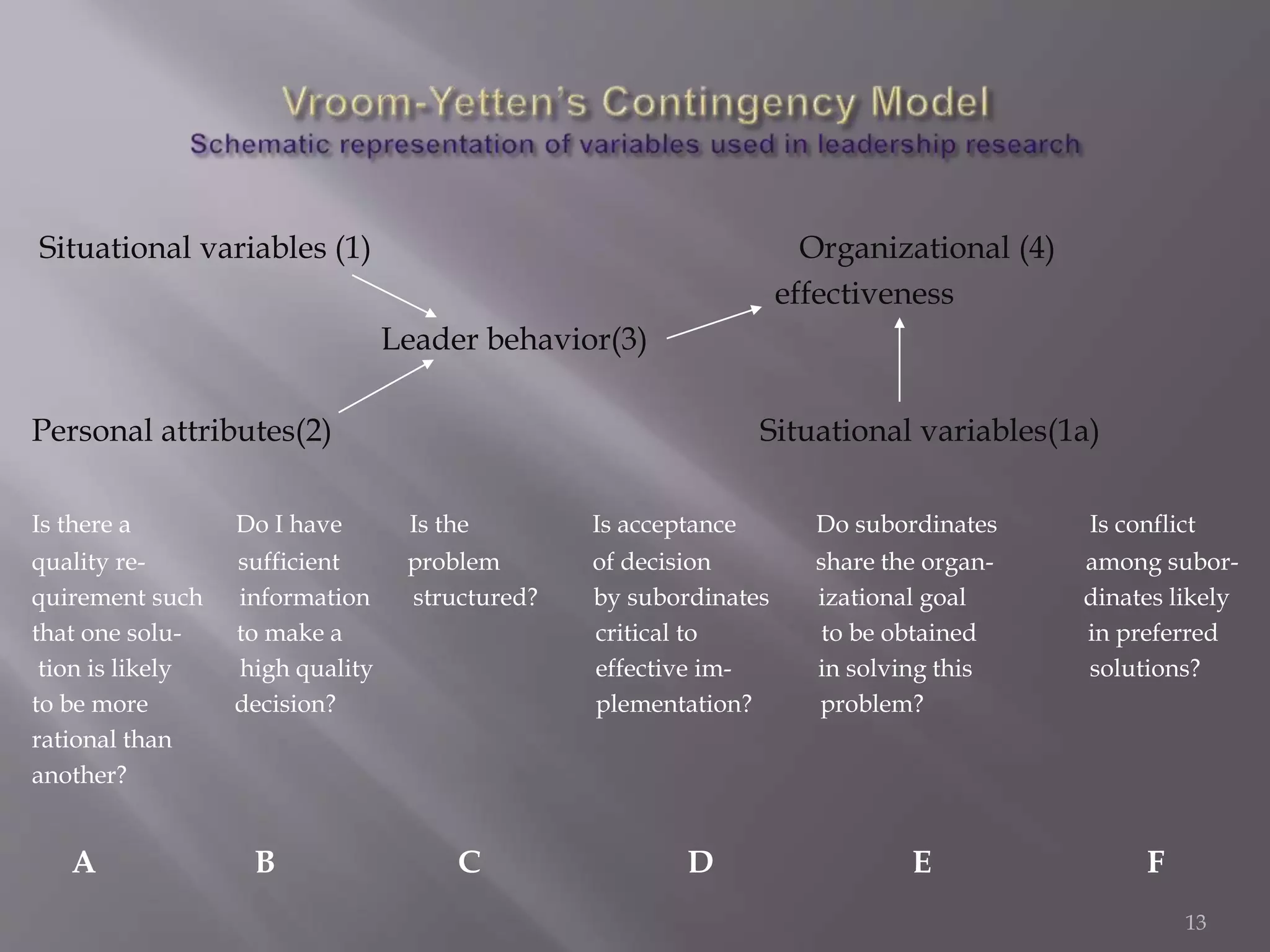
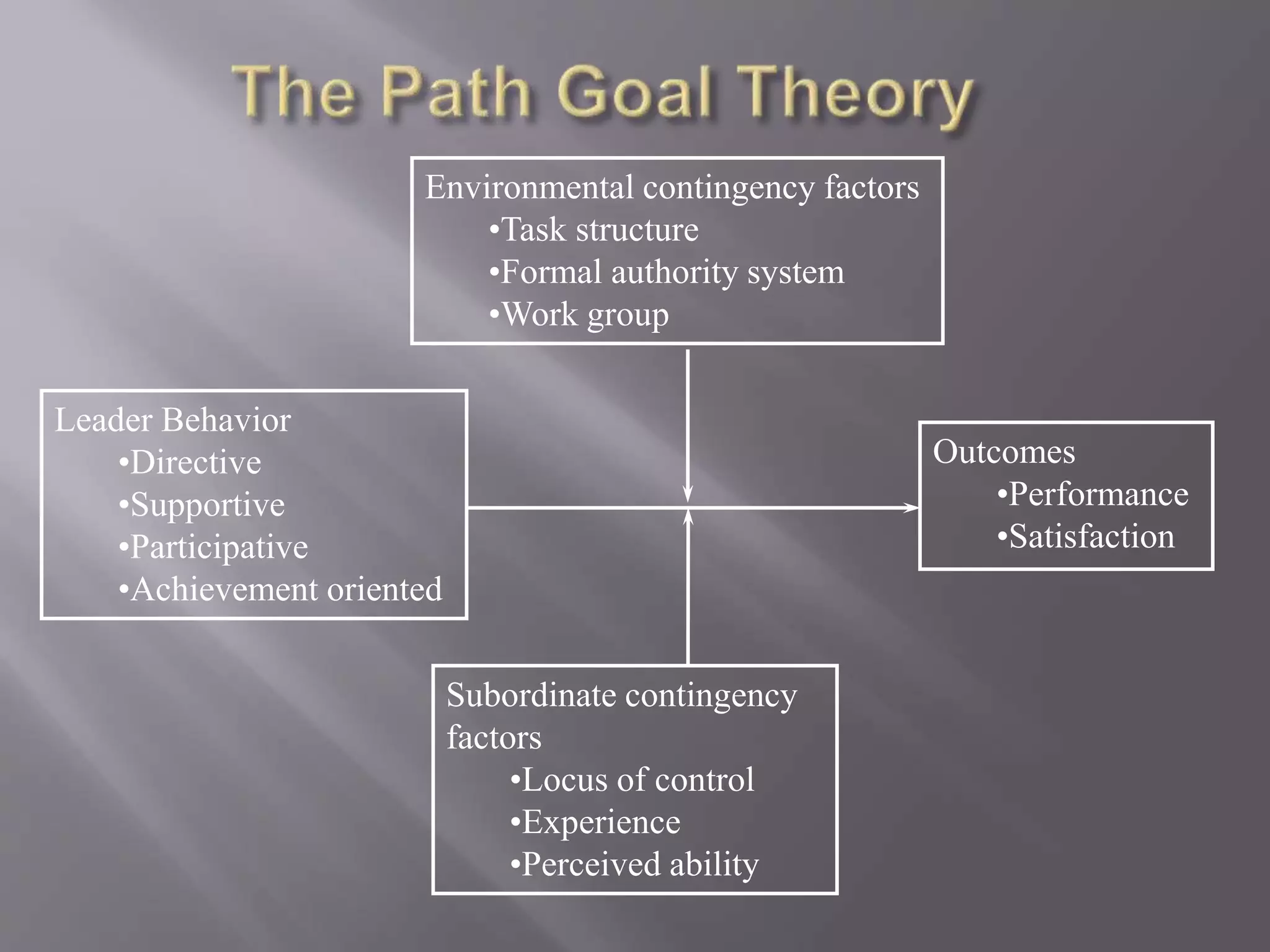
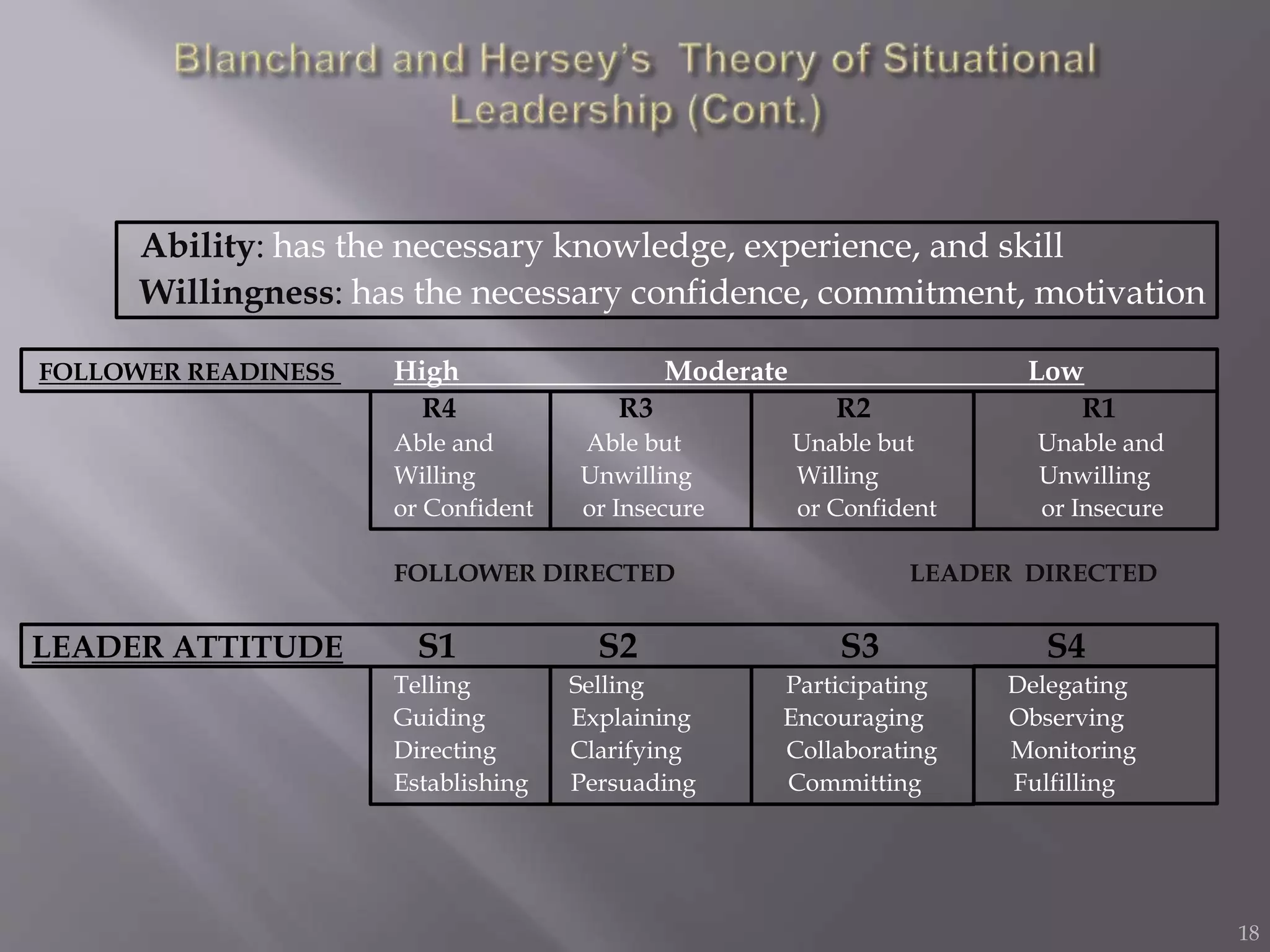
The contingency theory of leadership assumes there is no single best leadership style and that effective leadership depends on factors such as the leader, followers, and situation. Some models within contingency theory include Fiedler's contingency model, House's path-goal theory, and Hersey-Blanchard's situational leadership. Fiedler's model states a leader's effectiveness depends on their leadership style and how favorable the situation is. It assesses style using a scale and suggests matching style to three situational factors: leader-member relations, task structure, and position power.