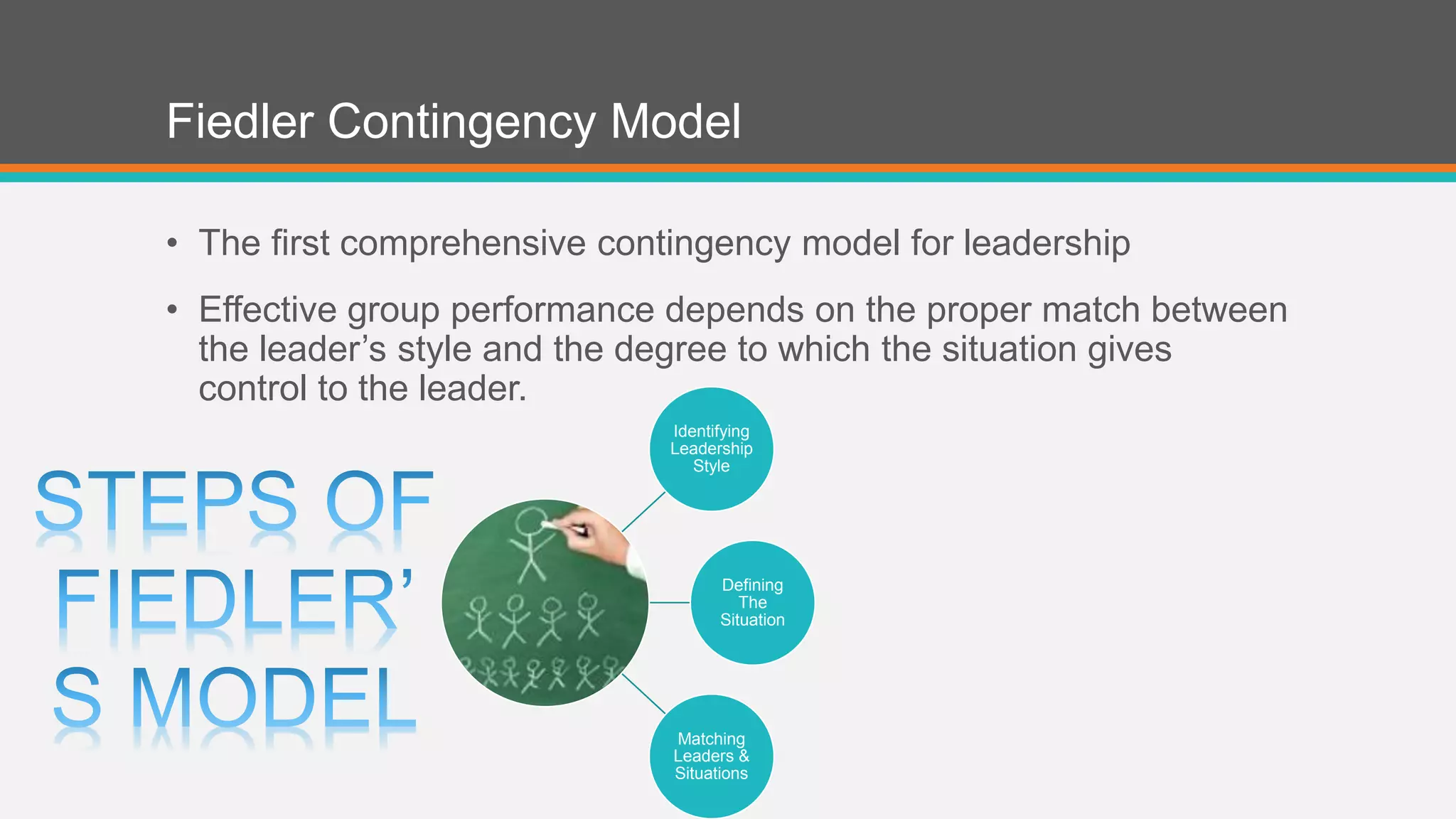
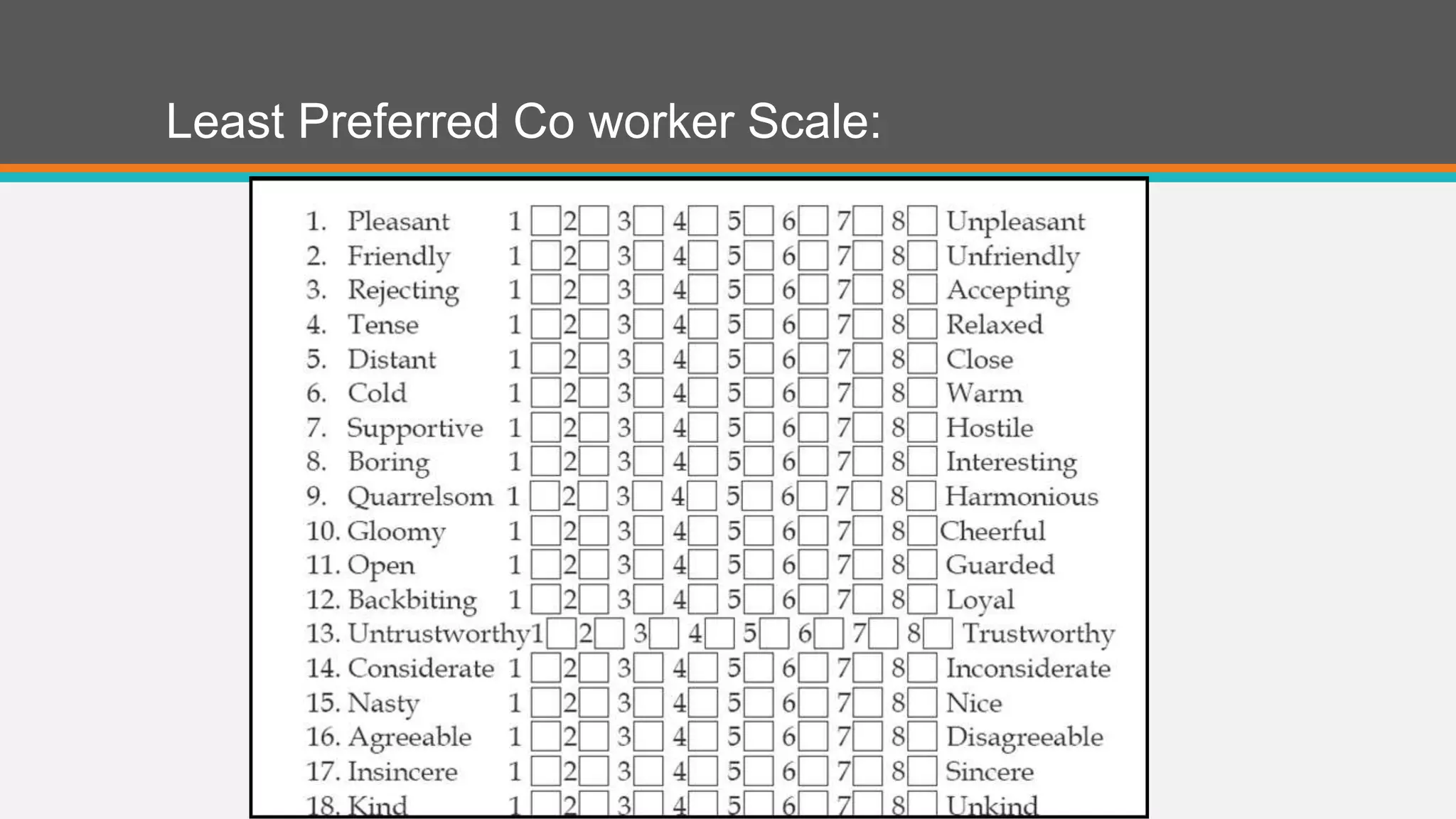
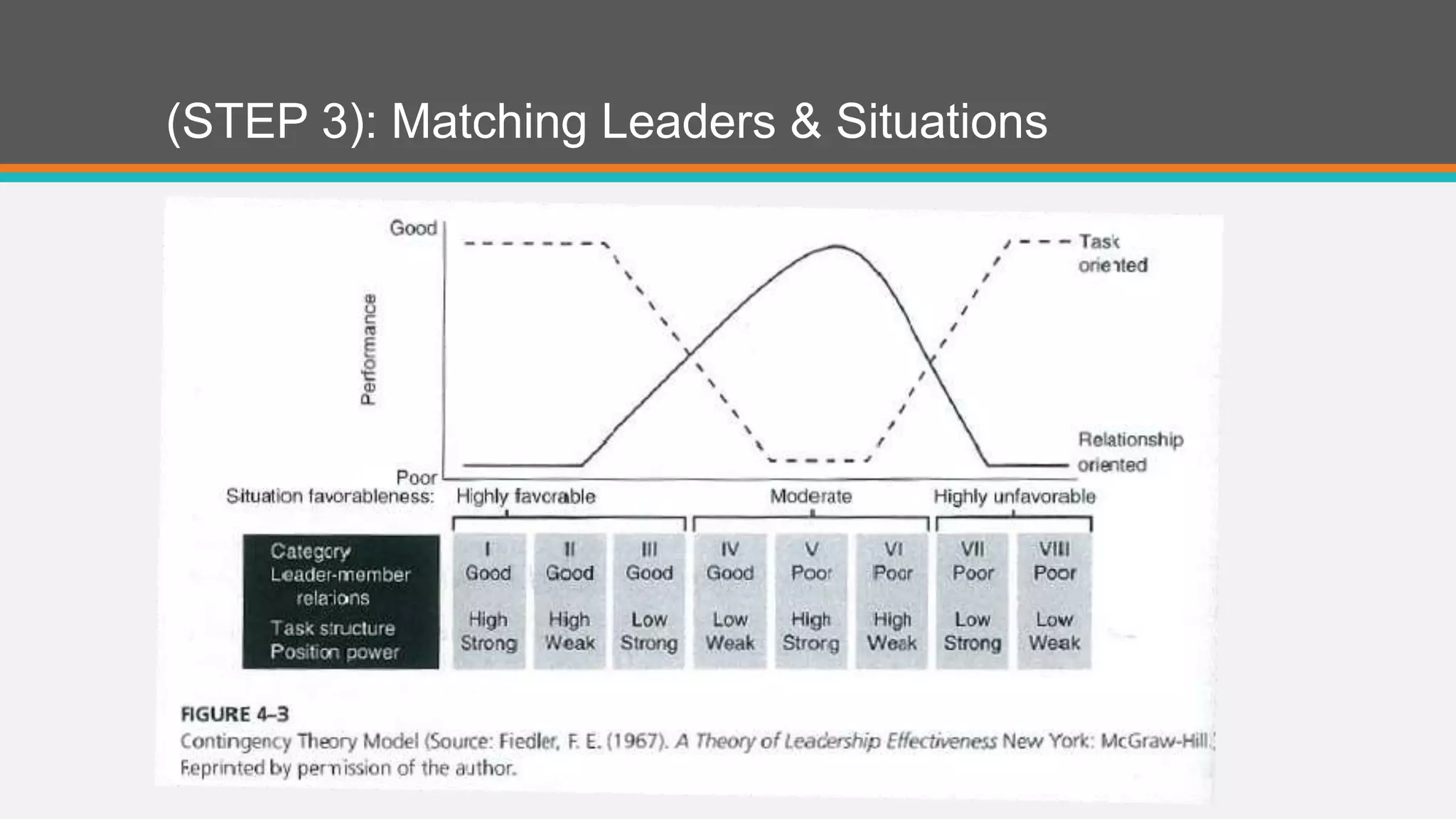
A contingency theory states that there is no single best way to lead and that the optimal leadership style depends on internal and external situational factors. Fred Fiedler proposed the contingency model which assesses a leader's style as either task-oriented or relationship-oriented using the Least Preferred Co-Worker questionnaire and matches that style to situational factors like leader-member relations, task structure, and position power to determine which style will be most effective. The model was later refined by cognitive resource theory which incorporated the role of stress, intelligence, and experience in leadership effectiveness.