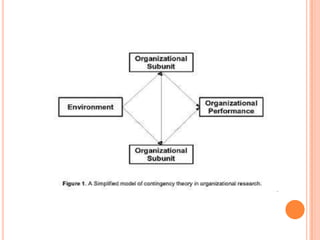
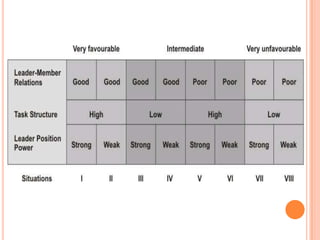
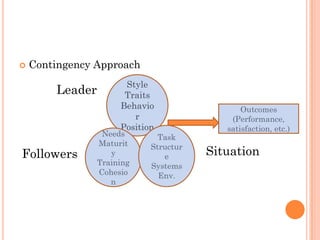
The document discusses the contingency leadership theory, which states that there is no single best leadership style and that the optimal leadership approach depends on situational factors. It provides examples of situational factors like the task structure, the leader's traits, and the followers' needs. The document also summarizes several contingency models of leadership and notes strengths like its predictive ability but also limitations like sometimes failing to fully explain leadership effectiveness.