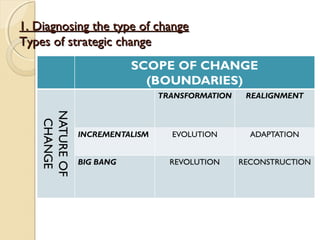
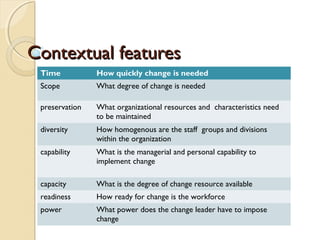
This document provides a framework for managing strategic change including diagnosing the type and context of change, analyzing forces for and against change, and identifying levers to manage change. It outlines four types of strategic change: adaptation, evolution, revolution, and reconstruction. The context of change is determined by factors like time, scope, preservation needs, diversity, capability, capacity, readiness, and power. Change is managed through styles like education, collaboration, and direction played by roles of change agents and strategic leadership. Levers for managing change involve structure, routines, symbols, politics, communication, and tactics.