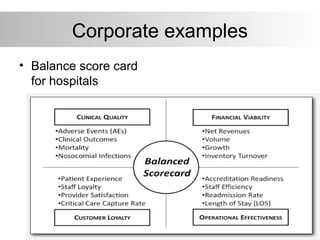
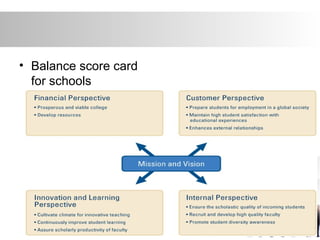
The balanced scorecard is a strategic planning and management system developed by Kaplan and Norton to align business activities with organizational vision and strategy. It adds non-financial metrics to traditional financial measures to provide managers a more balanced view of performance. The balanced scorecard translates strategy into objectives and initiatives, communicates goals across levels, and enables strategic learning through real-time performance measurement and feedback. It covers four perspectives: financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth.