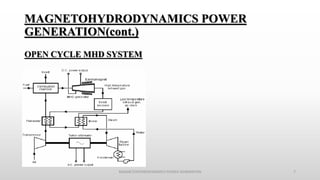
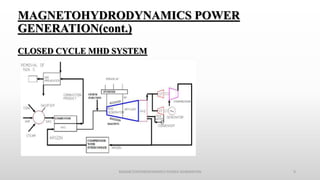
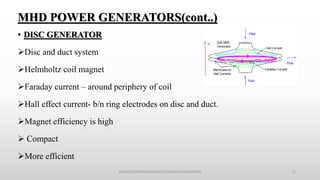
The document discusses magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) as a method of power generation, highlighting its advantages over conventional techniques, such as the absence of mechanical parts and high efficiency. It details components of both open and closed cycle MHD systems, various types of MHD generators, and the principles of MHD propulsion, especially in spacecraft. The conclusion emphasizes MHD's potential despite current industrial applications being limited due to challenges in ionizing fluid conductors.










![MAGNETOHYDRODYANMIC PROPULSION
Propeller is replaced with electrodes.
Current is passed through electrodes in presence of magnetic field.
𝑓 = 𝑖[𝑣 × 𝑏]
Water is forced to flow to direction opposite to current flow.
MAGNETOHYDRODYNAMICS POWER GENERATION 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ajithjayachandran-151011060620-lva1-app6891/85/magnetohydrodynamic-power-generation-14-320.jpg)