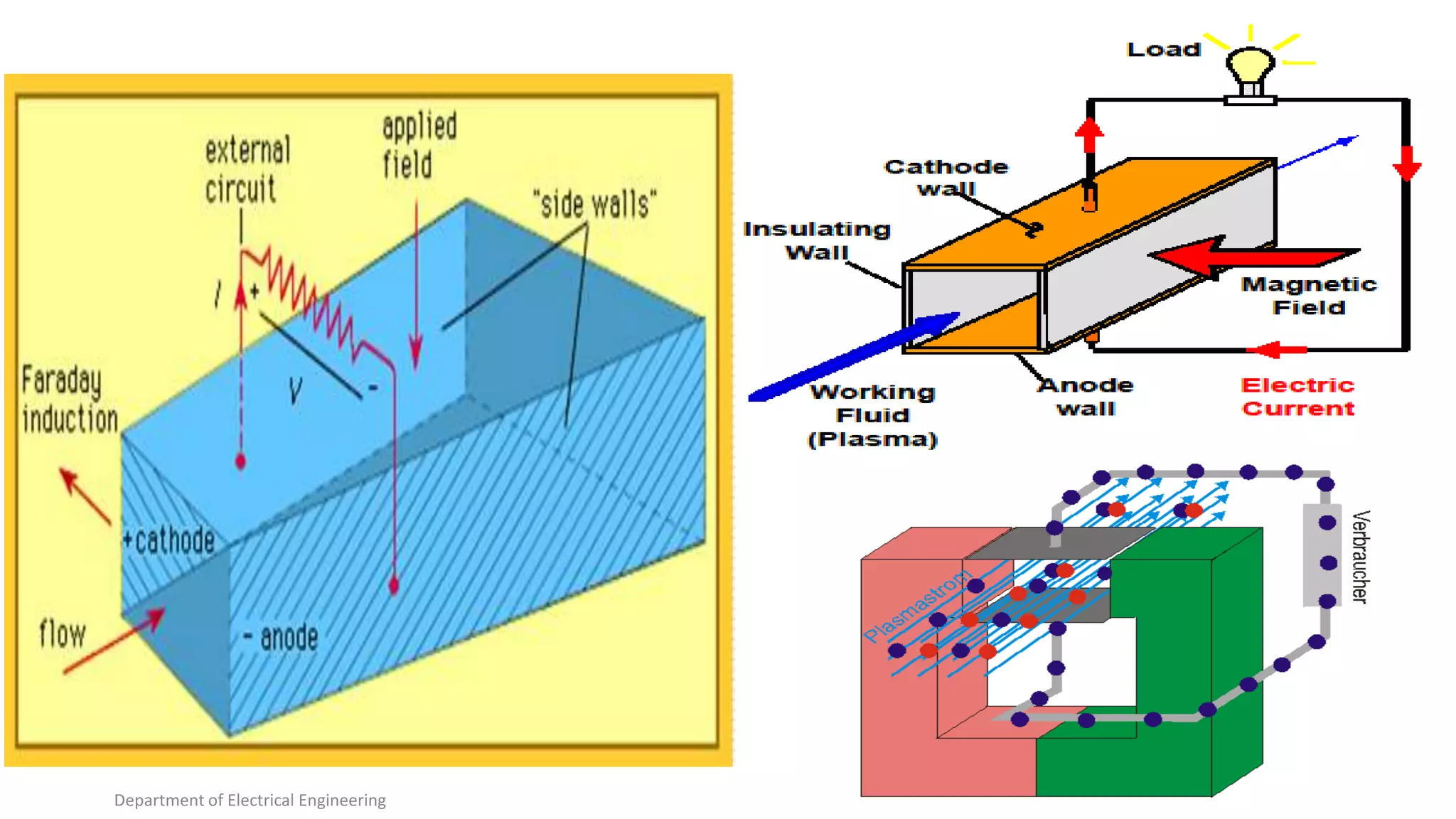
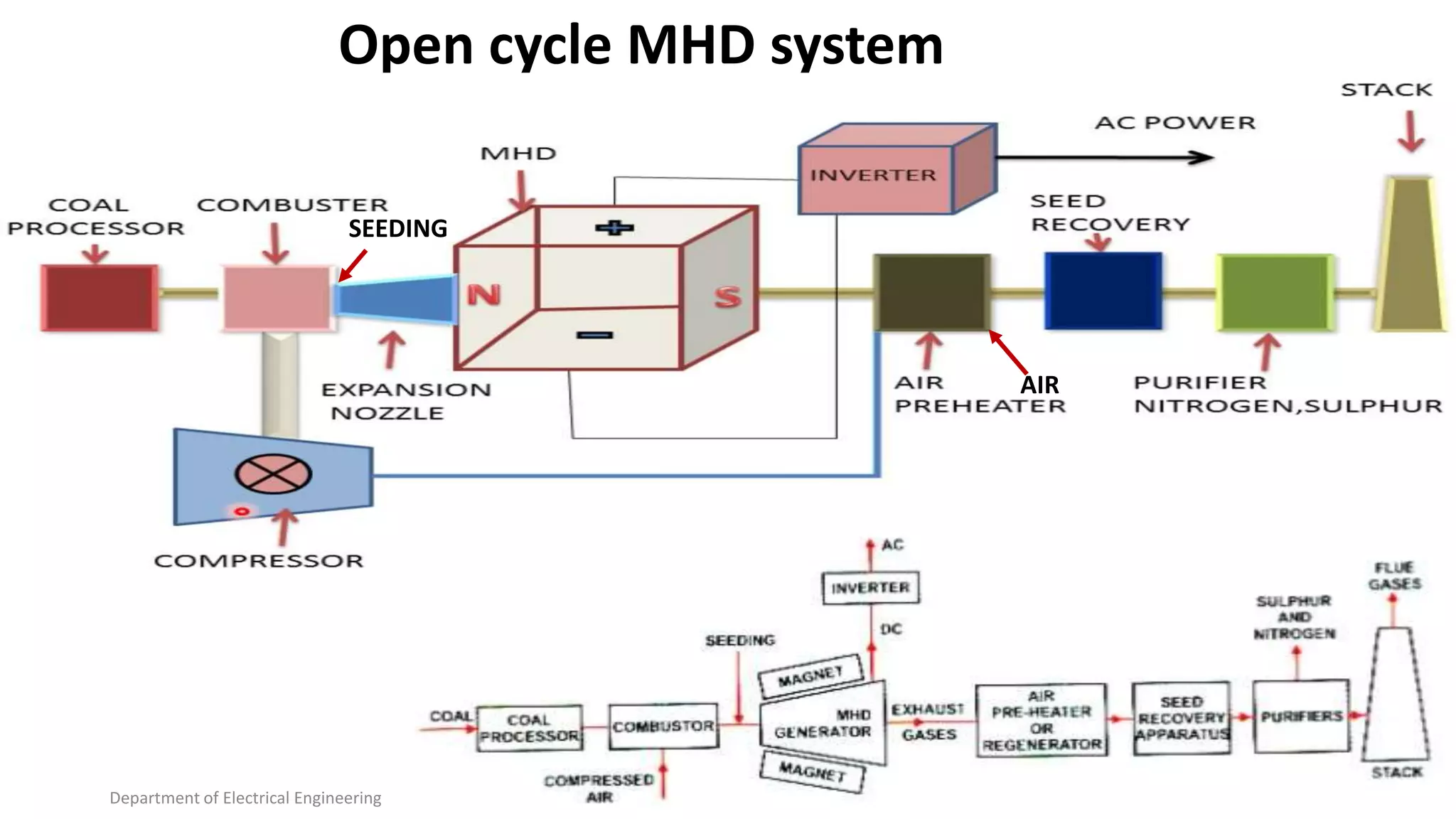
The document provides an overview of magneto hydro dynamic (MHD) power generation, detailing its principles, advantages, and future prospects. It describes MHD as a high-efficiency, low-pollution method of direct energy conversion from heat to electricity, with growing research and potential for widespread adoption. Despite its advantages, such as reduced generation costs and pollution-free output, MHD systems face challenges like high operational costs and the need for significant infrastructure.