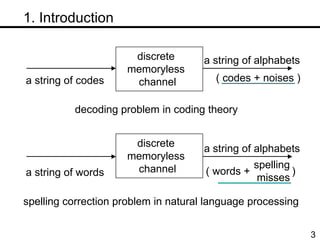
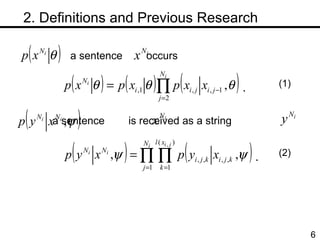
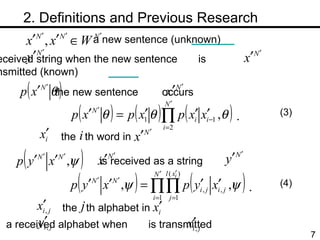
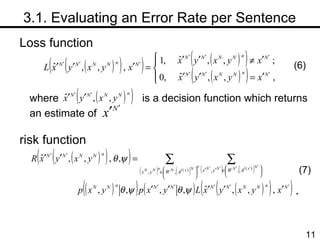
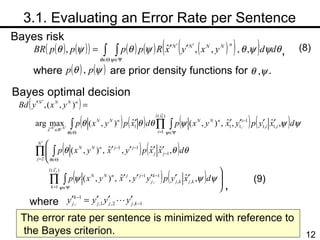
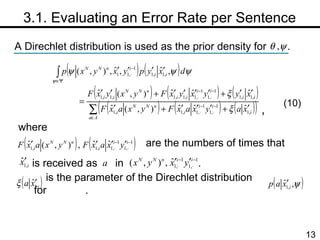
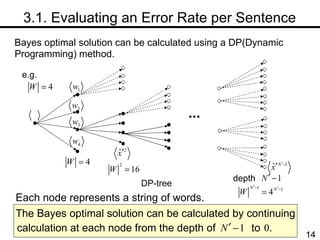
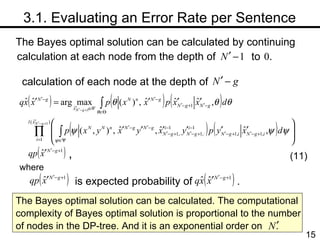
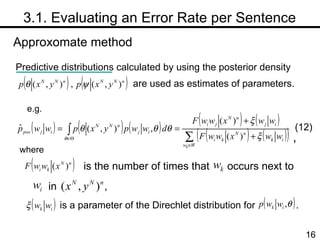
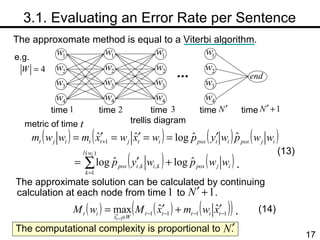
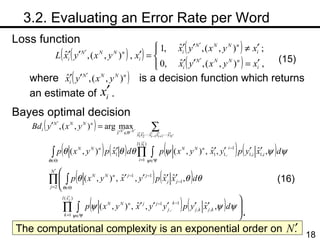
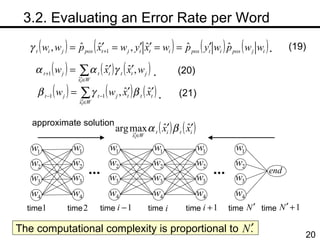
The document discusses methods for statistical spelling correction based on decision theory. It defines the spelling correction problem and previous approaches. It then presents two new methods: 1) Evaluating the error rate per sentence using Bayes optimal and approximate algorithms based on dynamic programming. 2) Evaluating the error rate per word also using Bayes optimal and approximate algorithms like the BCJR algorithm. The goal is to minimize error rates with computational efficiency for real-world applications.