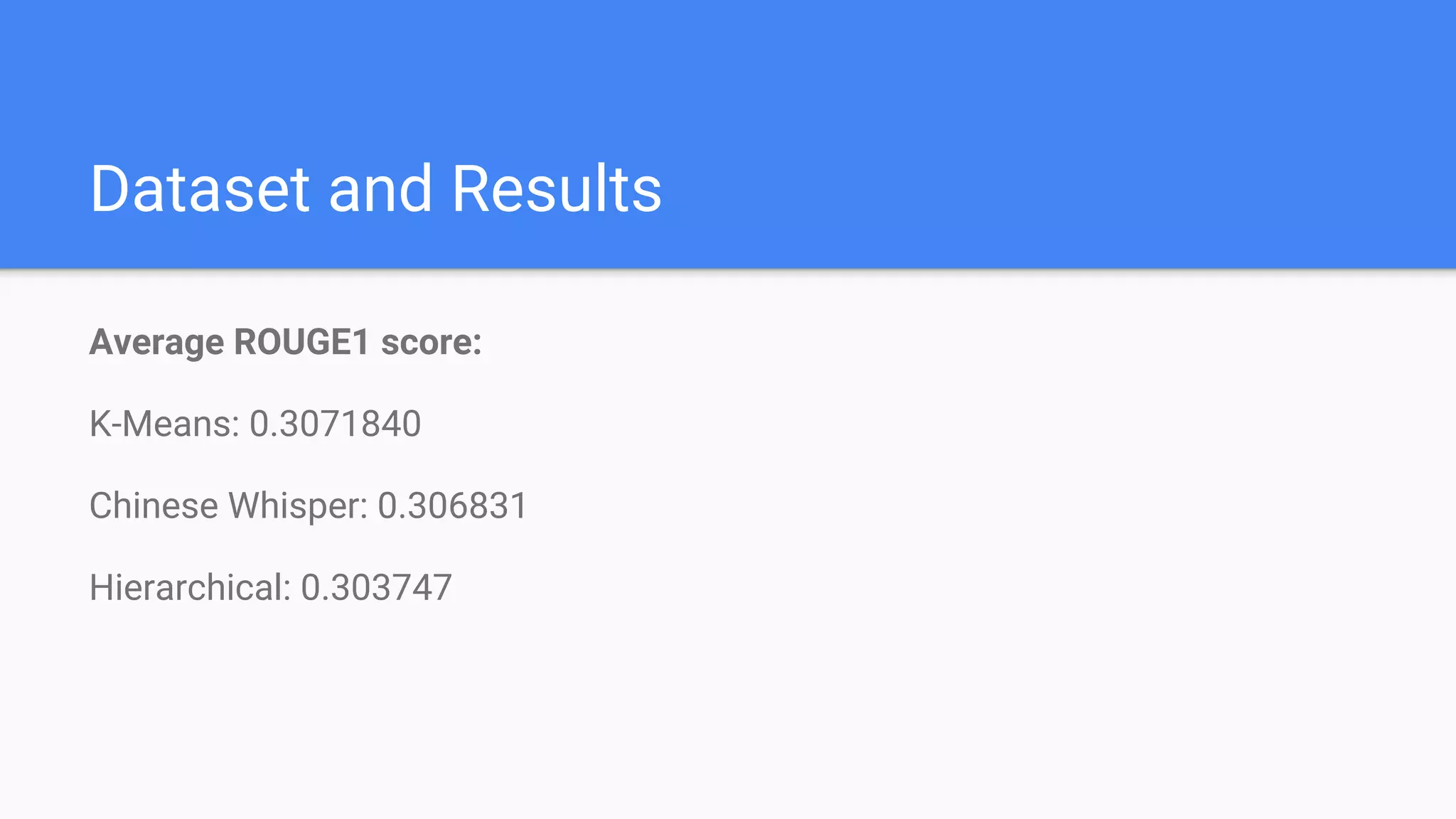
The document discusses an approach for automatic summarization of multiple documents using clustering algorithms and submodular functions. It describes a greedy method that balances coverage and diversity scores to optimize the generated summary while overcoming computational challenges associated with candidate summaries. The results show the effectiveness of the technique with an average ROUGE-1 score and highlight its applicability in various NLP tasks.