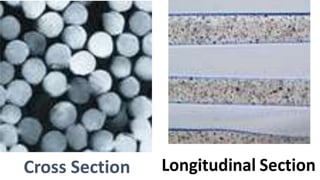
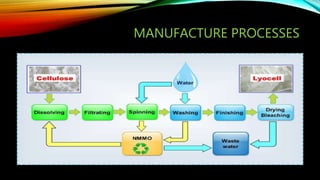
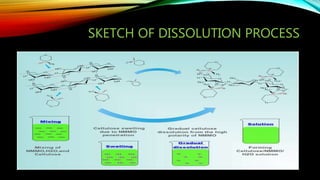
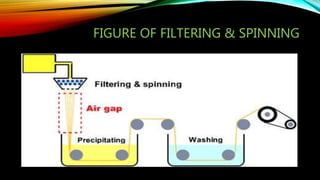
Lyocell is a man-made cellulosic fiber made from dissolving wood pulp. It has a homogeneous and dense physical structure compared to other regenerated cellulosic fibers like rayon. Lyocell is produced through a process involving dissolving wood pulp in NMMO solvent, filtering and spinning the solution into fibers, then washing and finishing the fibers. Lyocell has high strength even when wet, is soft and absorbent, and is more sustainable than synthetic fibers. Its main applications are in clothing, home textiles and medical fabrics.