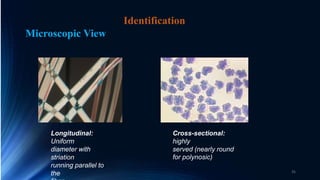
The document discusses different types of regenerated cellulose fibers including lyocell, linen, modal, and alginate. It provides details on the production process of lyocell fibers using wood pulp and NMMO solvent. Key properties of lyocell include its softness, absorbency, strength, and biodegradability. It is used to make clothing, home textiles, and other products. The document also summarizes the manufacturing process and properties of other regenerated fibers such as linen, modal, and viscose rayon.