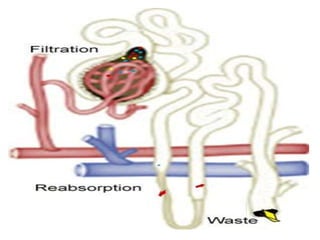
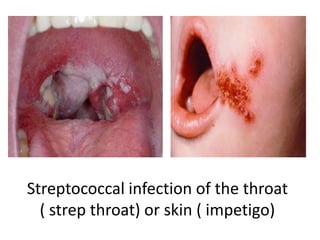
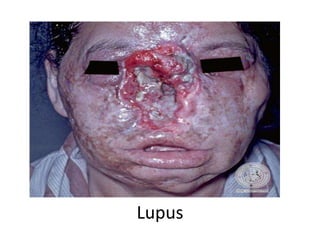
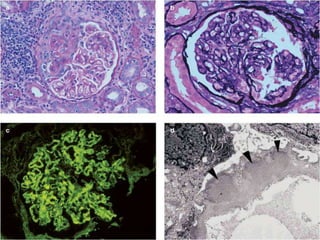
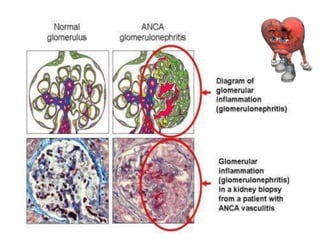
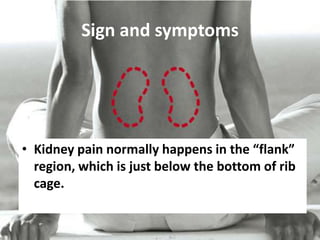
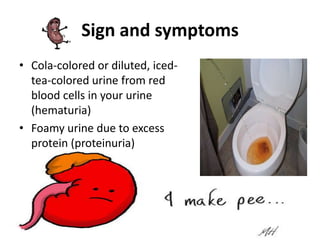
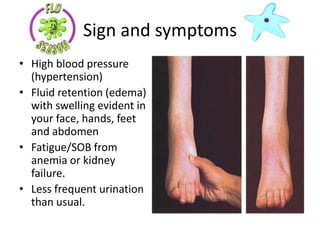
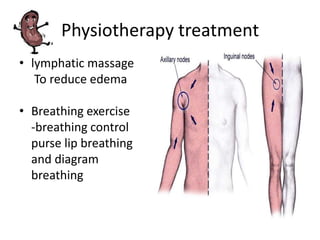
The document provides information about glomerulonephritis, including its anatomy, functions, causes, symptoms, treatment, and benefits of exercise. Glomerulonephritis involves inflammation of the glomeruli in the kidneys and can be caused by infections, autoimmune diseases, diabetes, and other conditions. Symptoms may include kidney pain, blood or protein in the urine, high blood pressure, swelling, and fatigue. Treatment focuses on controlling symptoms through medications, diet changes, dialysis if needed, and lifestyle modifications like exercise, which can help increase energy, relieve stress, improve sleep and overall functioning.