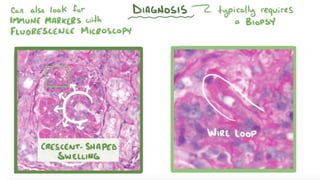
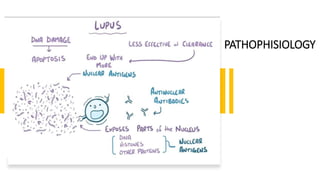
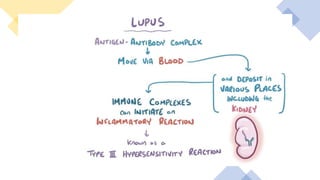
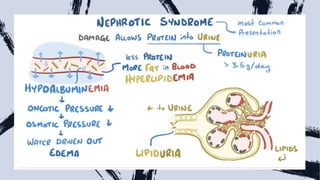
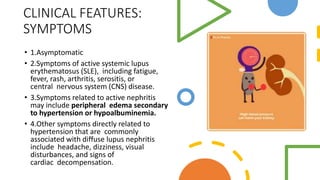
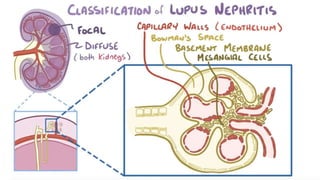
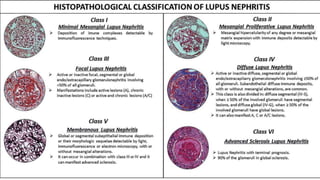
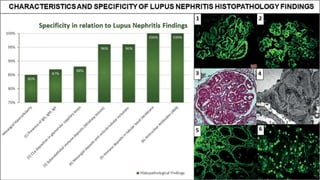
Lupus nephritis is a serious manifestation of systemic lupus erythematosus where the kidneys are damaged. It is characterized by autoantibodies that form immune complexes and deposit in the glomeruli, causing inflammation. A renal biopsy is required for diagnosis and classification. Treatment depends on the class, with classes III and IV requiring aggressive immunosuppression including corticosteroids and other agents to reduce inflammation and prevent loss of renal function. Factors like genetics, estrogen, and ultraviolet light exposure are believed to contribute to lupus development.









![LABORATORY TESTS
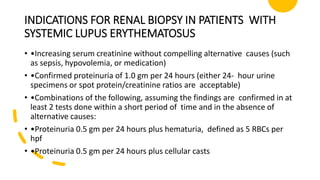
• •Blood urea nitrogen (BUN)
• •Serum creatinine
• •Urine R/M/E (to check for protein, red blood cells [RBCs], and cellular casts)
• •A spot urine test for creatinine and protein concentration (normal creatinine
excretion is 1000 mg/24 h/1.75 m 2; normal protein excretion is 150-200 mg/24
h/1.75 m 2; normal urinary protein-to-creatinine ratio is <0.2)
• •A 24-hour urine test for creatinine clearance and protein excretion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lupusnephritisnids-200930145316/85/Lupus-nephritis-nids-18-320.jpg)
![LABORATORY
TESTS
• •ANA [for diagnosis SLE]
• •Antibodies to double-stranded DNA
(dsDNA), ↑
• •Complement (C3, C4, and CH50), ↓
• •Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
(ESR), ↑
• •C-reactive protein (CRP) levels. ↔
• •Anti-C1q antibodies ↑ [less sensitive
then Anti dsDNA, but more specific]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lupusnephritisnids-200930145316/85/Lupus-nephritis-nids-19-320.jpg)