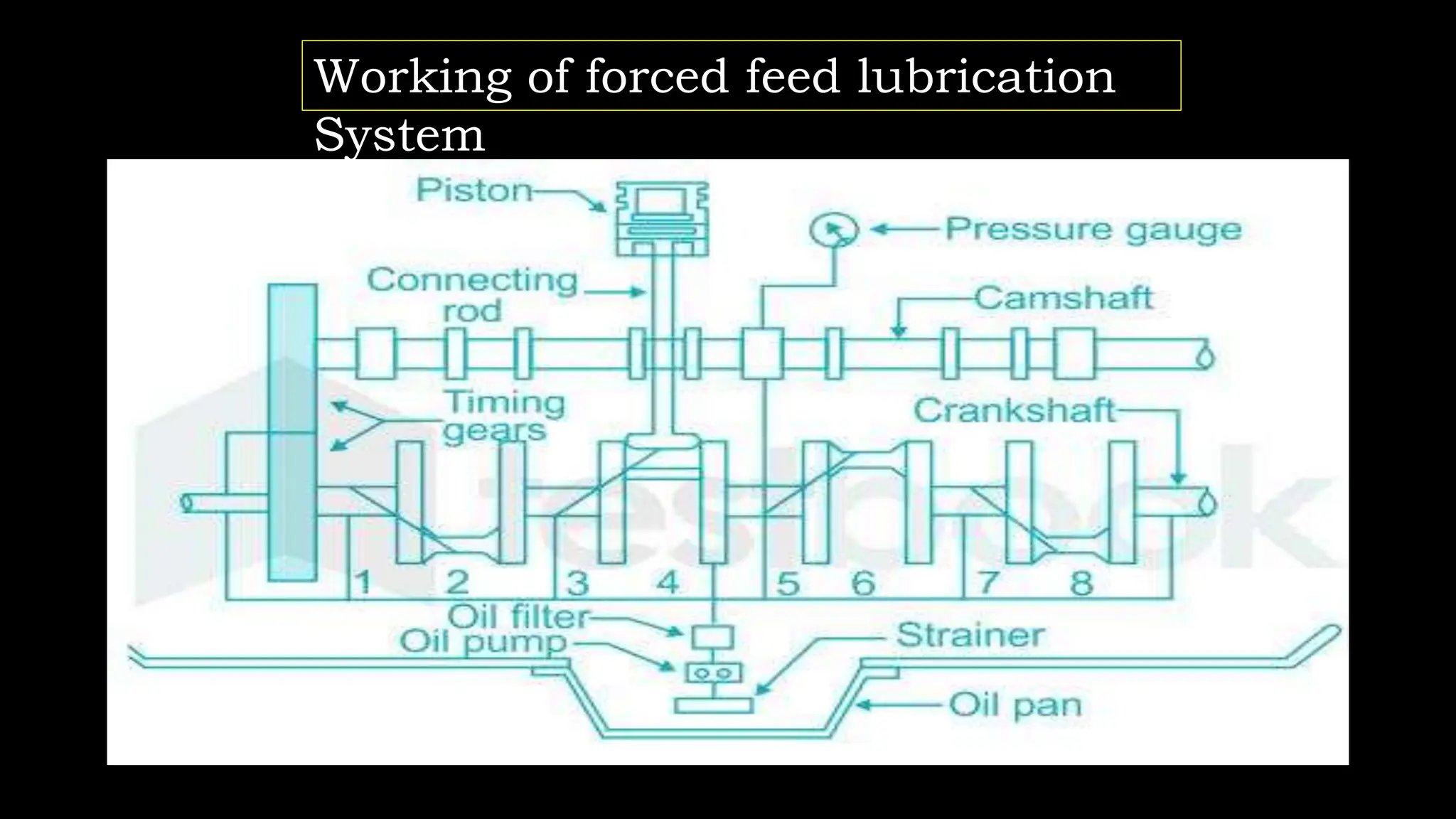
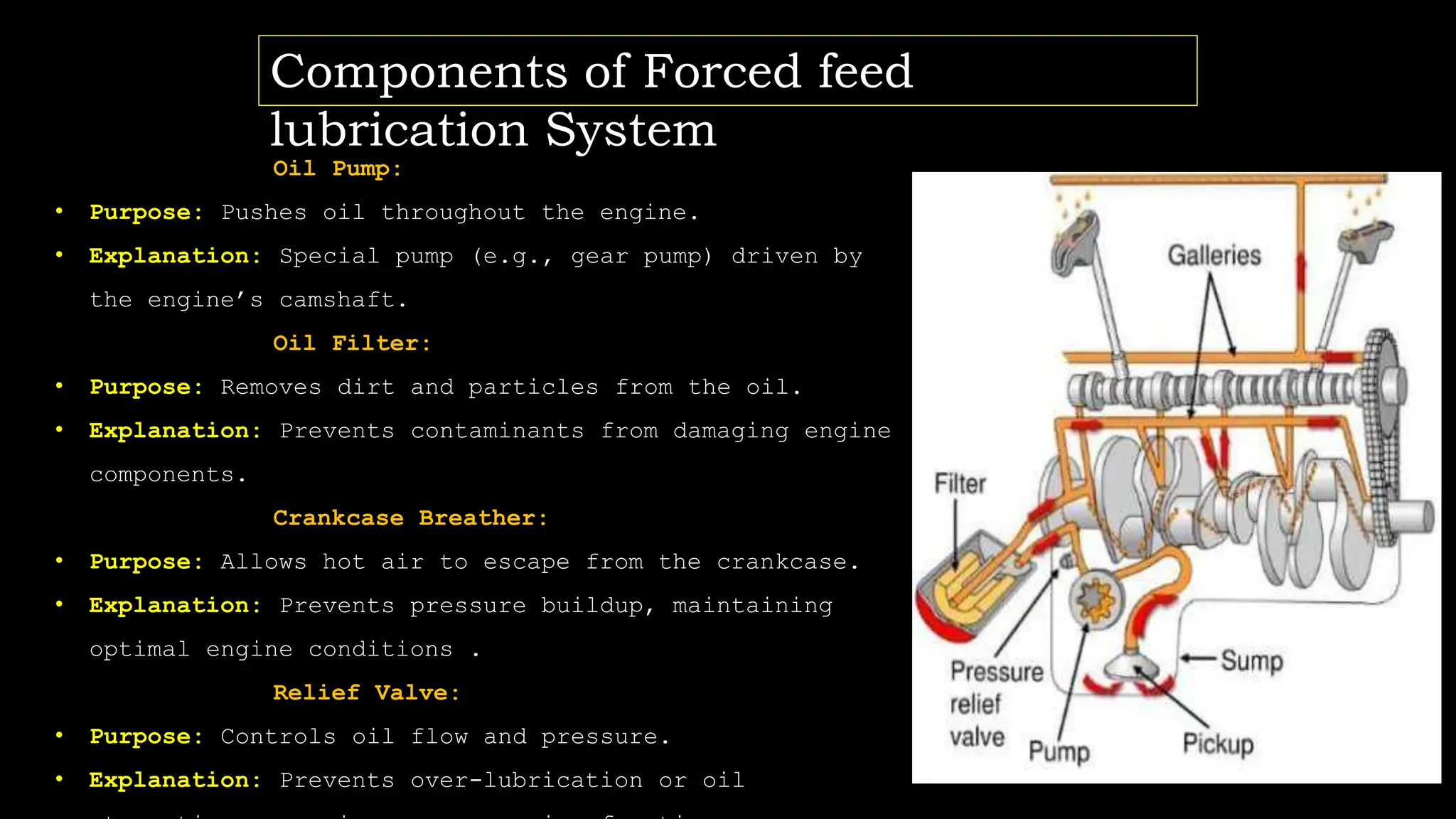
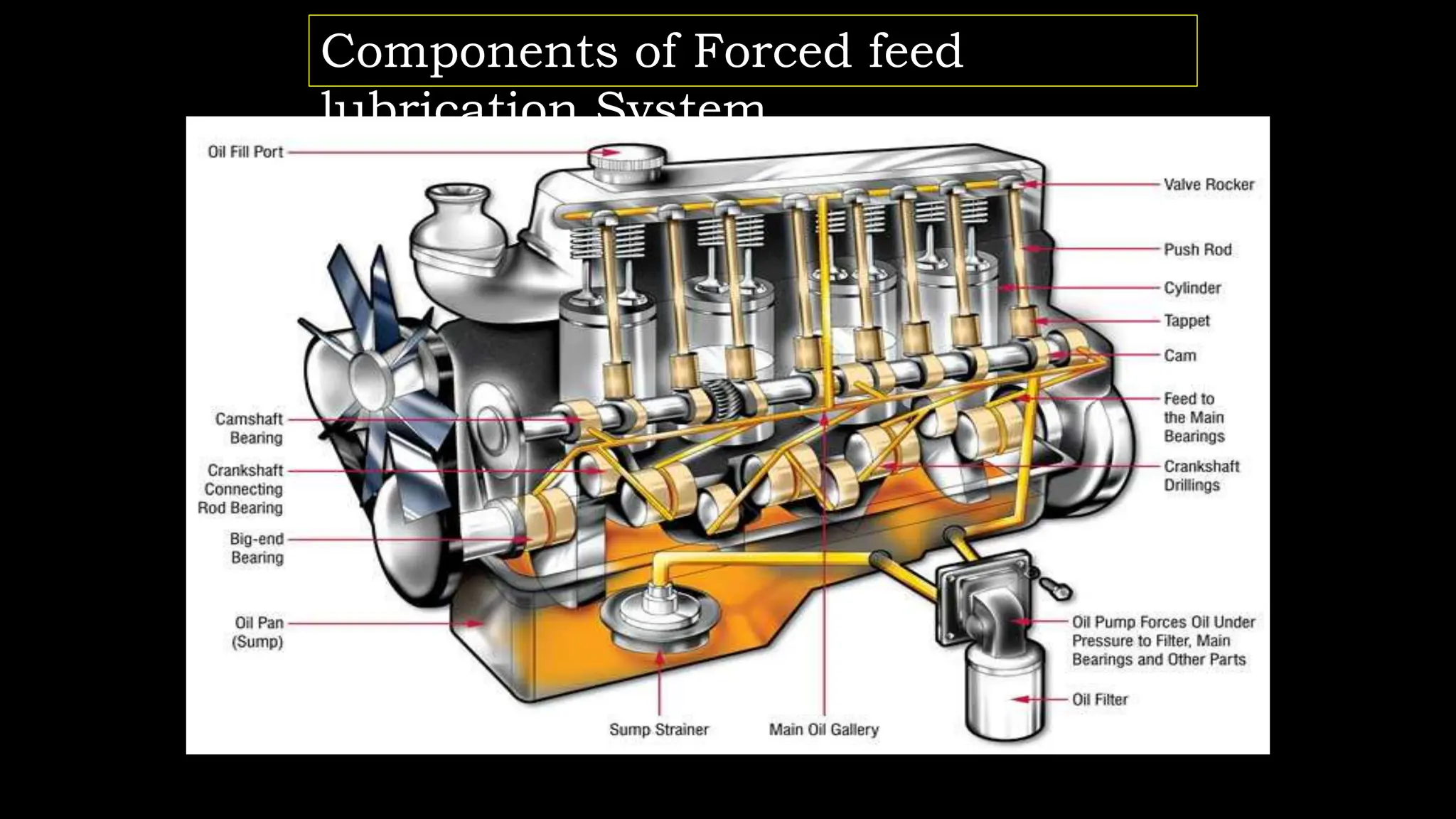
The document presents an overview of lubrication, defining it as the application of lubricants to reduce friction and wear in mechanical systems. It details the purpose of lubrication, including wear reduction, cooling, sealing, and cleaning, and explains the forced feed lubrication system, which pumps oil directly to engine parts. Key components such as the oil pump, oil filter, crankcase breather, and relief valve are also described, highlighting their functions in ensuring proper lubrication and maintaining engine conditions.