Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX





![Definition
The mathematical definition of convolution in
discrete time domain is
(We will discuss in discrete time domain only.)
where x[n] is input signal, h[n] is impulse
response, and y[n] is output. * denotes
convolution. Notice that we multiply the terms
of x[k] by the terms of a time-shifted h[n] and
add them up.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ltisystemakept-150224072631-conversion-gate02/85/Lti-system-akept-7-320.jpg)


This document discusses linear time-invariant (LTI) systems and convolution. It begins by defining LTI systems and convolution for both continuous and discrete time. Convolution is described as a way to construct the output of a system given its impulse response. Applications in digital signal processing and image processing are mentioned. Convolution filtering plays an important role in edge detection and related image processing algorithms. The mathematical definition of discrete time convolution is provided. An example problem calculating outputs for different inputs using convolution is given at the end.






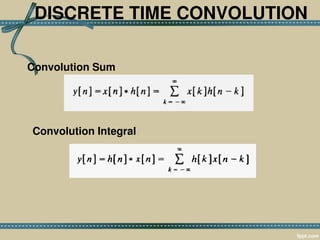
![Definition
The mathematical definition of convolution in
discrete time domain is
(We will discuss in discrete time domain only.)
where x[n] is input signal, h[n] is impulse
response, and y[n] is output. * denotes
convolution. Notice that we multiply the terms
of x[k] by the terms of a time-shifted h[n] and
add them up.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ltisystemakept-150224072631-conversion-gate02/85/Lti-system-akept-7-320.jpg)

