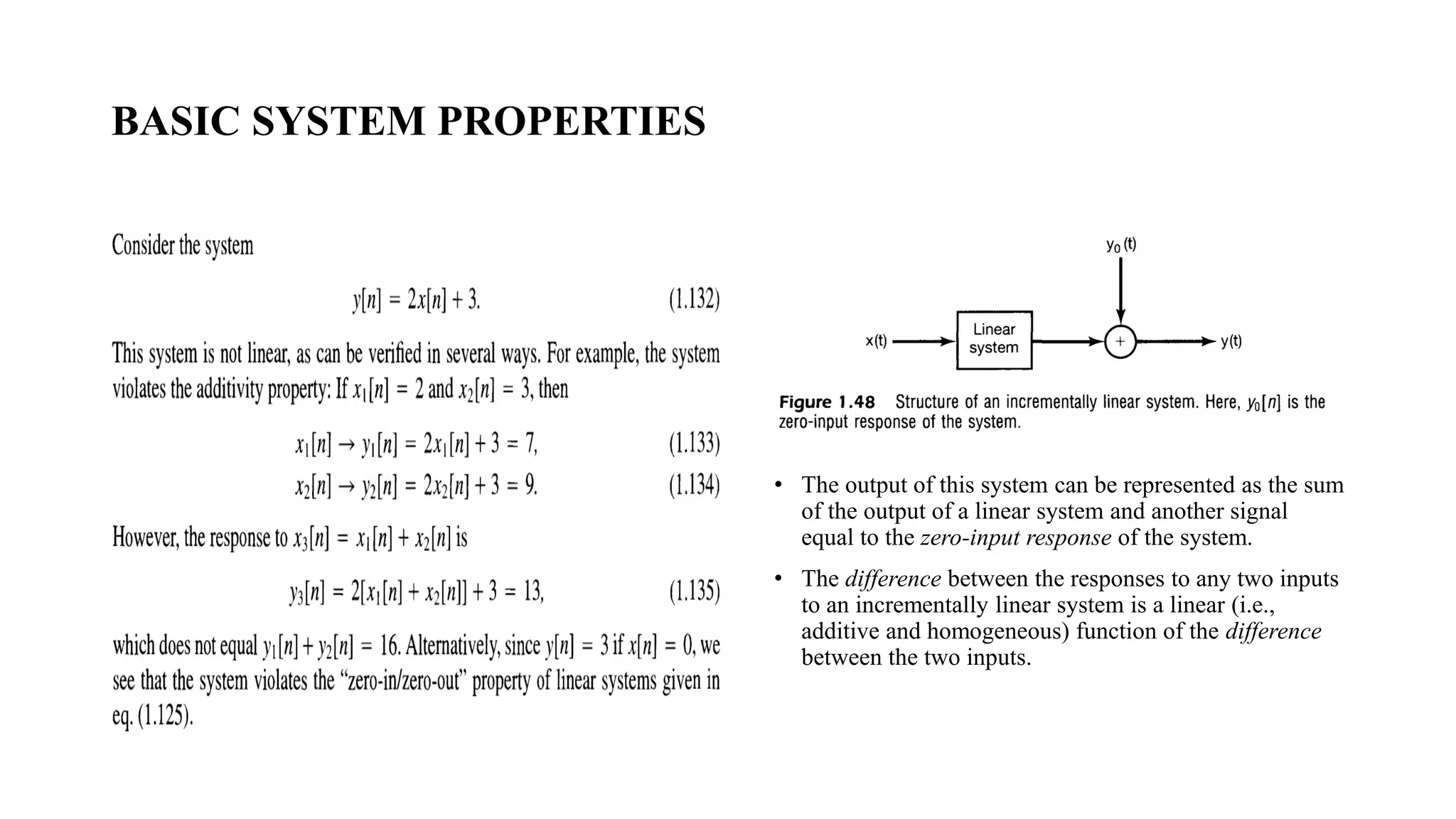
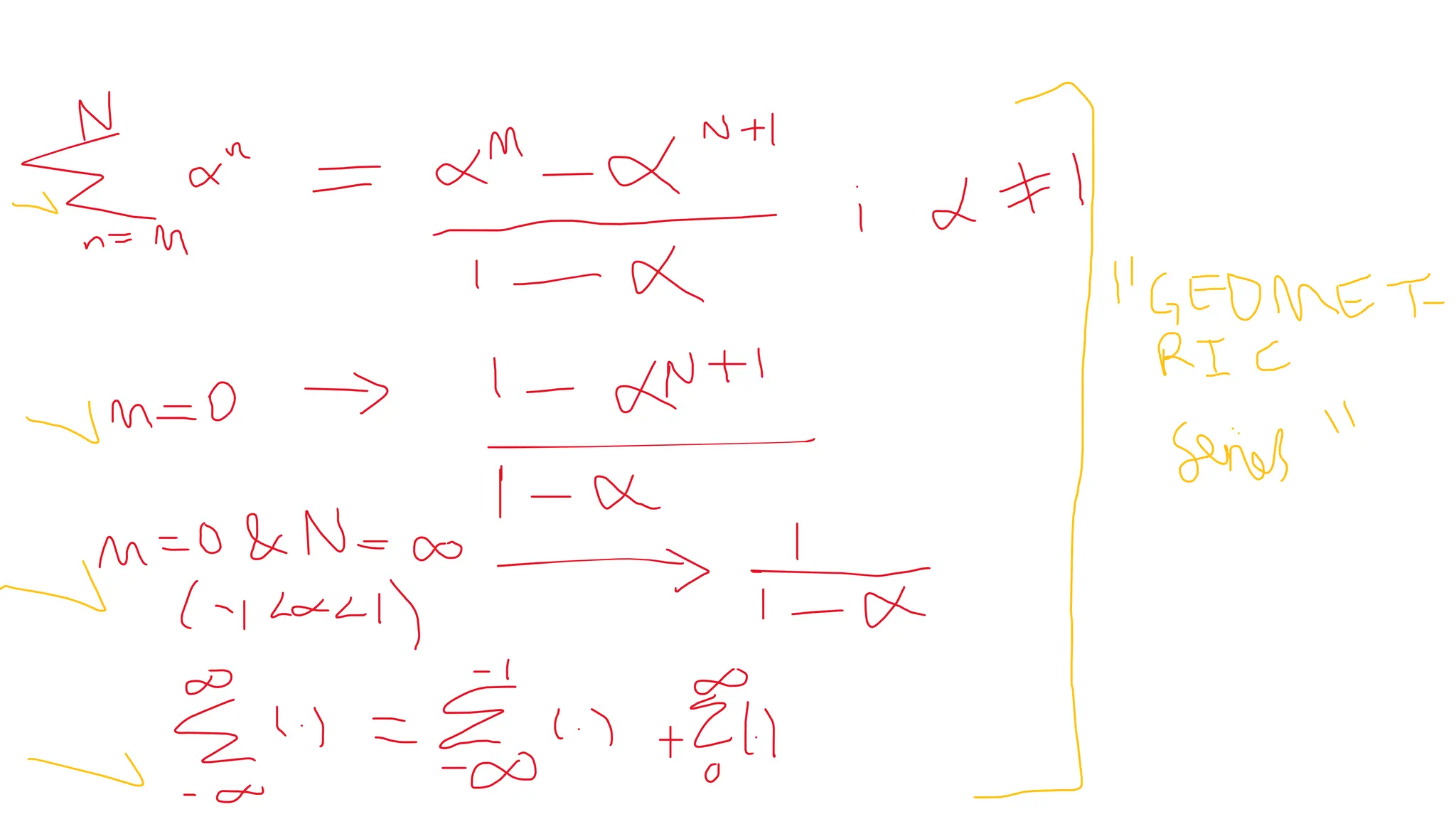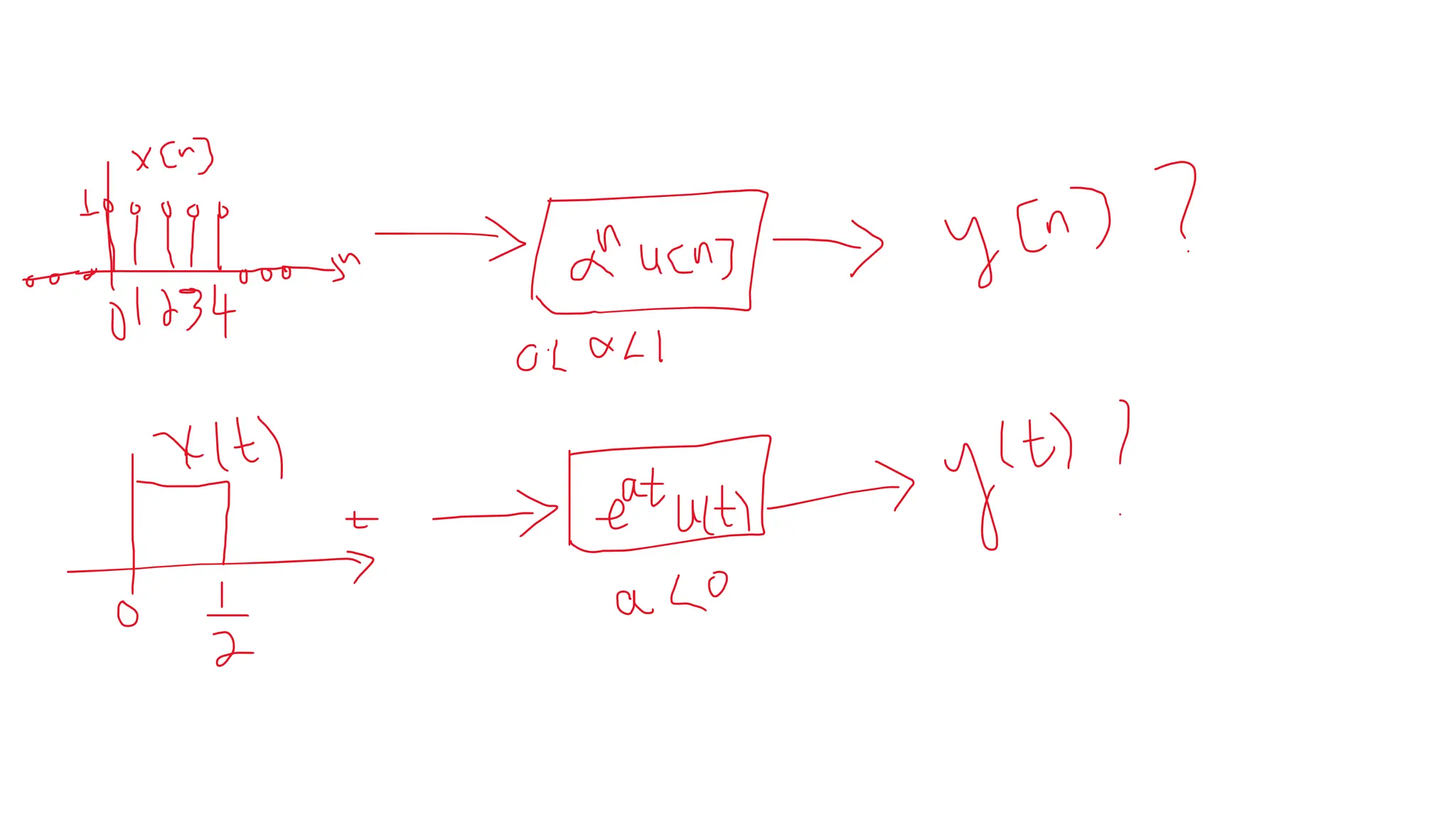- Linear systems have the properties of additivity and homogeneity, meaning the output is the sum of the individual outputs in response to each input, and scaling the input scales the output accordingly.
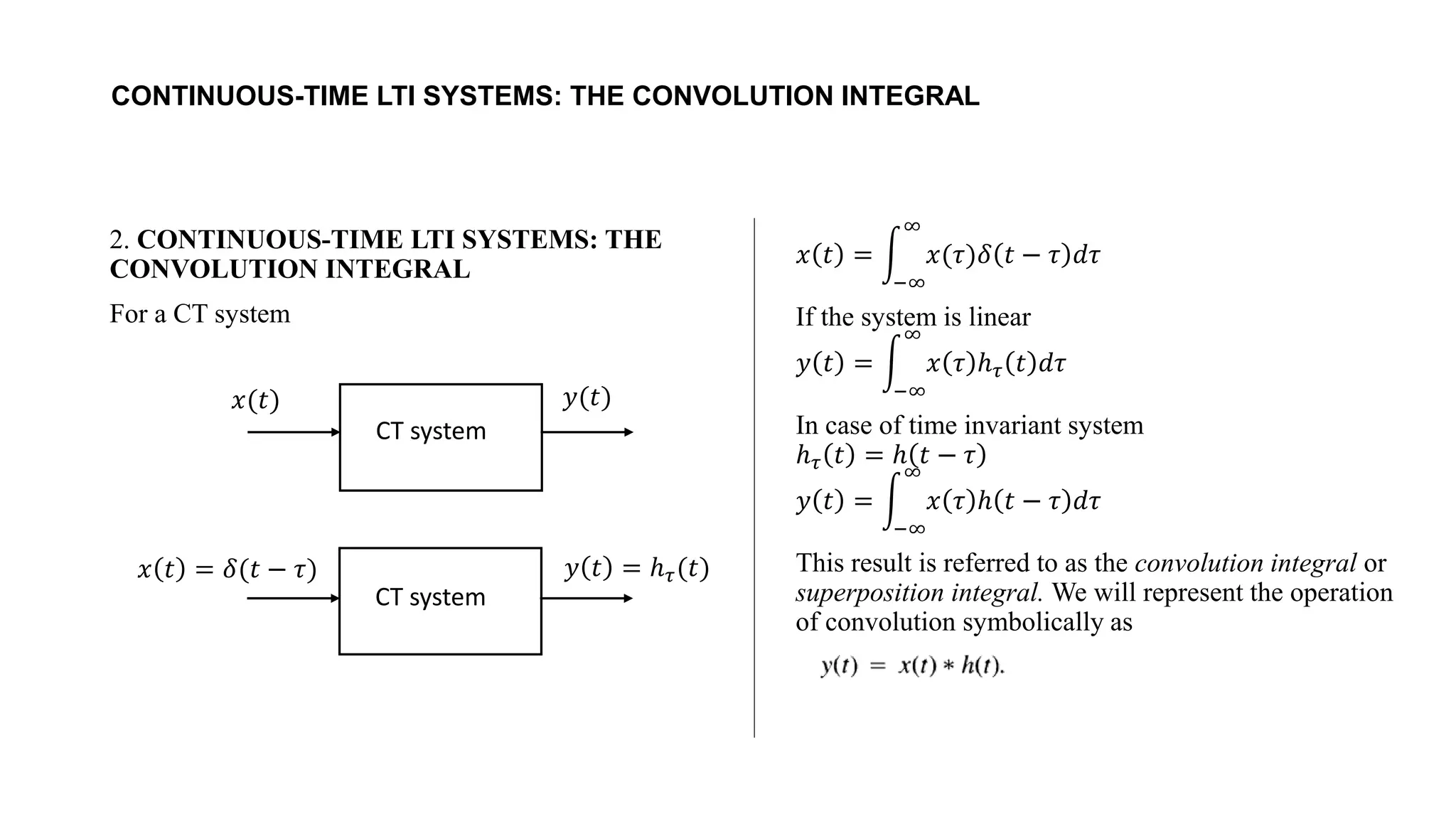
- For both discrete-time and continuous-time linear time-invariant (LTI) systems, the output can be expressed as the convolution of the input signal and the impulse response of the system.
- The convolution represents the superposition of scaled and delayed versions of the impulse response that combine to form the output signal. This convolution representation fully characterizes the behavior of an LTI system.



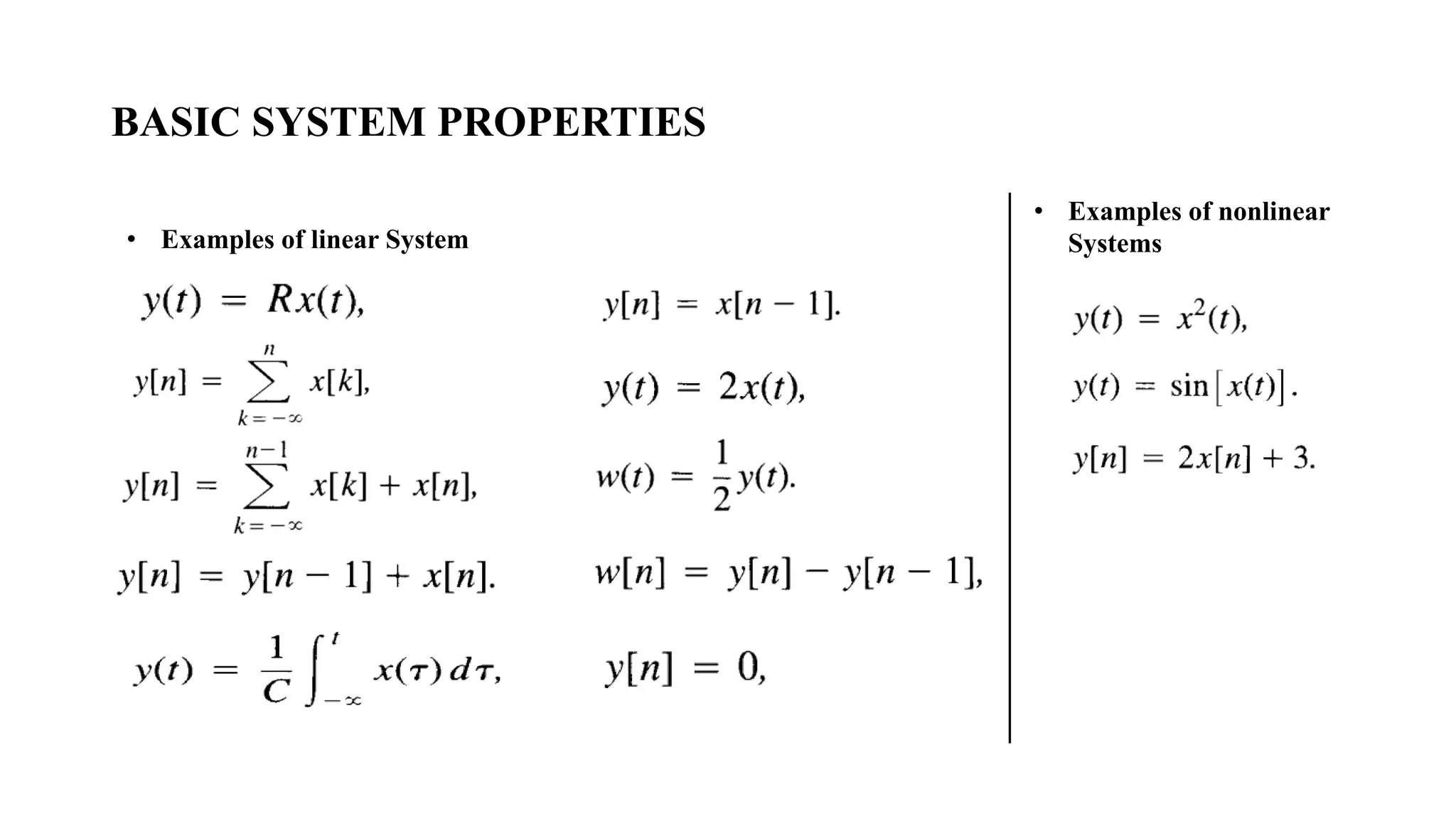
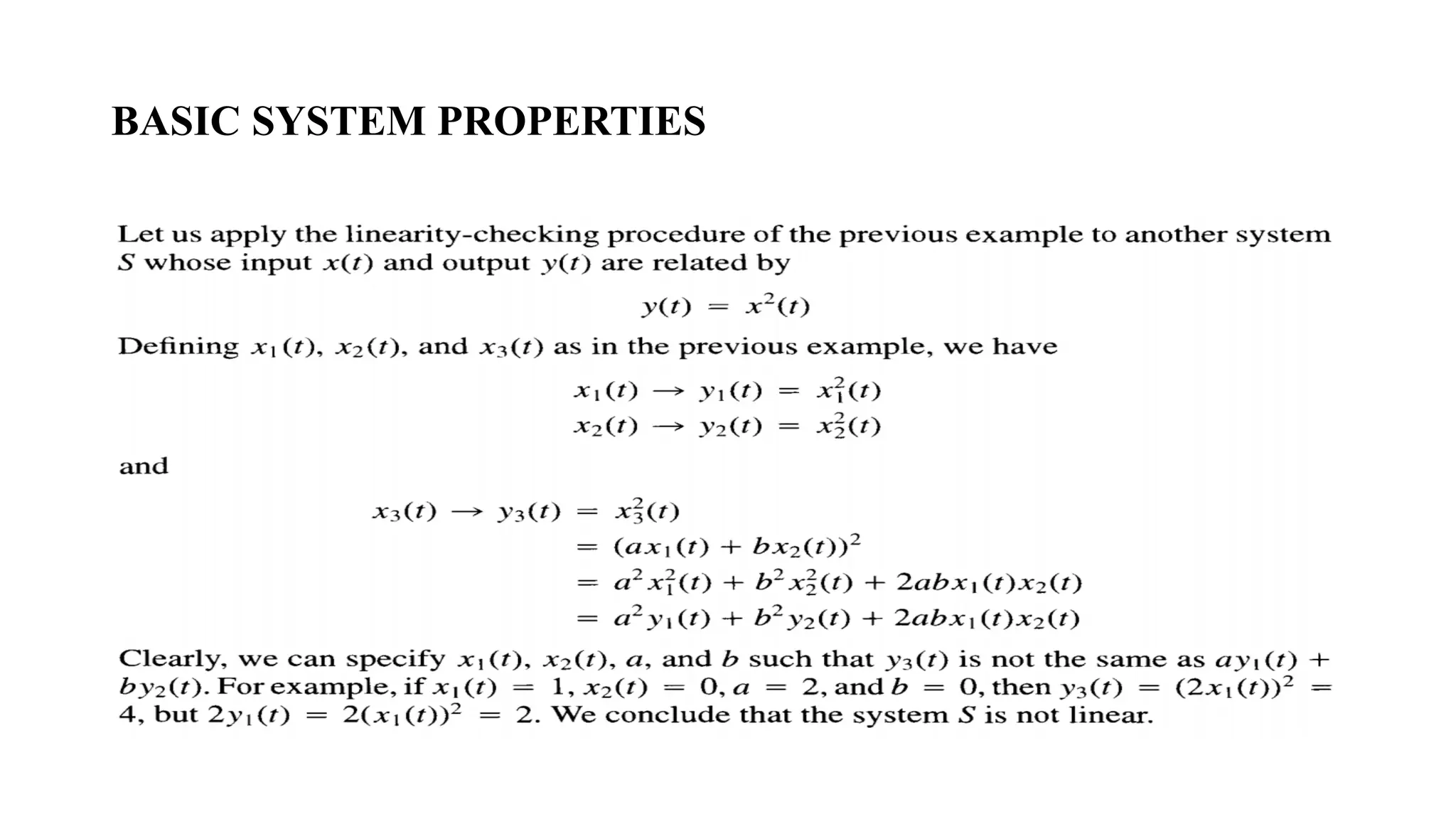
![BASIC SYSTEM PROPERTIES
• Example :
𝑦 𝑡 =
𝑛=−∞
∞
𝑥(𝑡)𝛿(𝑡 − 𝑛𝑇)
Let 𝑥1 𝑡 → 𝑦1 𝑡 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑥2 𝑡 → 𝑦2 𝑡
𝑥 𝑡 = 𝛼𝑥1 𝑡
𝑦 𝑡 =
𝑛=−∞
∞
𝑥 𝑡 𝛿 𝑡 − 𝑛𝑇
= σ𝑛=−∞
∞
𝛼𝑥1 𝑡 𝛿 𝑡 − 𝑛𝑇 = 𝛼𝑦1 𝑡
(homogeneous)
𝑥 𝑡 = 𝑥1 𝑡 + 𝑥2(𝑡)
𝑦 𝑡 =
𝑛=−∞
∞
𝑥 𝑡 𝛿 𝑡 − 𝑛𝑇
=
𝑛=−∞
∞
[𝑥1 𝑡 + 𝑥2(𝑡)] 𝛿 𝑡 − 𝑛𝑇
=
𝑛=−∞
∞
𝑥1 𝑡 𝛿 𝑡 − 𝑛𝑇 +
𝑛=−∞
∞
𝑥2 𝑡 𝛿 𝑡 − 𝑛𝑇
= 𝑦1 𝑡 + 𝑦2(𝑡)
(additive)
The system is linear](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/signalandsystemchapter2-part12new-231020181443-c8898968/75/signal-and-system-chapter2-part1-2new-pdf-5-2048.jpg)


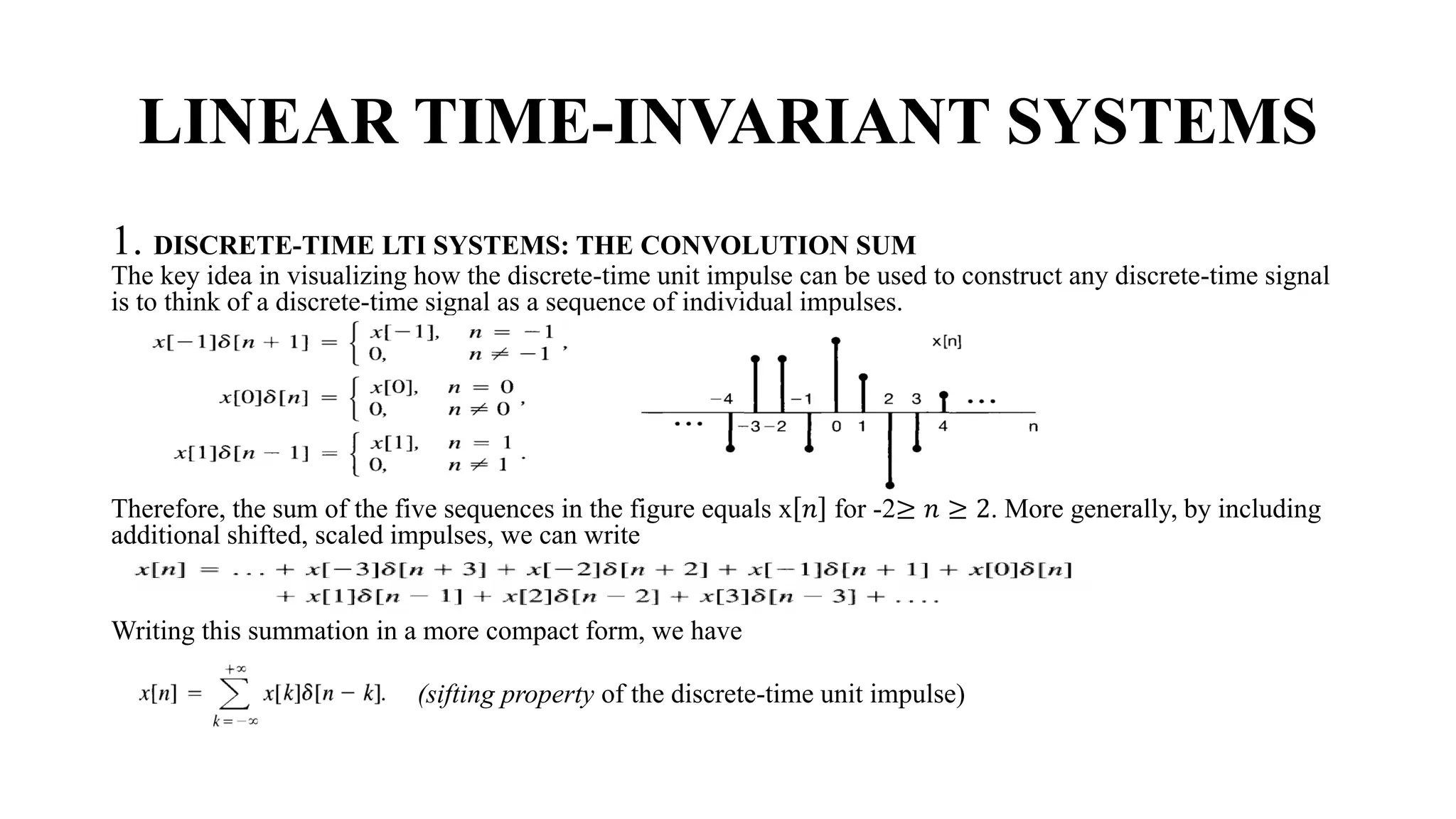
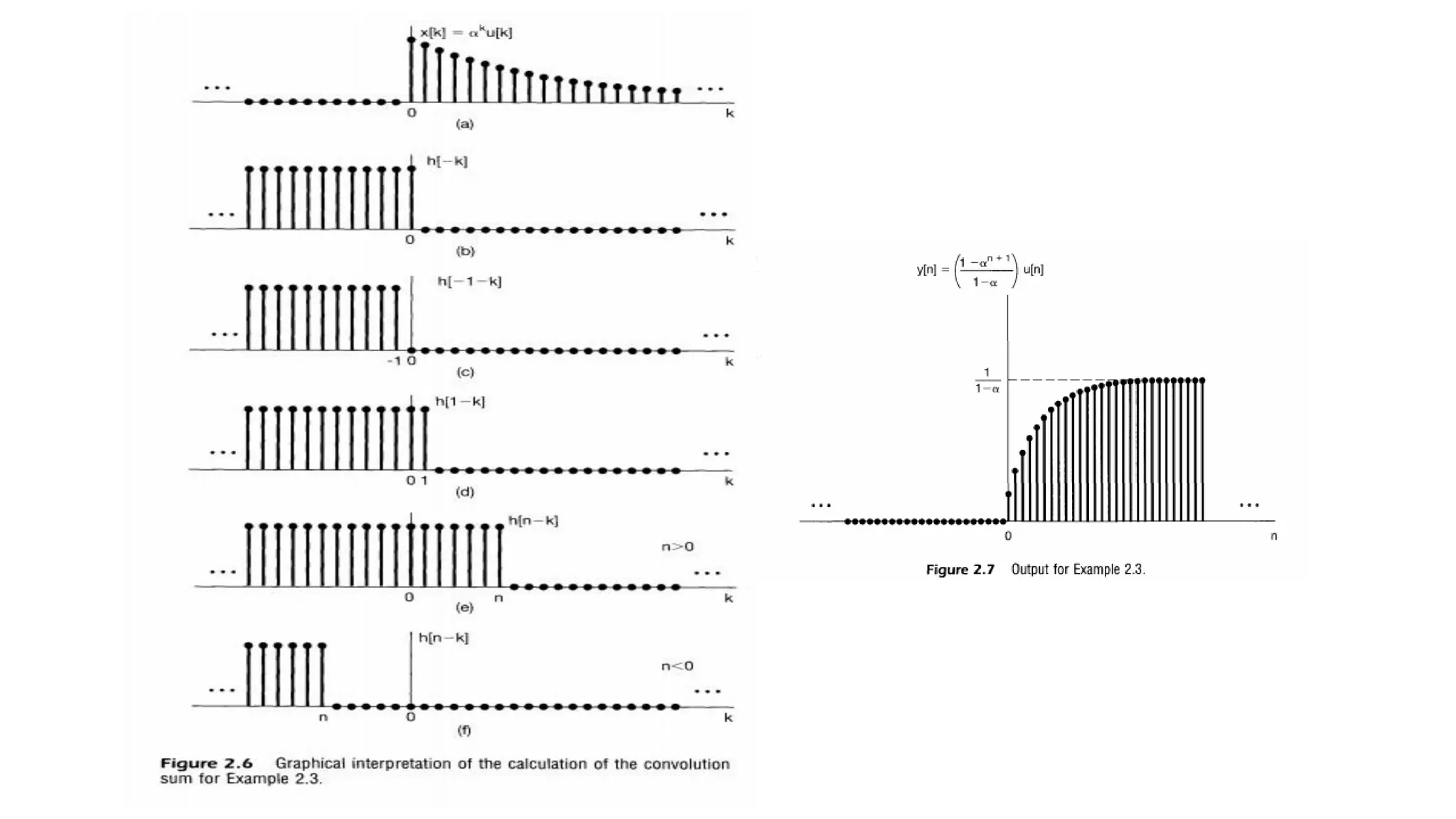
![DISCRETE-TIME LTI SYSTEMS: THE CONVOLUTION SUM
• An example, consider 𝑥 𝑛 = 𝑢 𝑛 , the unit step. In this case, since 𝑢 𝑘 = 0 for k < 0, and 𝑢 𝑘 = 1 for k ≥
0,
Because the sequence 𝛿[𝑛 − 𝑘] is nonzero only when 𝑘 = 𝑛, the summation on the righthand side of the
equation below "sifts" through the sequence of values 𝑥[𝑘] and preserves only the value corresponding to k = n.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/signalandsystemchapter2-part12new-231020181443-c8898968/75/signal-and-system-chapter2-part1-2new-pdf-12-2048.jpg)
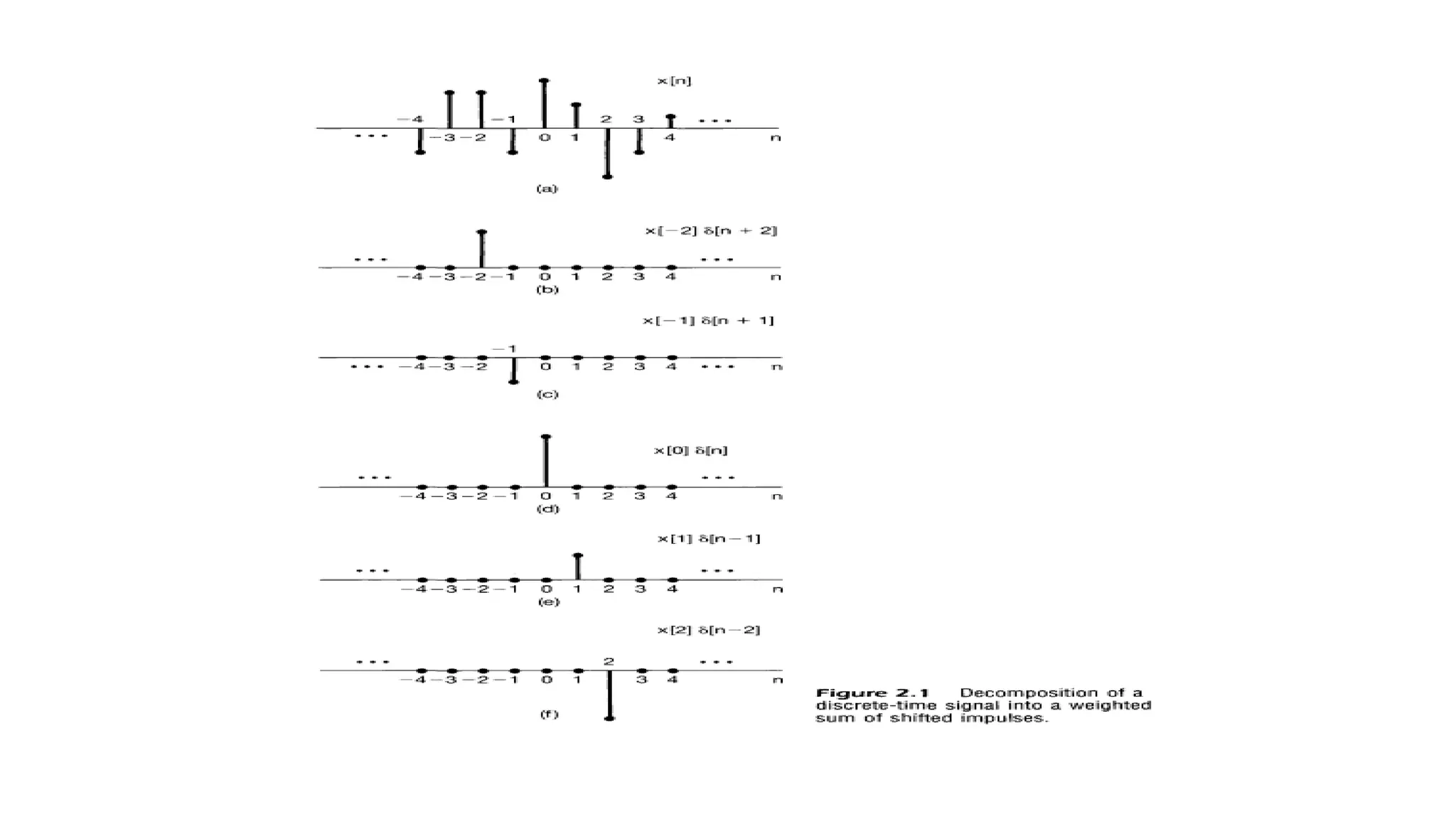
![The Discrete-Time Unit Impulse Response and the Convolution
Sum Representation of LTI Systems
• The Discrete-Time Unit Impulse Response and the Convolution Sum Representation of LTI Systems
• The response of a linear system to 𝑥[𝑛] will be the superposition of the scaled responses of the system to each of
these shifted impulses.
• Moreover, the property of time invariance tells us that the responses of a time-invariant system to the time-shifted
unit impulses are simply time-shifted versions of
one another.
• The convolution-sum representation for discrete-time systems that are both linear and time invariant results from
putting these two basic facts together.
• Consider the response of a linear (but possibly time-varying) system to an arbitrary input 𝑥[𝑛]
• If we know the response of a linear system to the set of shifted unit impulses, we can construct the response to an
arbitrary input.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/signalandsystemchapter2-part12new-231020181443-c8898968/75/signal-and-system-chapter2-part1-2new-pdf-13-2048.jpg)
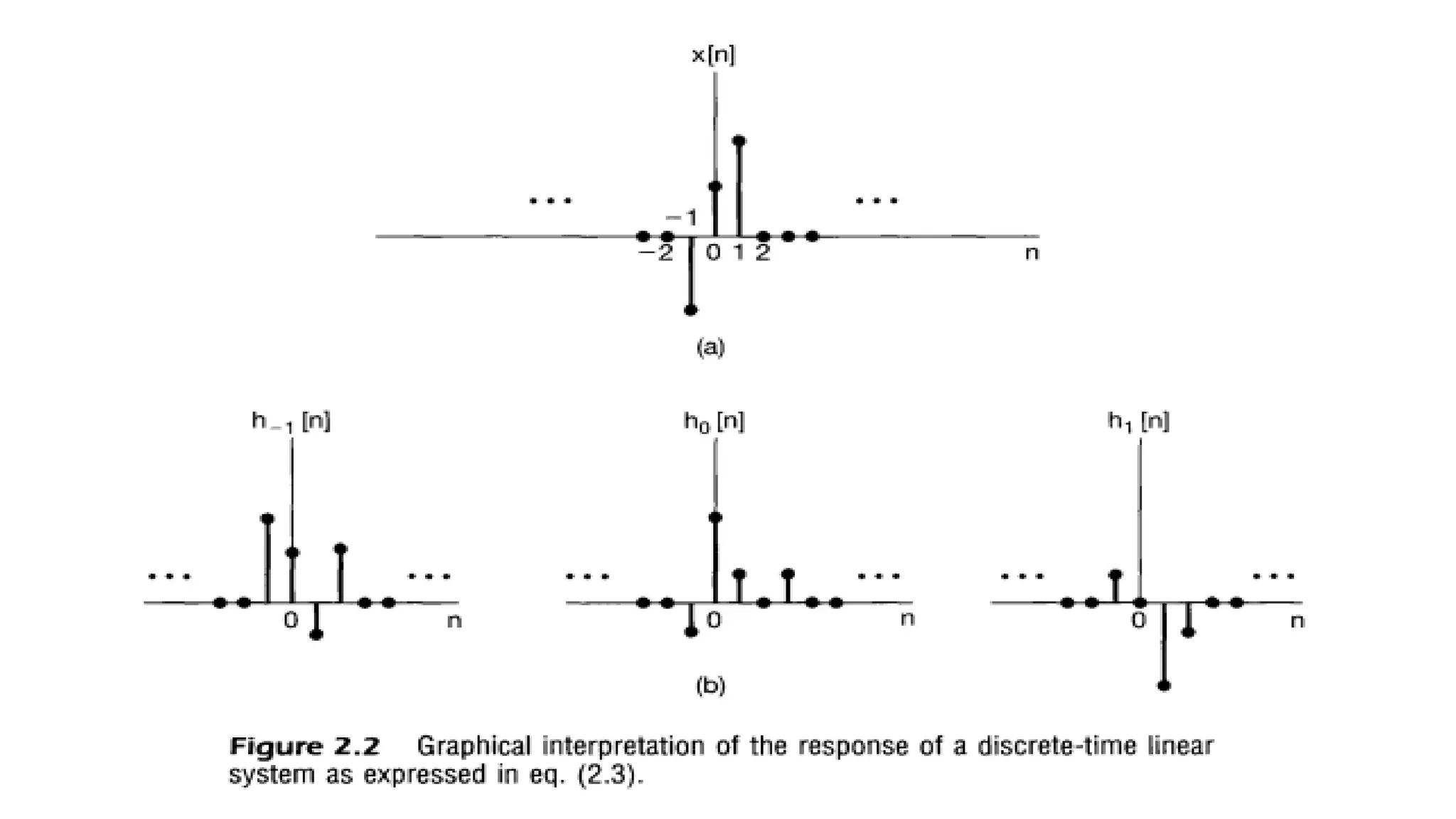
![DISCRETE-TIME LTI SYSTEMS: THE CONVOLUTION SUM
• In general, of course, the responses ℎ𝑘[𝑛] need not be related to each other for different values of k. However,
if the linear system is also time invariant, then these responses to time-shifted unit impulses are all time-
shifted versions of each other. Specifically, since 𝛿[𝑛 − 𝑘]is a time-shifted version of 𝛿[𝑛], the response
ℎ𝑘[𝑛] is a time-shifted version of ℎ0[𝑛]; i.e.,
• For notational convenience, we will drop the subscript on ℎ0[𝑛] and define the unit impulse (sample) response
• That is, h[n] is the output of the LTI system when 𝛿[𝑛] is the input. Then for an LTI system.
This result is referred to as the convolution sum or superposition
sum. We will represent the operation of convolution
symbolically as](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/signalandsystemchapter2-part12new-231020181443-c8898968/75/signal-and-system-chapter2-part1-2new-pdf-15-2048.jpg)
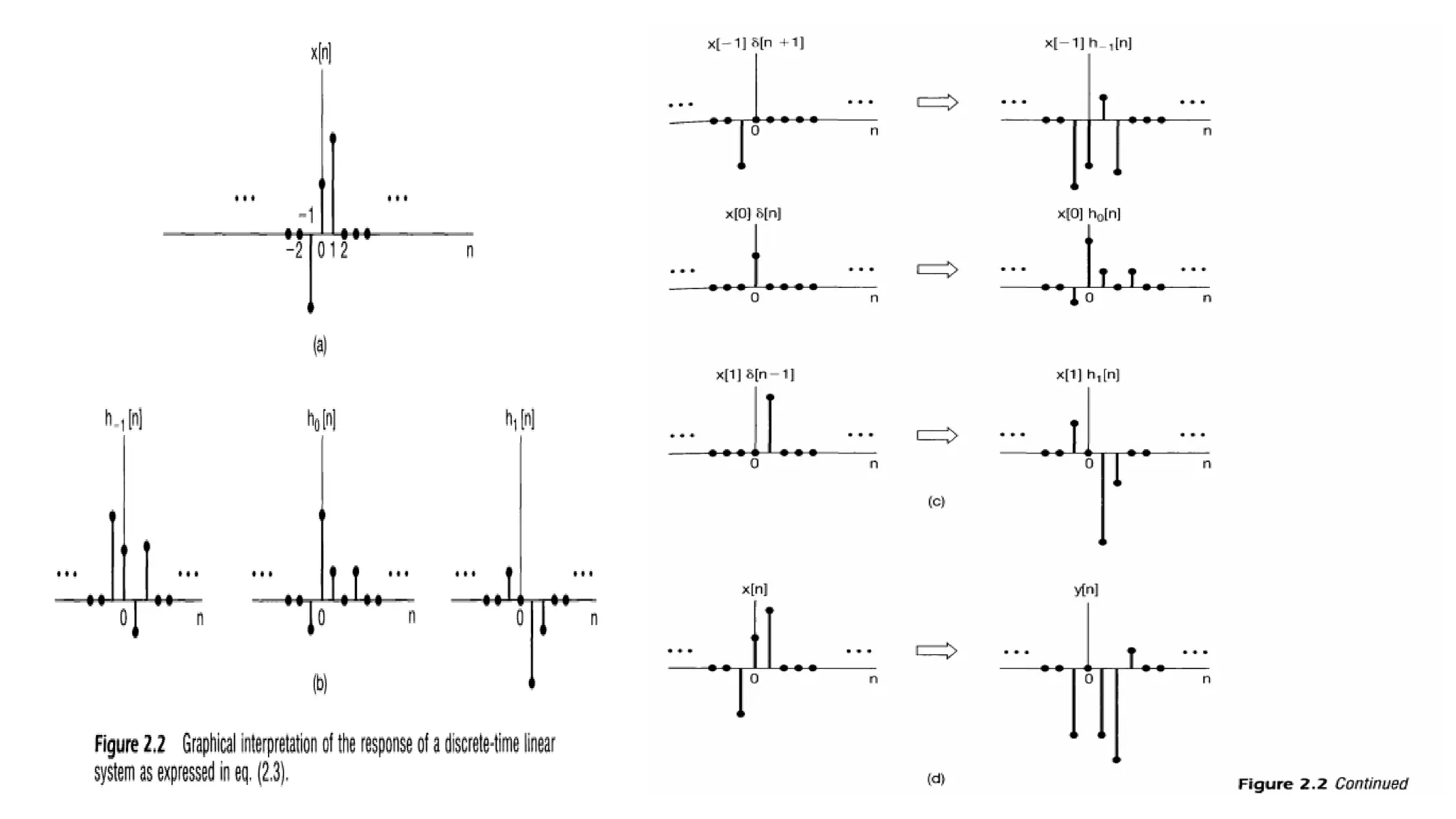
![DISCRETE-TIME LTI SYSTEMS: THE CONVOLUTION SUM
• The convolution sum expresses the response of an LTI system to an arbitrary input in terms of the system's
response to the unit impulse. From this, we see that an LTI system is completely characterized by its response
to a single signal, namely, its response to the unit impulse.
• In the case of an LTI system, the response due to the input 𝑥 𝑘 applied at 𝑘 time is 𝑥 𝑘 ℎ 𝑛 − 𝑘 ; i.e., it is a
shifted and scaled version (an "echo") of ℎ[𝑛]. As before, the actual output is the superposition of all these
responses.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/signalandsystemchapter2-part12new-231020181443-c8898968/75/signal-and-system-chapter2-part1-2new-pdf-17-2048.jpg)
![DISCRETE-TIME LTI SYSTEMS: THE CONVOLUTION SUM
• Consider an input x 𝑛 and a unit impulse response ℎ[𝑛] given by](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/signalandsystemchapter2-part12new-231020181443-c8898968/75/signal-and-system-chapter2-part1-2new-pdf-18-2048.jpg)