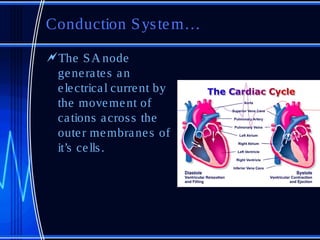
The document provides information on cardiovascular anatomy and physiology for veterinary technicians. It discusses the major components and functions of the cardiac system including the heart chambers and valves, conduction system, blood vessels, and cardiac cycle. It also covers some common cardiac pathologies such as heart failure, valvular disease, patent ductus arteriosus, and persistent right aortic arch.