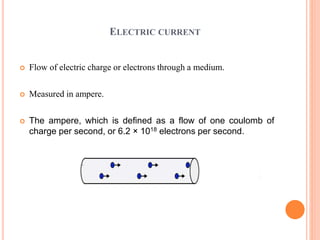
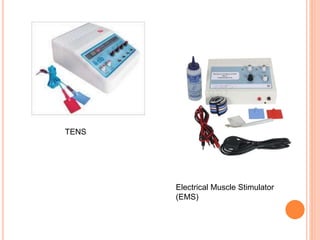
Electrotherapy uses electricity as the primary energy source to treat various diseases and disorders through non-surgical means. It involves applying electrical forces to the body to produce physiological changes for therapeutic purposes. Electrotherapy includes low, medium, and high frequency currents, as well as phototherapy, electrodiagnosis, and biofeedback. Low frequency currents below 1000 cycles per second are primarily used to stimulate nerves and muscles, while medium frequencies between 1000-10,000 cycles per second deeply stimulate muscles and nerves for muscle re-education. High frequencies above 10,000 cycles per second produce deep heat in tissues.