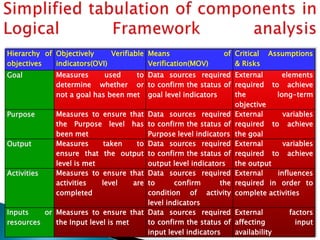
The document discusses the logical framework approach, which is a technique used to plan, monitor, and evaluate extension projects. It was initially developed for USAID in 1970. The logical framework involves a hierarchy of objectives from goals to inputs, along with objectively verifiable indicators, means of verification, and critical assumptions. It helps reveal the logic and major elements of a project to evaluate and monitor progress. Using a logical framework ensures objectives are clear and critical assumptions are identified. It also helps with monitoring, establishing accountability, and understanding project sustainability.