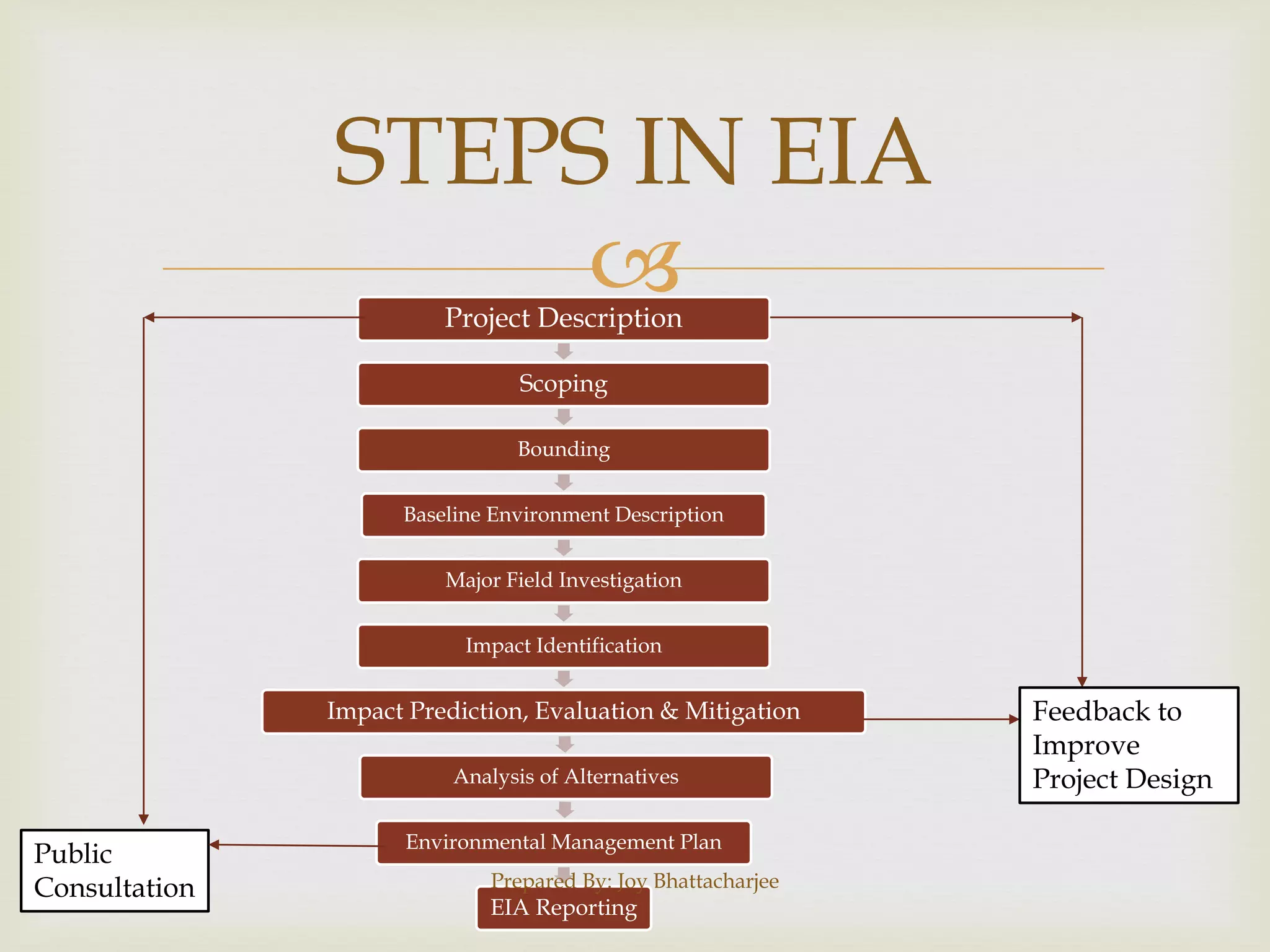
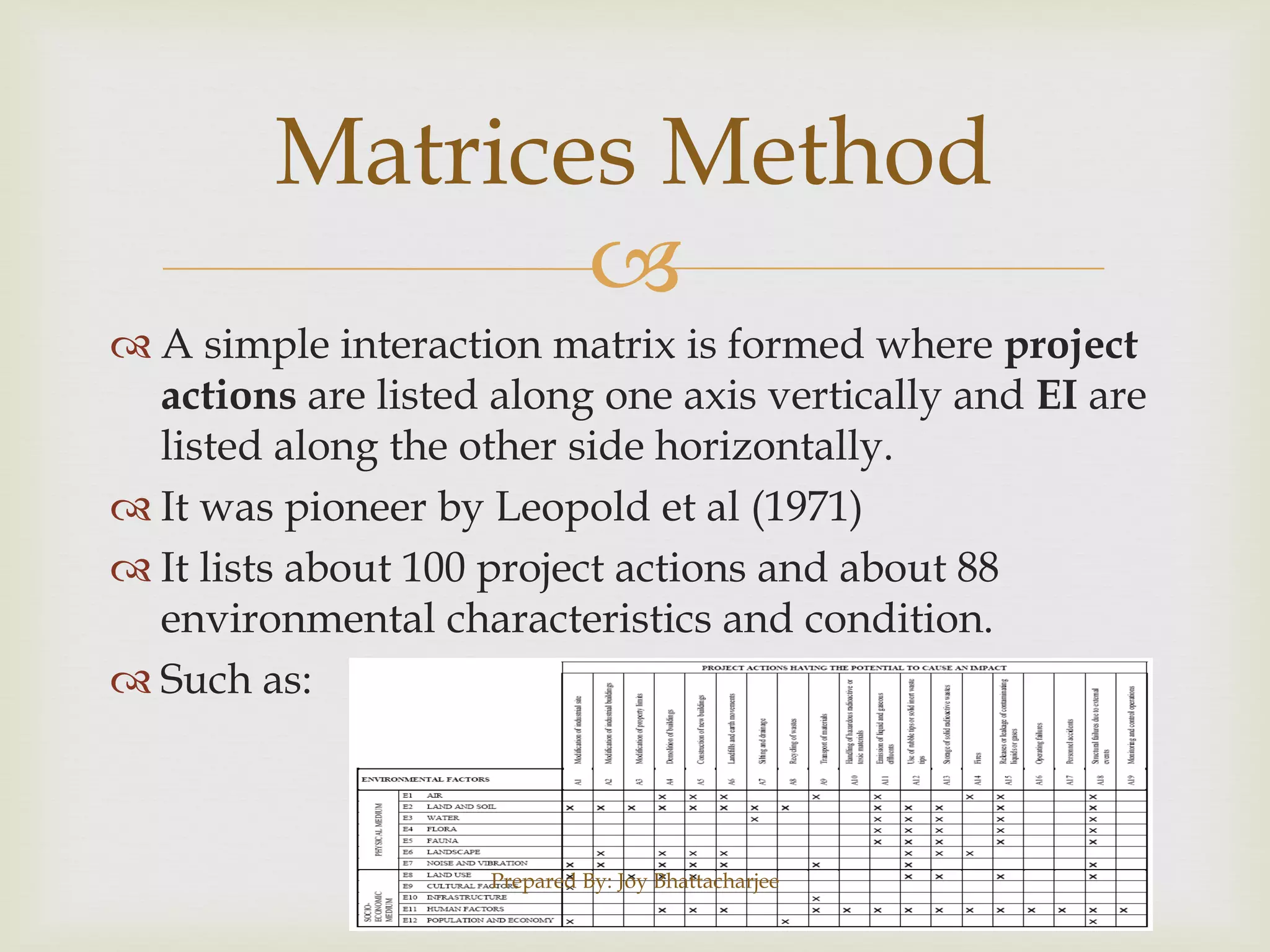
The document discusses the concept of the environment, highlighting its components and the significance of Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) in predicting and mitigating the effects of proposed projects. It outlines the systematic steps involved in EIA, such as project description, scoping, and impact identification, which ensure that development is balanced with environmental sustainability. The document emphasizes the importance of public participation and the need for informed decision-making in project planning to promote positive environmental outcomes.