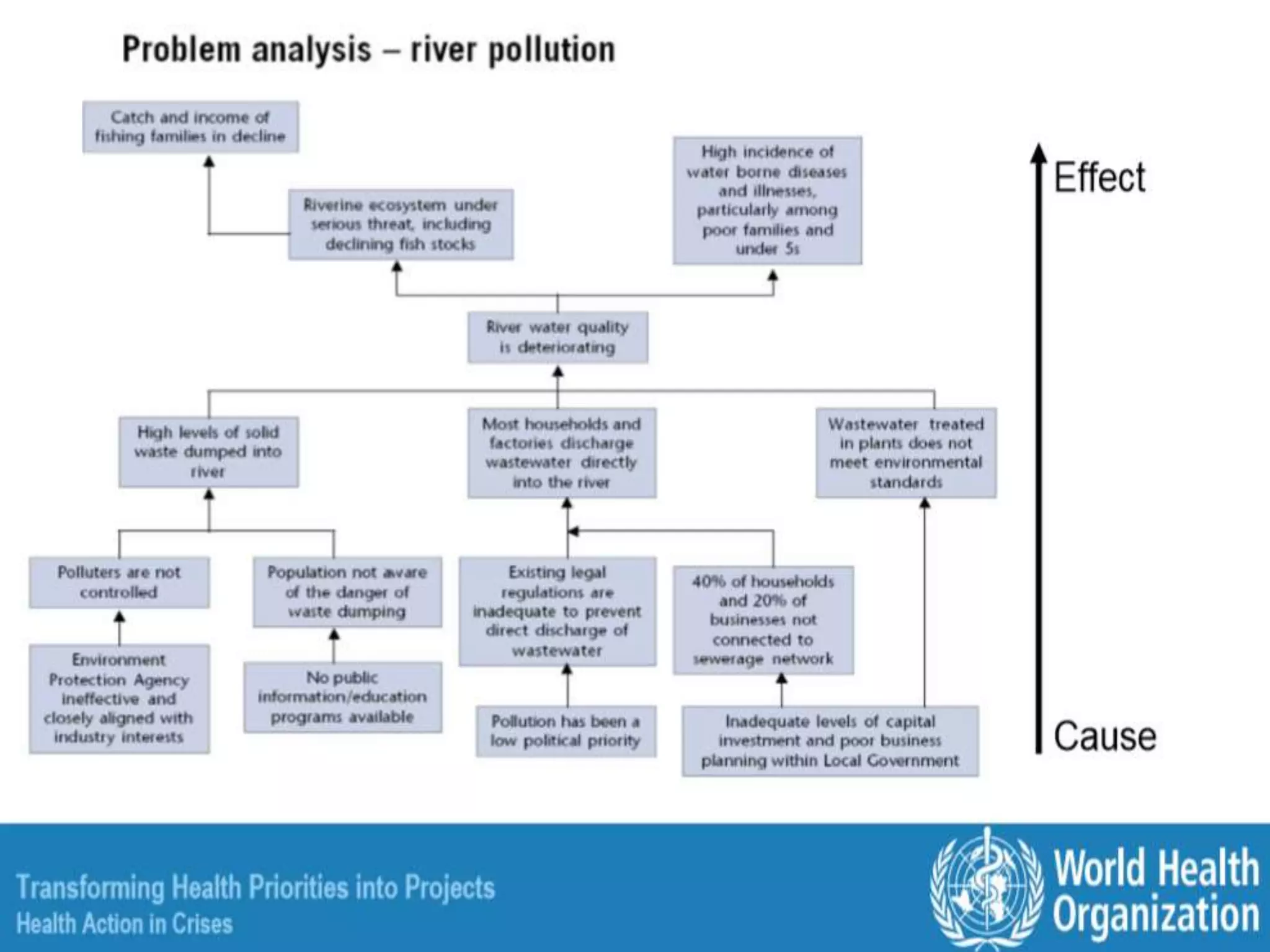
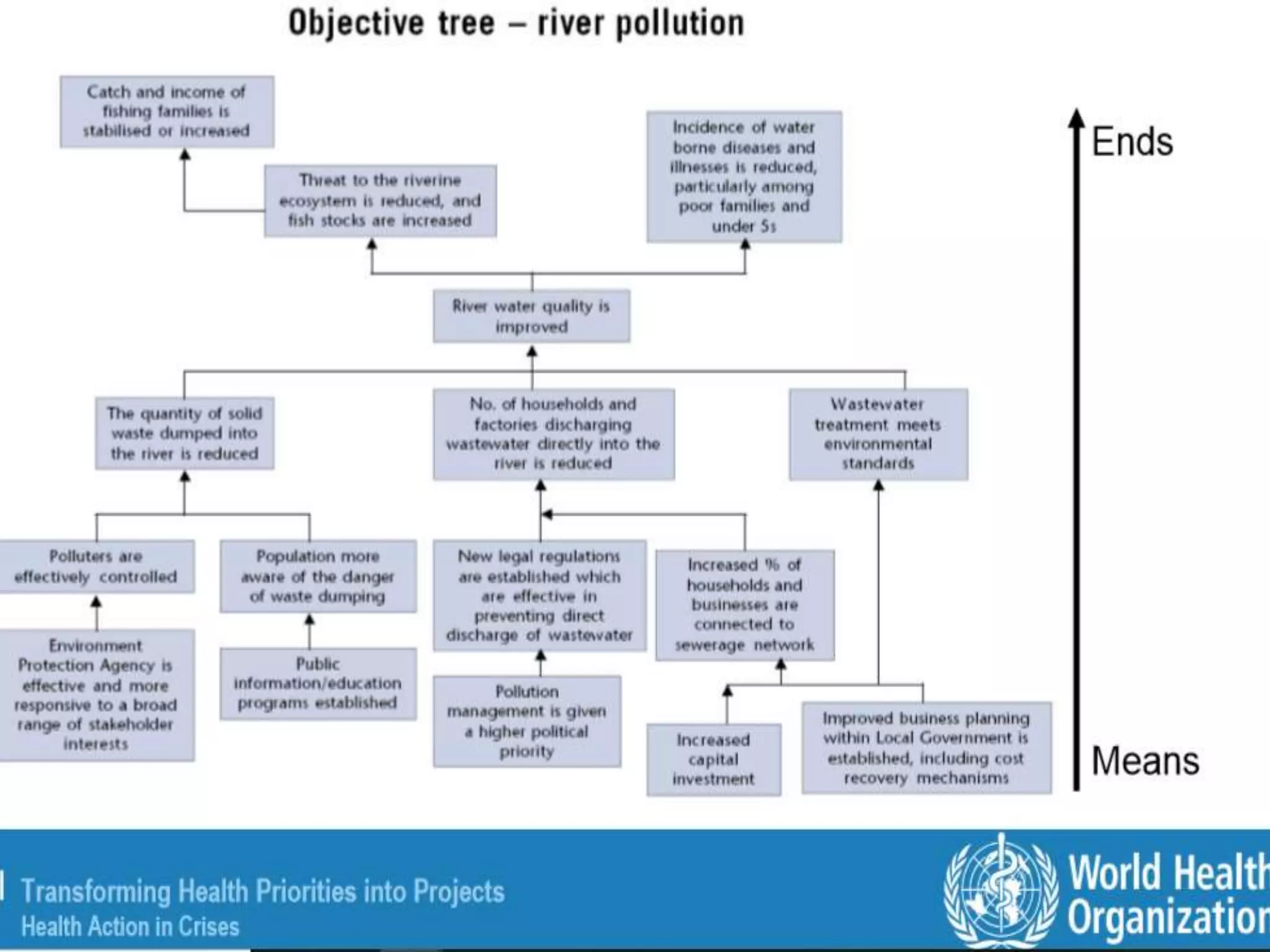
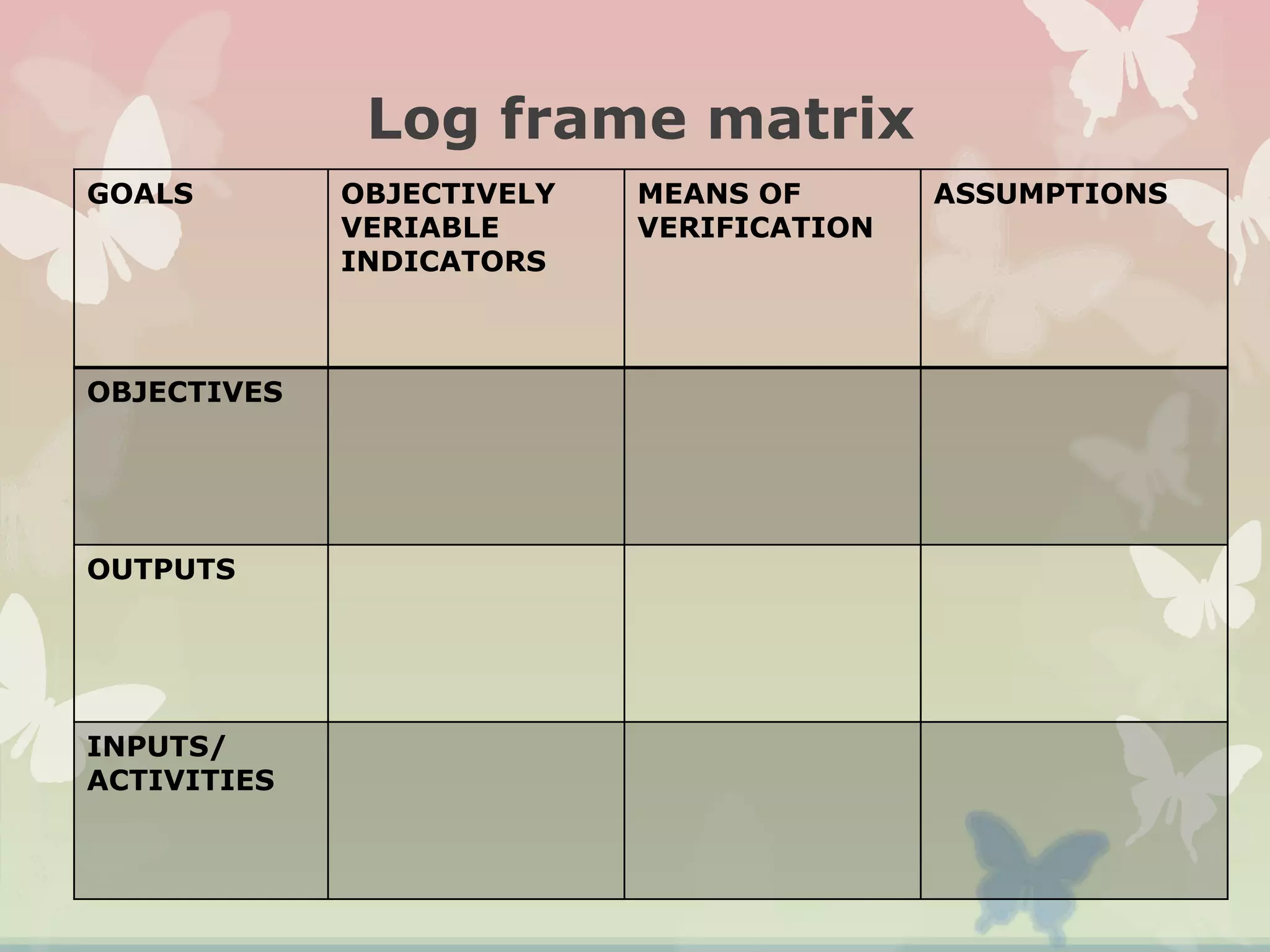
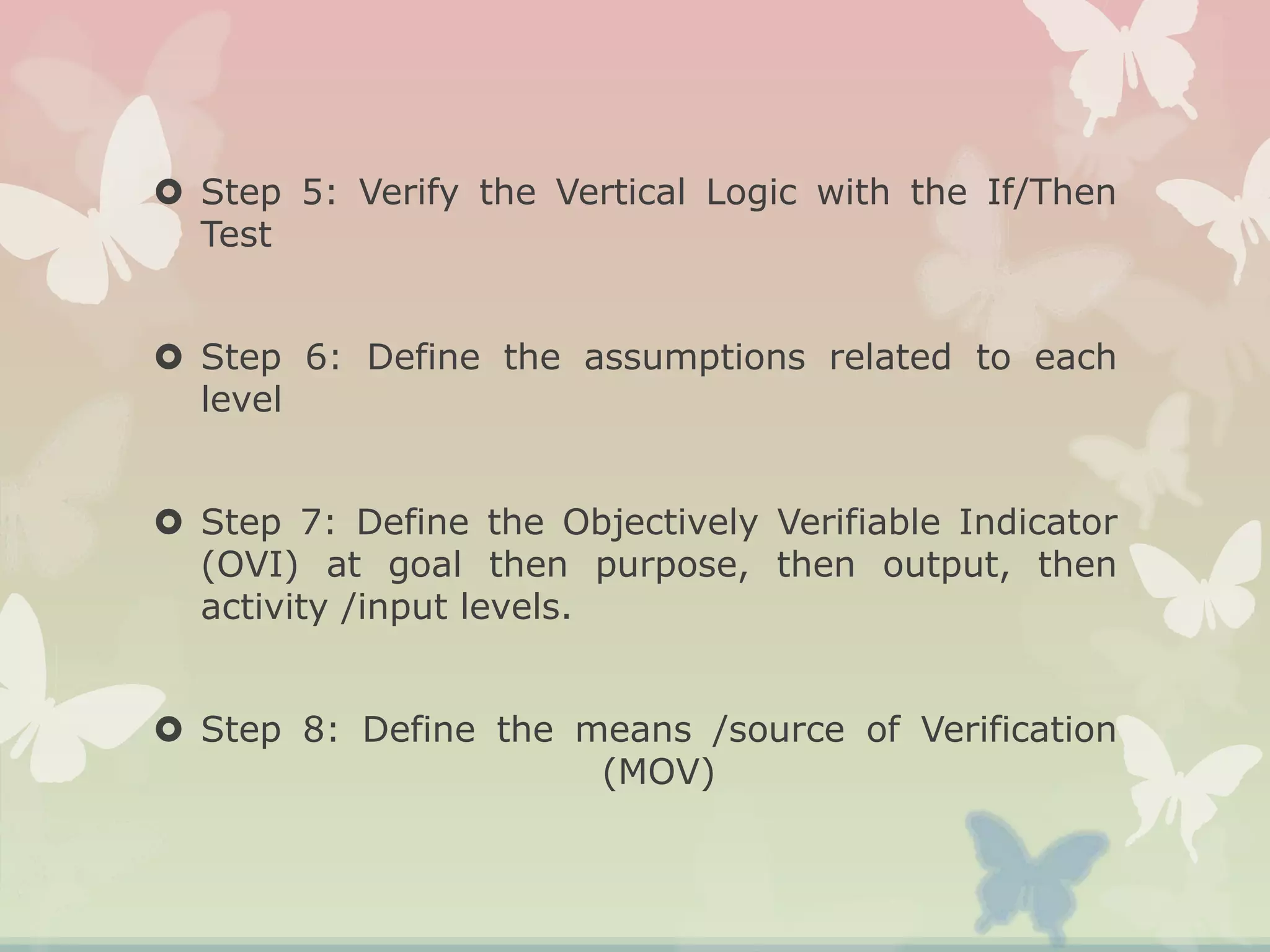
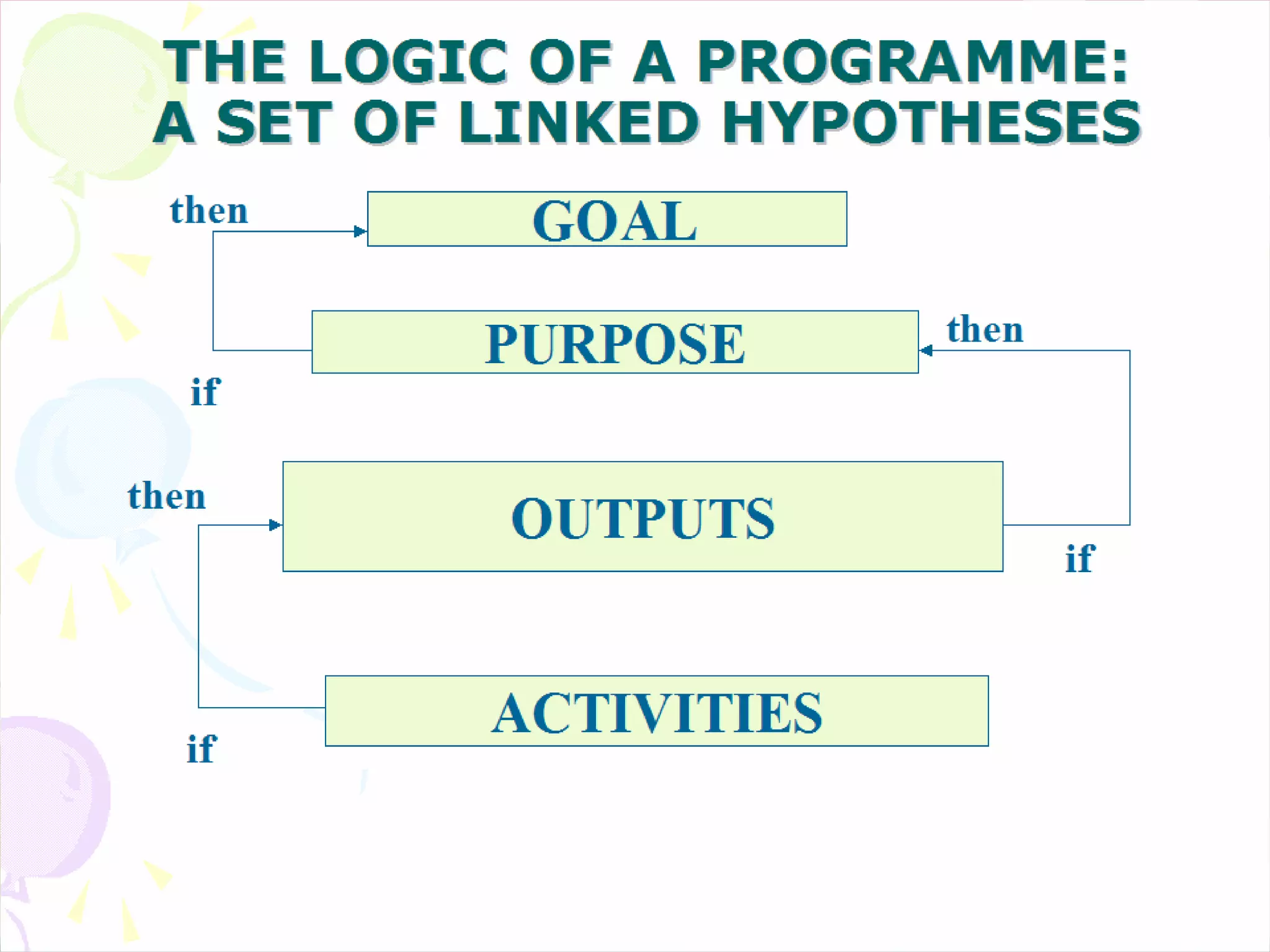
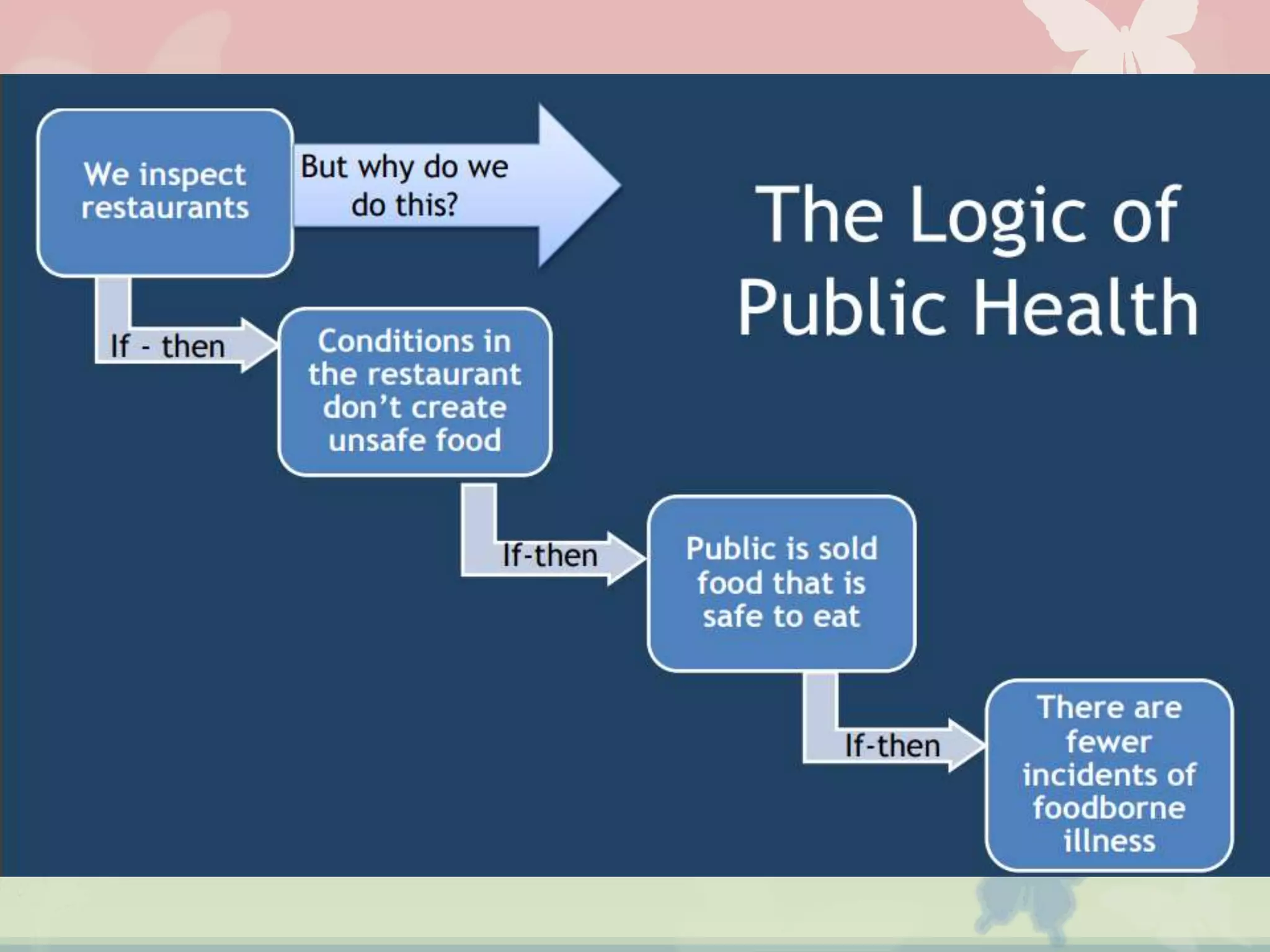
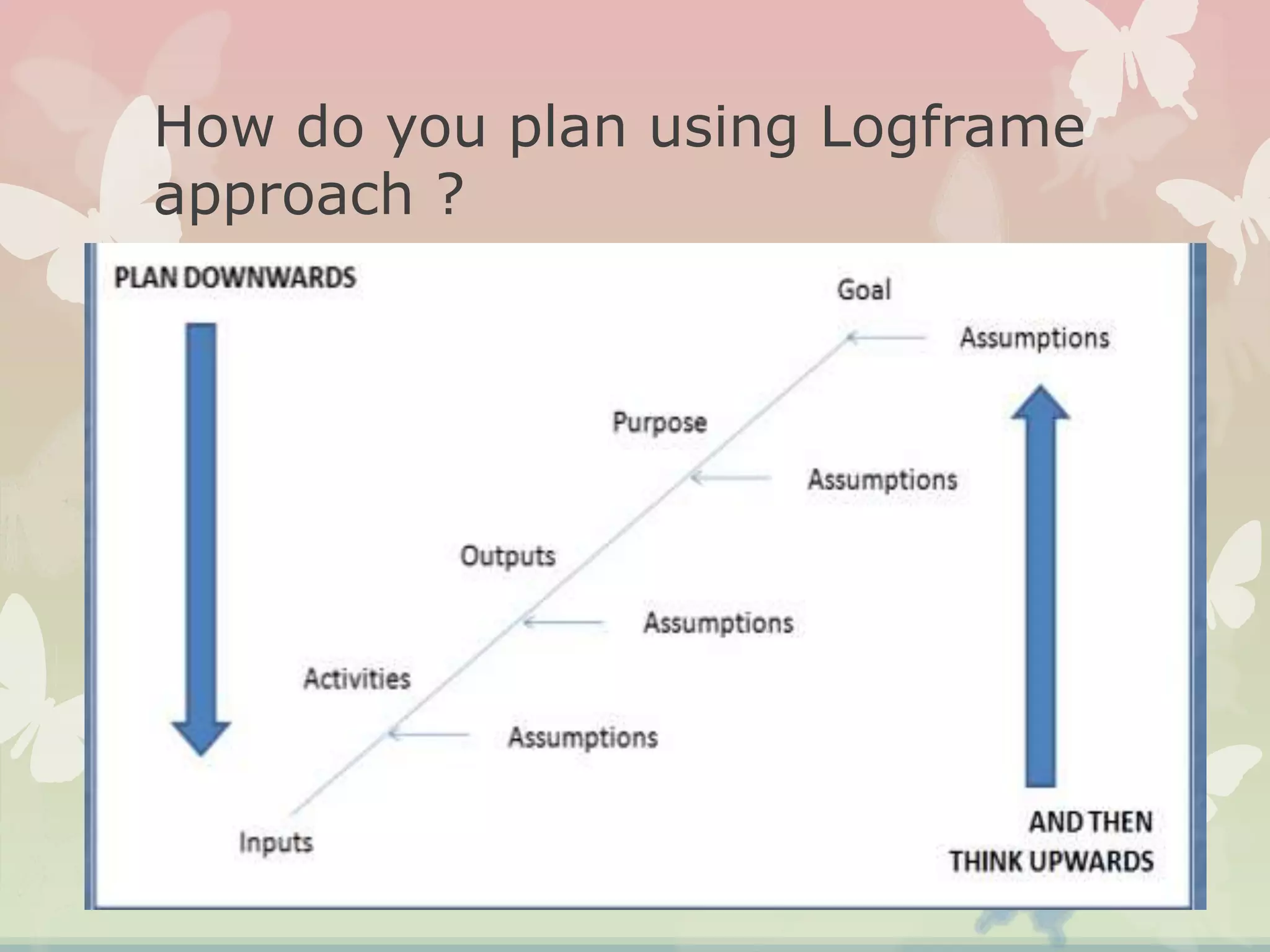
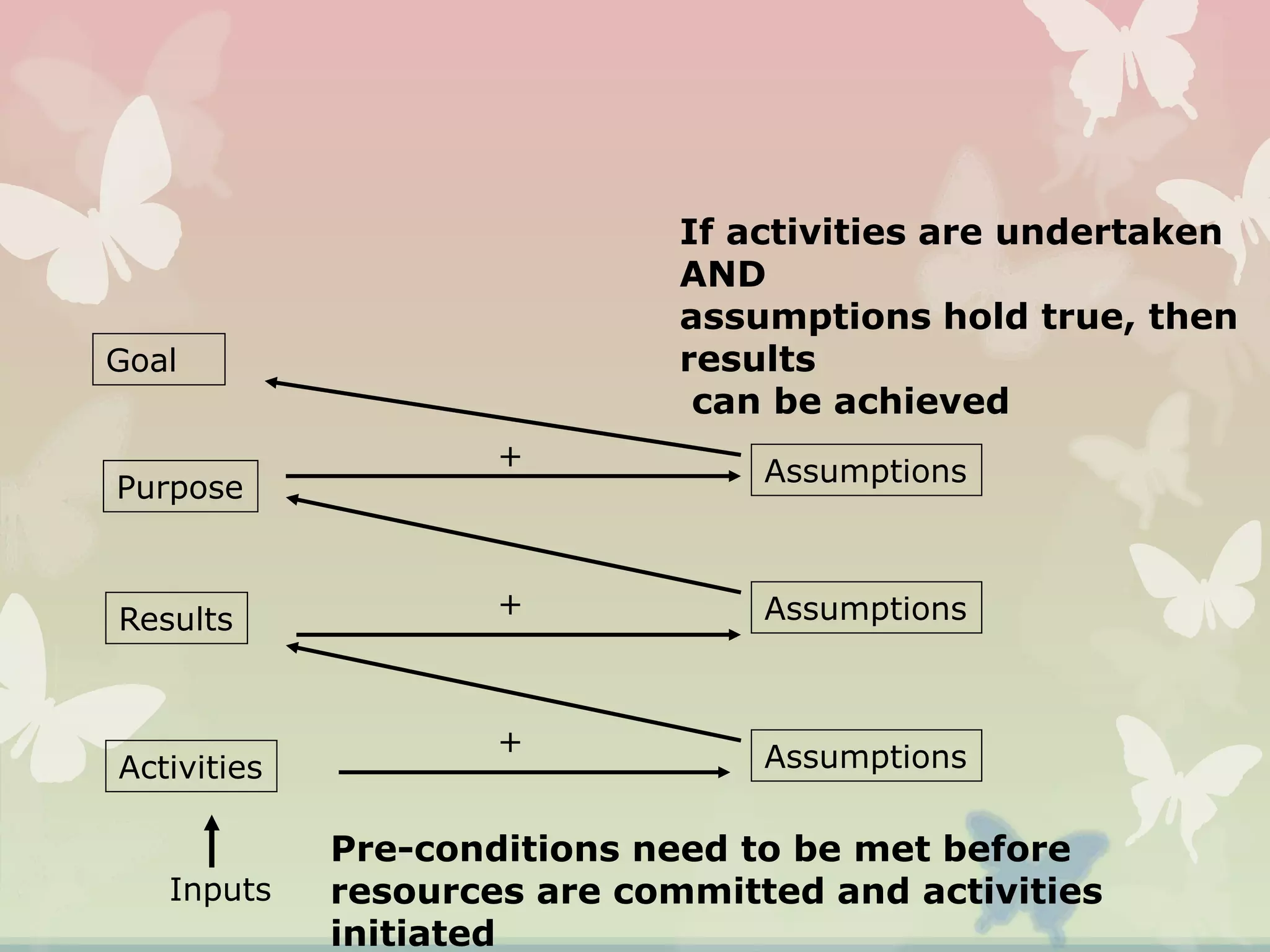
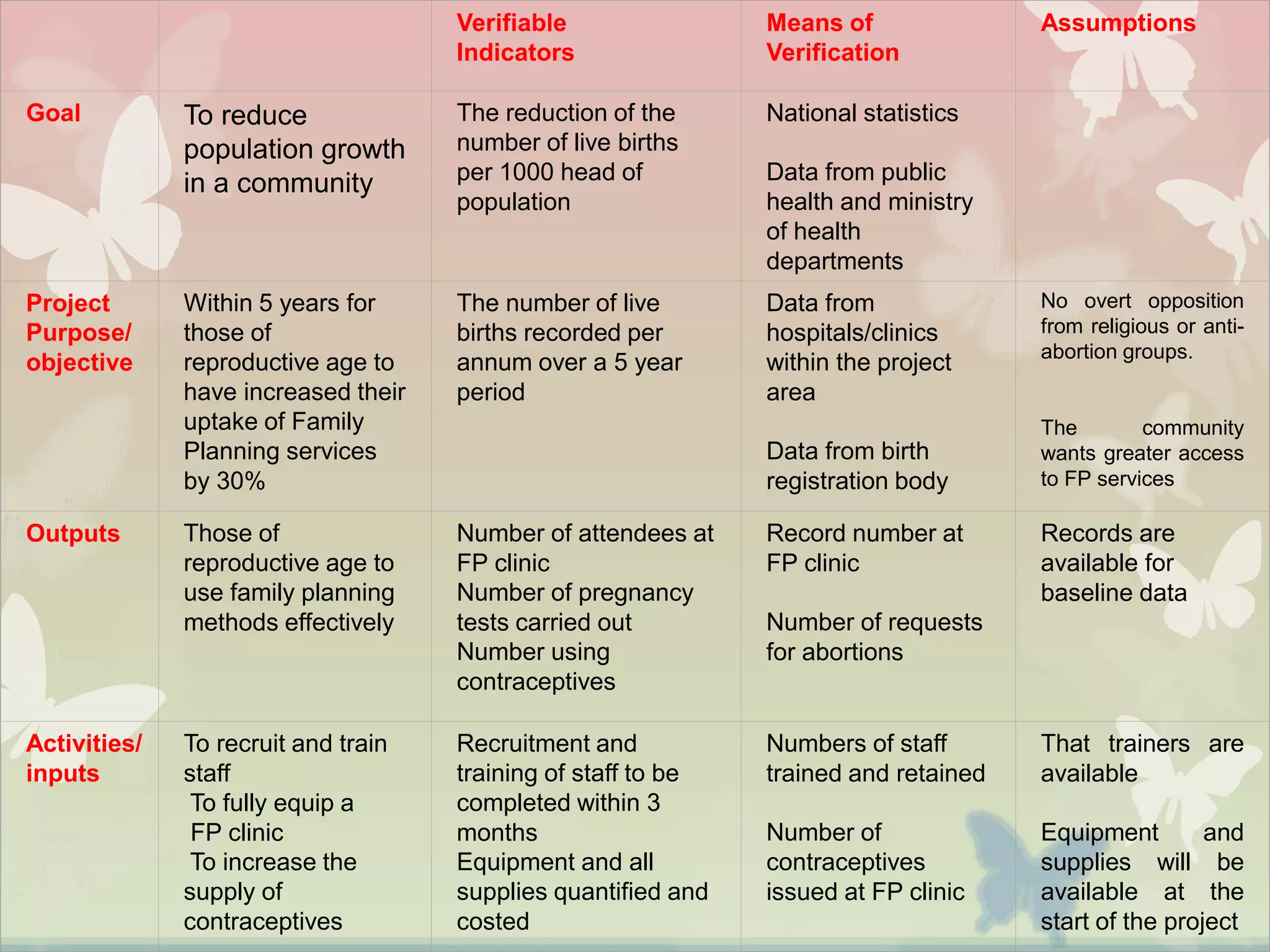
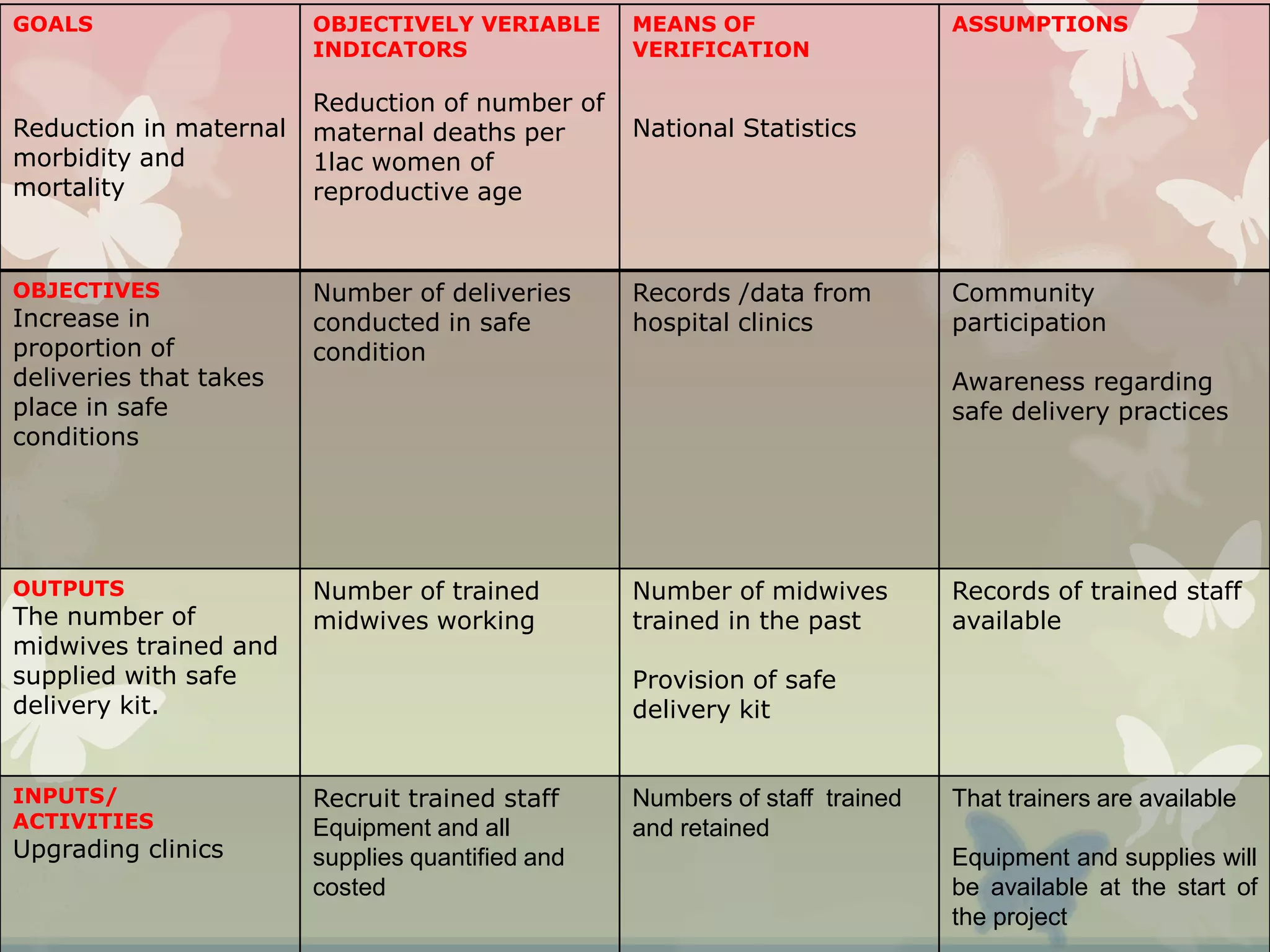
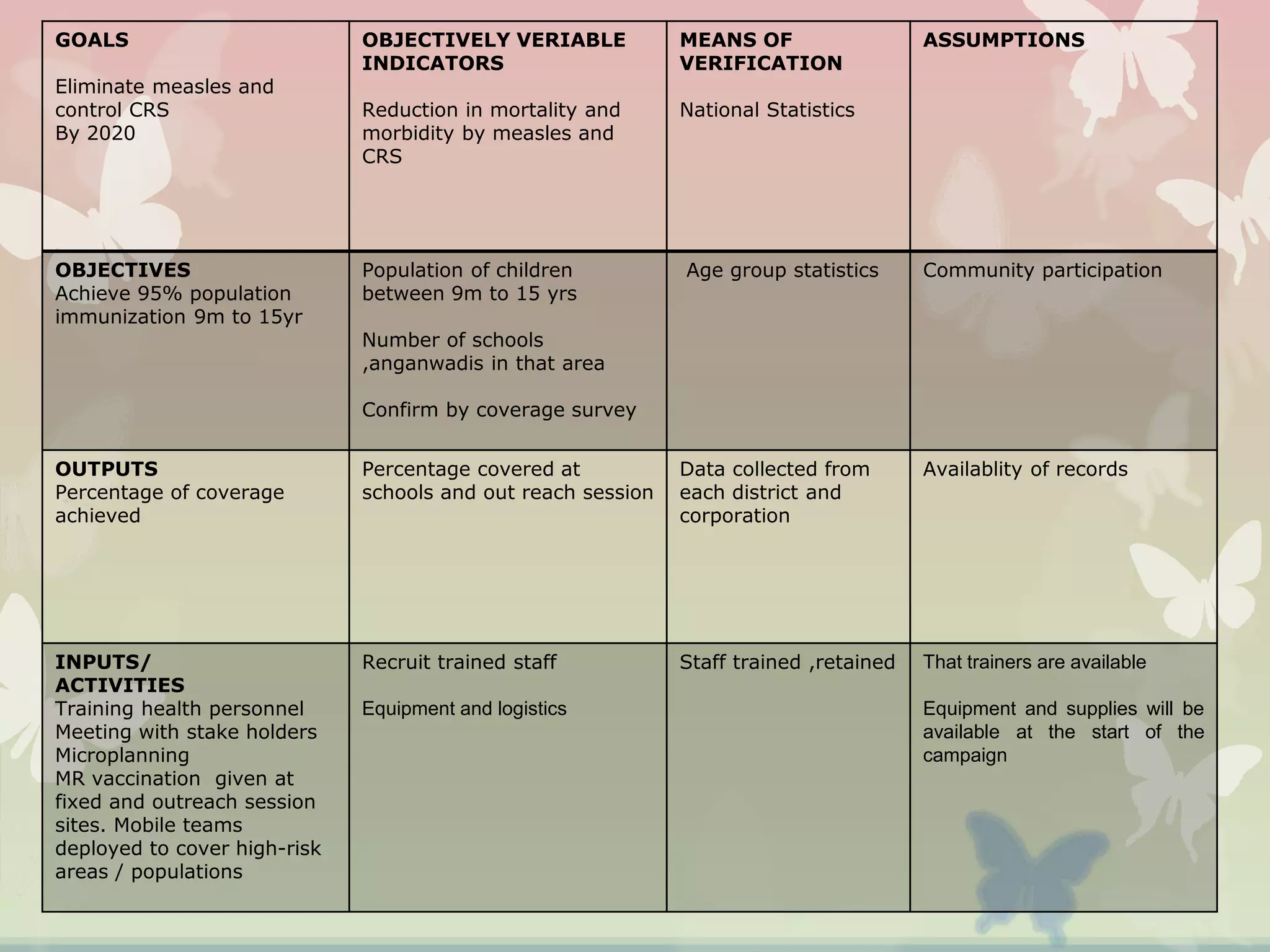
This document provides an overview of the logical framework approach for project planning and management. It describes the key elements of a logical framework including goals, objectives, outputs, inputs/activities, indicators, and assumptions. It outlines the phases and 8 steps to develop a logical framework matrix including defining the goal and objectives, identifying outputs and activities, and specifying indicators, means of verification, and assumptions. The advantages of the logical framework are that it helps design comprehensive and feasible plans, provides a structure for monitoring and evaluation, and reduces project management time and effort.