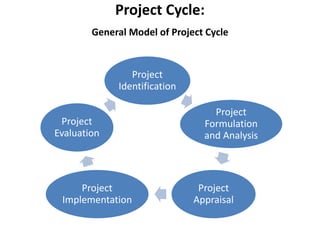
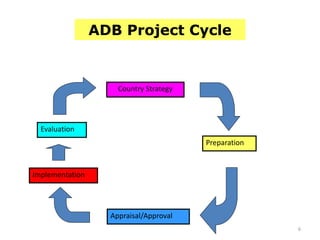
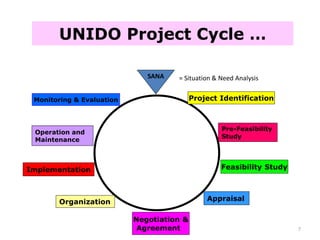
The document discusses the stages of a typical project cycle. It begins with project identification, then progresses to formulation and analysis, appraisal, implementation, and evaluation. Several examples of common project cycles are provided, including those used by the World Bank, Asian Development Bank, and UNIDO. A project cycle generally involves pre-investment, investment, and operation stages. Key steps within these stages include developing a project concept note, conducting feasibility studies, gaining approval or agreement, organization, implementation, operation and maintenance, monitoring, and evaluation.