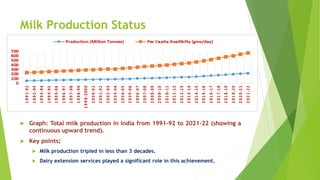
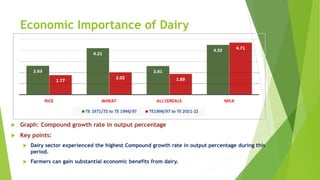
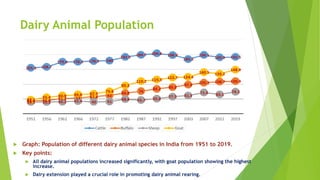
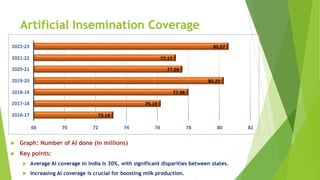
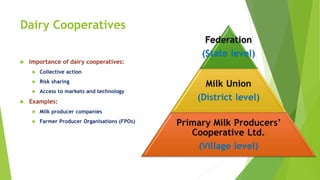
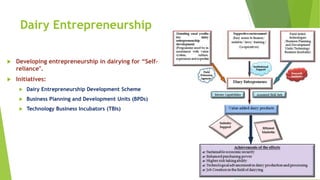
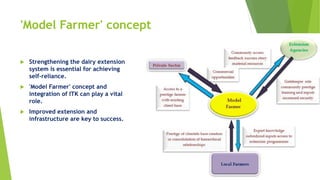
The document discusses the crucial role of dairy farming in India's economy and its potential to alleviate poverty among smallholder farmers. It outlines strategies for sustainable dairy development, including enhancing agricultural extension services and integrating indigenous knowledge to improve productivity and food security. The emphasis is on creating a self-reliant dairy sector through various government schemes and promoting entrepreneurship within rural communities.