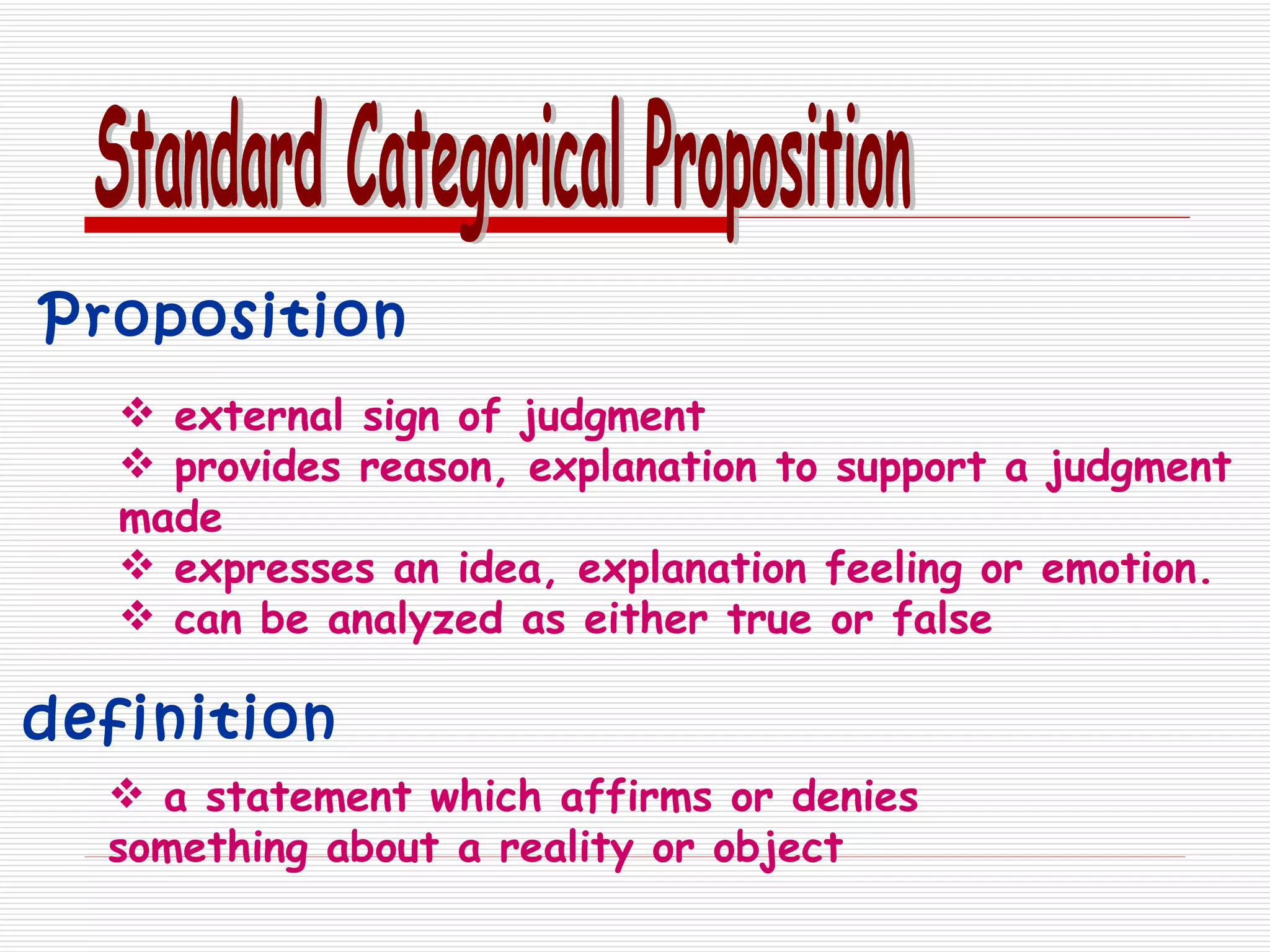
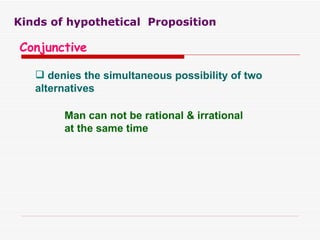
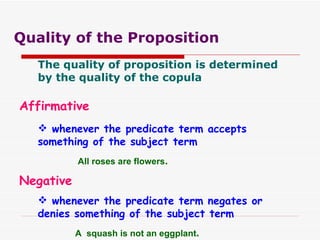
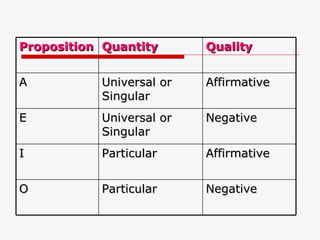
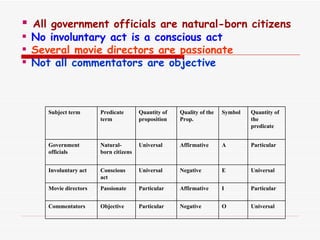
The document discusses standard categorical propositions, defining them as statements that affirm or deny aspects of reality. It outlines the elements of propositions, such as subject terms, predicate terms, and copulas, as well as how different types of propositions (categorical, hypothetical, conditional, disjunctive, and conjunctive) can be analyzed. Additionally, it explains the quantity (universal, singular, particular) and quality (affirmative, negative) of propositions and how these characteristics influence the relationships between subject and predicate terms.