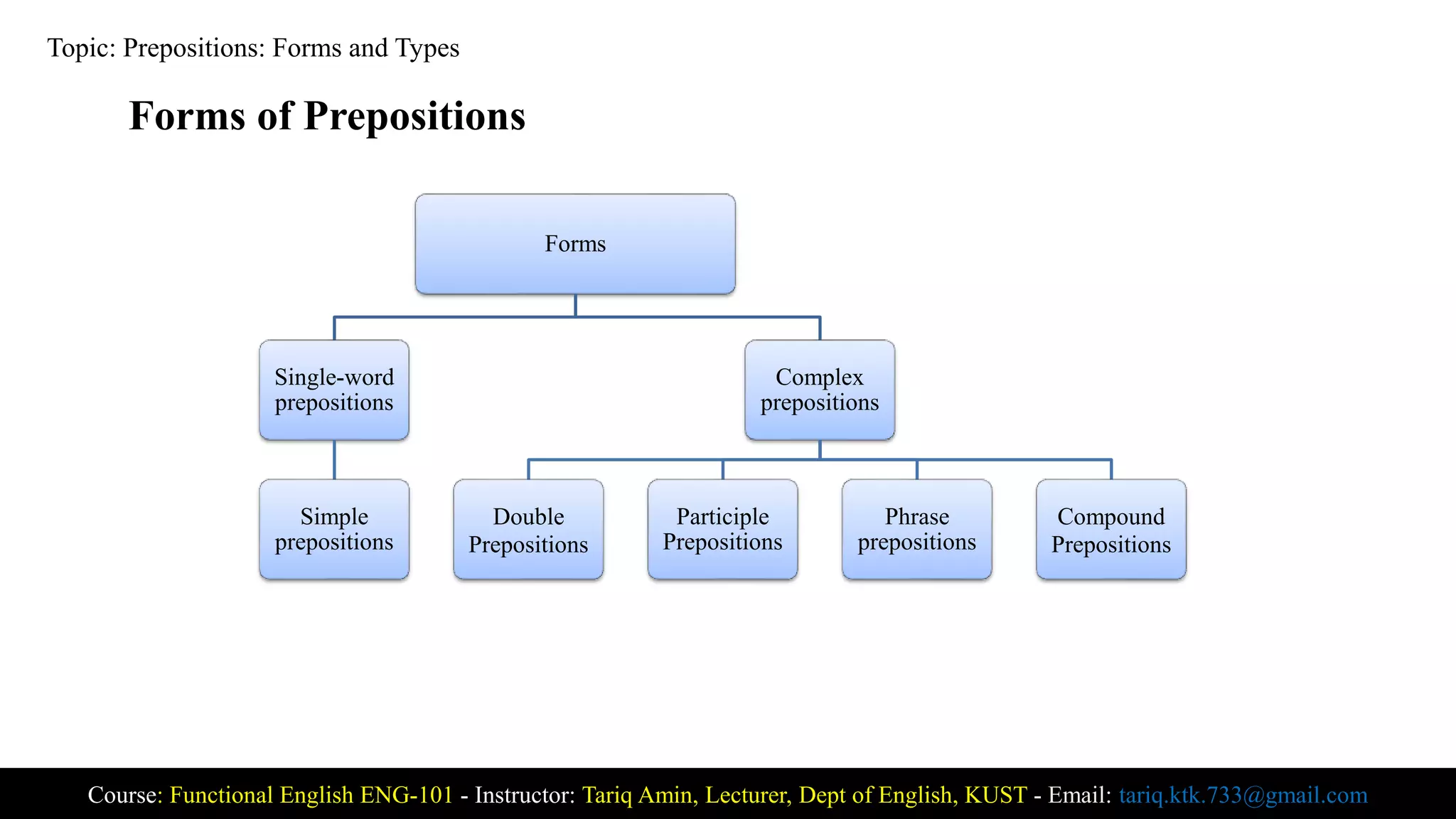
The document is a lecture on prepositions, defining them as words that establish relationships between nouns or pronouns and other elements of a sentence. It covers different forms and types of prepositions, including single-word, complex, compound, phrase, and participle prepositions, as well as their objects. Additionally, it categorizes prepositions into types based on their function, such as those indicating place, time, and direction.